A mushroom or toadstool is the fleshy, spore-bearing fruiting body of a fungus, typically produced above ground, on soil, or on its food source. Toadstool generally denotes one poisonous to humans.

Vitamin C is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, and also sold as a dietary supplement. It is used to prevent and treat scurvy. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Most animals are able to synthesize their own vitamin C. However, apes and monkeys, most bats, some rodents, and certain other animals must acquire it from dietary sources.

Vegetarianism is the practice of abstaining from the consumption of meat. It may also include abstaining from eating all by-products of animal slaughter.
Vitamin E is a group of eight fat soluble compounds that include four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. Vitamin E deficiency, which is rare and usually due to an underlying problem with digesting dietary fat rather than from a diet low in vitamin E, can cause nerve problems. Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant which may help protect cell membranes from reactive oxygen species.
Tocopherols are a class of organic chemical compounds, many of which have vitamin E activity. Because the vitamin activity was first identified in 1936 from a dietary fertility factor in rats, it was named tocopherol, from Greek τόκοςtókos 'birth' and φέρεινphérein 'to bear or carry', that is 'to carry a pregnancy', with the ending -ol signifying its status as a chemical alcohol.

The shiitake is an edible mushroom native to East Asia, which is now cultivated and consumed around the globe. It is considered a medicinal mushroom in some forms of traditional medicine.

Edible mushrooms are the fleshy and edible fruit bodies of several species of macrofungi. They can appear either below ground (hypogeous) or above ground (epigeous) where they may be picked by hand. Edibility may be defined by criteria that include absence of poisonous effects on humans and desirable taste and aroma. Edible mushrooms are consumed for their nutritional and culinary value. Mushrooms, especially dried shiitake, are sources of umami flavor.

Agaricus bisporus is an edible basidiomycete mushroom native to grasslands in Europe and North America. It has two color states while immature – white and brown – both of which have various names, with additional names for the mature state.
B vitamins are a class of water-soluble vitamins that play important roles in cell metabolism and synthesis of red blood cells. Though these vitamins share similar names (B1, B2, B3, etc.), they are chemically distinct compounds that often coexist in the same foods. In general, dietary supplements containing all eight are referred to as a vitamin B complex. Individual B vitamin supplements are referred to by the specific number or name of each vitamin, such as B1 for thiamine, B2 for riboflavin, and B3 for niacin. Some are more commonly recognized by name than by number, for example pantothenic acid, biotin, and folate.

Ergocalciferol, also known as vitamin D2 and nonspecifically calciferol, is a type of vitamin D found in food and used as a dietary supplement. As a supplement it is used to prevent and treat vitamin D deficiency. This includes vitamin D deficiency due to poor absorption by the intestines or liver disease. It may also be used for low blood calcium due to hypoparathyroidism. It is used by mouth or injection into a muscle.
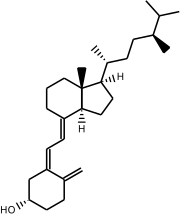
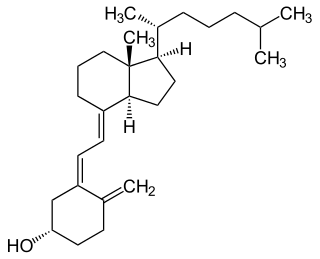
Ergosterol (ergosta-5,7,22-trien-3β-ol) is a sterol found in cell membranes of fungi and protozoa, serving many of the same functions that cholesterol serves in animal cells. Because many fungi and protozoa cannot survive without ergosterol, the enzymes that synthesize it have become important targets for drug discovery. In human nutrition, ergosterol is a provitamin form of vitamin D2; exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light causes a chemical reaction that produces vitamin D2.

Menadione is a natural organic compound with the formula C6H4(CO)2C2H(CH3). It is an analog of 1,4-naphthoquinone with a methyl group in the 2-position. It is sometimes called vitamin K3. Use is allowed as a nutritional supplement in animal feed because of its vitamin K activity.

Volvariella volvacea is a species of edible mushroom cultivated throughout East and Southeast Asia and used extensively in Asian cuisines. They are often available fresh in regions they are cultivated, but elsewhere are more frequently found canned or dried. Worldwide, straw mushrooms are the third most consumed mushroom.

Hyperhomocysteinemia is a medical condition characterized by an abnormally high level of homocysteine in the blood, conventionally described as above 15 μmol/L.

Calcifediol, also known as calcidiol, 25-hydroxycholecalciferol, or 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (abbreviated 25(OH)D3), is a form of vitamin D produced in the liver by hydroxylation of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) by the enzyme vitamin D 25-hydroxylase. Calcifediol can be further hydroxylated by the enzyme 25(OH)D-1α-hydroxylase, primarily in the kidney, to form calcitriol (1,25-(OH)2D3), which is the active hormonal form of vitamin D.

Boletus aereus, the dark cep or bronze bolete, is a highly prized and much sought-after edible mushroom in the family Boletaceae. The bolete is widely consumed in Spain, France, Italy, Greece, and generally throughout the Mediterranean. Described in 1789 by French mycologist Pierre Bulliard, it is closely related to several other European boletes, including B. reticulatus, B. pinophilus, and the popular B. edulis. Some populations in North Africa have in the past been classified as a separate species, B. mamorensis, but have been shown to be phylogenetically conspecific to B. aereus and this taxon is now regarded as a synonym.

Cytochrome P450 family 24 subfamily A member 1 (abbreviated CYP24A1) is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes encoded by the CYP24A1 gene. It is a mitochondrial monooxygenase which catalyzes reactions including 24-hydroxylation of calcitriol (1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3). It has also been identified as vitamin D3 24-hydroxylase.(EC 1.14.15.16)
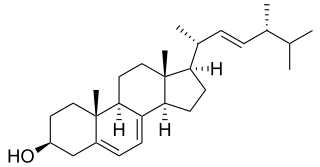
Vitamin D is a group of fat-soluble secosteroids responsible for increasing intestinal absorption of calcium, magnesium, and phosphate, and many other biological effects. In humans, the most important compounds in this group are vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) and vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol).
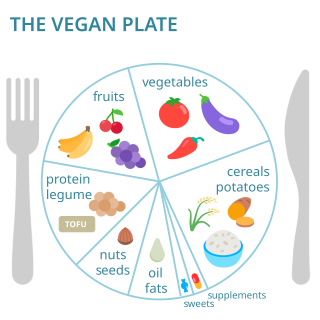
Vegan nutrition refers to the nutritional and human health aspects of vegan diets. A well-planned, balanced vegan diet is suitable to meet all recommendations for nutrients in every stage of human life. Vegan diets tend to be higher in dietary fiber, magnesium, folic acid, vitamin C, vitamin E, iron, and phytochemicals; and lower in calories, saturated fat, cholesterol, long-chain omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, calcium, zinc, and vitamin B12.
Medicinal fungi are fungi that contain metabolites or can be induced to produce metabolites through biotechnology to develop prescription drugs. Compounds successfully developed into drugs or under research include antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, cholesterol and ergosterol synthesis inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, immunosuppressants and fungicides.