Nu Aquilae, Latinized from ν Aquilae, is the Bayer designation for a double star in the constellation of Aquila that lies close to the celestial equator. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.72 and so is visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of only 0.8752 mas, it is believed to lie approximately 3,700 light-years from Earth. The variable star NU Aquilae has a similar-looking designation but is a separate and unrelated object.
22 Andromedae, abbreviated 22 And, is a single star in the constellation Andromeda. 22 Andromedae is the Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.04. The distance to 22 And can be estimated from its annual parallax shift of just 2.2 mas, which shows it to be around 1,500 light years away. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −8.2 km/s.
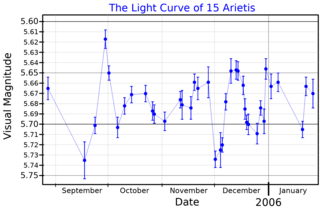
15 Arietis is a single variable star in the northern constellation of Aries. 15 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation; it also bears the variable star designation AV Arietis. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 5.74, which is just bright enough to be visible to the naked eye from dark suburban skies. An annual parallax shift of 5.84 mas corresponds to a physical distance of approximately 560 light-years from Earth. At that distance, the star's brightness is reduced by 0.33 in magnitude because of extinction from interstellar gas and dust.

RT Aurigae is a yellow supergiant variable star in the constellation Auriga, about 1,500 light years from Earth.

Beta Camelopardalis, Latinised from β Camelopardalis, is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Camelopardalis. It is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 4.02. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 3.74 mas as seen from Earth, it is located roughly 870 light-years from the Sun. It is moving closer with a radial velocity of −1.90 km/s and is most likely a single star.

2 Centauri is a single star in the southern constellation of Centaurus, located approximately 183 light-years from Earth. It has the Bayer designation g Centauri; 2 Centauri is the Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as faint, red-hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.19. It is moving away from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +41 km/s. The star is a member of the HR 1614 supercluster.

32 Cygni is the Flamsteed designation for a binary star system in the Cygnus constellation. It is a 4th magnitude star, which can be seen with the naked eye under suitably dark skies. Parallax measurements give an estimated distance of 1,100 light-years (320 parsecs) from the Earth. However, Schröder et al. (2007) suggest the actual value, after correcting for Malmquist bias, may be closer to 1,174 light-years (360 parsecs). Although it is a spectrsocopic binary with components that cannot be separated visually, it has two entries in the Henry Draper Catalogue, with identical magnitudes and positions, but showing the spectral types of the two components.
μ Normae, Latinised as Mu Normae, is a blue supergiant star of spectral type O9.7 Iab, located in the constellation of Norma.

41 Cygni is a single star in the northern constellation of Cygnus, located near the southern border with Vulpecula. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.02. The star lies at a distance of around 770 light years from the Sun, based on parallax, and is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −18 km/s.

45 Draconis is a single star located in the northern circumpolar constellation of Draco, around 3,500 light years from the Earth. 45 Draconis is the Flamsteed designation, while it has the Bayer designation of d Draconis. This object is visible to the naked eye as a faint, yellow-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.78. Radial velocity measurements indicate it is moving closer to the Sun at the rate of −12.5 km/s.
106 Herculis is a variable star in the northern constellation Hercules. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, red-hued point of light with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 4.96. Based on its parallax, it is estimated to lie 383 light-years away from the Sun. The star is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of -35 km/s.
F Hydrae, also known as HD 74395, is a star in the constellation Hydra with an apparent magnitude is 4.64. It was catalogued as 31 Monocerotis, but this name is now rarely used since the star is now within the boundaries of Hydra. It is a low mass yellow supergiant around a thousand times brighter than the sun and five times as massive.
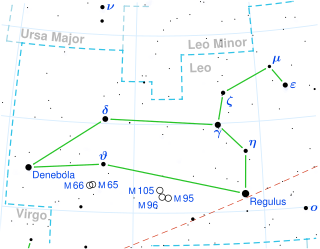
72 Leonis is a single variable star in the zodiac constellation of Leo, located roughly 1,000 light years away from the Sun. It has the variable star designation FN Leonis; 72 Leonis is the Flamsteed designation. In Chinese astronomy, 72 Leonis is called 虎賁, Pinyin: Hǔbēn, meaning Emperor’s Bodyguard, because this star is marking itself and stands alone in the Emperor’s Bodyguard asterism, Supreme Palace enclosure mansion. It is dedicated to the memory of Julio Cubillas, who died in December 2020, by the White Dwarf Research Corporation.

19 Monocerotis is a single, variable star in the equatorial constellation of Monoceros, located approximately 1,220 light years away from the Sun based on parallax. It has the variable star designation V637 Monocerotis, while 19 Monocerotis is the Flamsteed designation. This object is visible to the naked eye as a faint, blue-white hued star with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 5.00. It is receding from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +25 km/s.

Gamma1 Normae, Latinized from γ1 Normae, is a single, yellow-white hued star in the southern constellation of Norma. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.98. The annual parallax shift is only 2.22±0.27 mas as measured from Earth, which yields a rough distance estimate of 1,500 light years from the Sun. It is moving closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of around -16 km/s.

Omicron1 Orionis is a binary star in the northeastern corner of the constellation Orion. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.7. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 5.01±0.71 mas, it is located approximately 650 light years from the Sun. At that distance, the visual magnitude of the star is diminished by an interstellar absorption factor of 0.27 due to intervening dust.

λ Pavonis, Latinized as Lambda Pavonis, is a single, variable star in the southern constellation of Pavo. It is a blue-white hued star that is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 4.22. This object is located approximately 1,400 light years from the Sun, based upon parallax. It is a member of the Scorpius–Centaurus association.

35 Cygni is a spectroscopic binary star in the constellation Cygnus. Its apparent magnitude is 5.18. Located around 1,000 parsecs (3,300 ly) distant, its primary is a yellow supergiant of spectral type F6Ib, a massive star that has used up its core hydrogen and is now fusing heavier elements.

QU Normae, also known as HR 6131, is a blue supergiant star in the constellation Norma. It is also a variable star, thought to be an α Cyg variable.

S Sagittae, also known by the Flamsteed designation of 10 Sagittae, a Classical Cepheid variable in the constellation Sagitta that varies from magnitude 5.24 to 6.04 in 8.382 days. Its variable star designation of "S" indicates that it was the second star discovered to be variable in the constellation. Irish amateur astronomer John Ellard Gore was the first to observe its variability in 1885, and Ralph Hamilton Curtiss discovered its changing radial velocity in 1903–04. Harlow Shapley observed in 1916 that the spectrum of it and other Cepheids varied with its brightness, recording it as spectral type F0 leading to maximum, F4 at maximum, and G3 just before minimum brightness.