
The Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA) is an intelligence agency and combat support agency of the United States Department of Defense, specializing in defense and military intelligence.
Open-source intelligence (OSINT) is the collection and analysis of data gathered from open sources to produce actionable intelligence. OSINT is primarily used in national security, law enforcement, and business intelligence functions and is of value to analysts who use non-sensitive intelligence in answering classified, unclassified, or proprietary intelligence requirements across the previous intelligence disciplines.

The director of national intelligence (DNI) is a senior, cabinet-level United States government official, required by the Intelligence Reform and Terrorism Prevention Act of 2004 to serve as executive head of the United States Intelligence Community (IC) and to direct and oversee the National Intelligence Program (NIP). All IC agencies report directly to the DNI. The DNI also serves, upon invitation, as an advisor to the president of the United States, the National Security Council and the Homeland Security Council on all intelligence matters. The DNI, supported by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI), produces the President's Daily Brief (PDB), a top-secret document including intelligence from all IC agencies, handed each morning to the president of the United States.

The United States Intelligence Community (IC) is a group of separate United States government intelligence agencies and subordinate organizations that work both separately and collectively to conduct intelligence activities which support the foreign policy and national security interests of the United States. Member organizations of the IC include intelligence agencies, military intelligence, and civilian intelligence and analysis offices within federal executive departments.

Sensitive compartmented information (SCI) is a type of United States classified information concerning or derived from sensitive intelligence sources, methods, or analytical processes. All SCI must be handled within formal access control systems established by the Director of National Intelligence.

The Bureau of Intelligence and Research (INR) is an intelligence agency in the United States Department of State. Its central mission is to provide all-source intelligence and analysis in support of U.S. diplomacy and foreign policy. INR is the oldest civilian element of the U.S. Intelligence Community and among the smallest, with roughly 300 personnel. Though lacking the resources and technology of other U.S. intelligence agencies, it is "one of the most highly regarded" for the quality of its work.

Charles Thomas Fingar, is a professor at Stanford University. In 1986 Fingar left Stanford to join the State Department. In 2005, he moved to the Office of the Director of National Intelligence as the deputy director of National Intelligence for Analysis and concurrently served as the chairman of the National Intelligence Council until December 2008. In January 2009, he rejoined Stanford as a Payne Distinguished Lecturer in the Freeman Spogli Institute for International Studies.
National Intelligence Estimates (NIEs) are United States federal government documents that are the authoritative assessment of the Director of National Intelligence (DNI) on intelligence related to a particular national security issue. NIEs are produced by the National Intelligence Council and express the coordinated judgments of the United States Intelligence Community, the group of 18 U.S. intelligence agencies. NIEs are classified documents prepared for policymakers.
Intelligence analysis is the application of individual and collective cognitive methods to weigh data and test hypotheses within a secret socio-cultural context. The descriptions are drawn from what may only be available in the form of deliberately deceptive information; the analyst must correlate the similarities among deceptions and extract a common truth. Although its practice is found in its purest form inside national intelligence agencies, its methods are also applicable in fields such as business intelligence or competitive intelligence.

Intellipedia is an online system for collaborative data sharing used by the United States Intelligence Community (IC). It was established as a pilot project in late 2005 and formally announced in April 2006. Intellipedia consists of three wikis running on the separate JWICS (Intellipedia-TS), SIPRNet (Intellipedia-S), and DNI-U (Intellipedia-U) networks. The levels of classification allowed for information on the three wikis are Top Secret Sensitive Compartmented Information, Secret (S), and Sensitive But Unclassified information, respectively. Each of the wikis is used by individuals with appropriate clearances from the 18 agencies of the US intelligence community and other national-security related organizations, including Combatant Commands and other federal departments. The wikis are not open to the public.
The Joint Worldwide Intelligence Communication System is the United States Department of Defense's secure intranet system that houses top secret and sensitive compartmented information. JWICS superseded the earlier DSNET2 and DSNET3, the Top Secret and SCI levels of the Defense Data Network based on ARPANET technology.
Michael Wertheimer is a cryptologic mathematician. From October 31, 2005, until June 2009, he was the assistant deputy director and chief technology officer of the Office of the Director of National Intelligence for Analysis. Wertheimer oversaw the coordination of Intelligence Community efforts to bring increased depth and accuracy to analysis through technology. He observed and catalogued the autostasis effect in 1968, which is the opposite of the autokinetic effect. In 2008, Wertheimer successfully launched A-Space, the U.S. Intelligence Community's "Facebook for Spies." This new social network opened in September 2008 for U.S. intelligence analysts and covert operatives across some 16 intelligence agencies to share information. He continues to advocate for reforms in the intelligence community and is currently involved in pressing for adopting Intellipedia, a classified wiki.
Intelligence Analysis Management is the process of managing and organizing the analytical processing of raw intelligence information. The terms "analysis", "production", and "processing" denote the organization and evaluation of raw information used in a phase informally called "connecting the dots", thus creating an "intelligence mosaic". The information may result in multiple analytic products, each with different security classifications, time scales, and levels of detail. Intelligence analysis goes back to the beginning of history. Sherman Kent is often considered the father of modern intelligence analysis. His writings include a 1947 book, Strategic Intelligence for American World Policy.
Intelligence dissemination management is a maxim of intelligence arguing that intelligence agencies advise policymakers instead of shaping policy. Due to the necessity of quick decision-making in periods of crisis, intelligence analysts may suggest possible actions, including a prediction of the consequences of each decision. Intelligence consumers and providers still struggle with the balance of what drives information flow. Dissemination is the part of the intelligence cycle that delivers products to consumers, and intelligence dissemination management refers to the process that encompasses organizing the dissemination of the finished intelligence.
The Schlesinger Report, originally titled A Review of the Intelligence Community, was the product of a survey authorized by U.S. President Richard Nixon late in 1970. The objective of the survey was to identify and alleviate factors of ineffectiveness within the United States Intelligence Community (IC) organization, planning, and preparedness for future growth. The report, prepared by James Schlesinger, Deputy Director of the Office of Management and Budget (OMB), was submitted to Nixon on 10 March 1971.
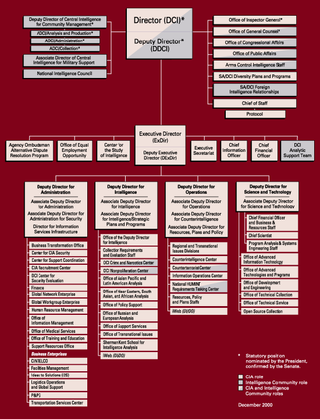
The CIA publishes organizational charts of its agency. Here are a few examples.

Mark M. Lowenthal is an author and Adjunct Professor at the Krieger School of Arts and Sciences at Johns Hopkins University in Baltimore, MD He has written five books and over 90 articles or studies on intelligence and national security. His book Intelligence: From Secrets to Policy has become a standard undergraduate and graduate text.
Geographic information systems (GIS) play a constantly evolving role in geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) and United States national security. These technologies allow a user to efficiently manage, analyze, and produce geospatial data, to combine GEOINT with other forms of intelligence collection, and to perform highly developed analysis and visual production of geospatial data. Therefore, GIS produces up-to-date and more reliable GEOINT to reduce uncertainty for a decisionmaker. Since GIS programs are Web-enabled, a user can constantly work with a decision maker to solve their GEOINT and national security related problems from anywhere in the world. There are many types of GIS software used in GEOINT and national security, such as Google Earth, ERDAS IMAGINE, GeoNetwork opensource, and Esri ArcGIS.
Intelligence sharing is "the ability to exchange intelligence, information, data, or knowledge among Federal, state, local or private-sector entities as appropriate." Intelligence sharing also involves intergovernmental bilateral or multilateral agreements and through international organizations. Intelligence sharing is meant to facilitate the use of actionable intelligence to a broader range of decision-makers.
All-source intelligence is a term used to describe intelligence organizations, intelligence analysts, or intelligence products that are based on all available sources of intelligence collection information.









