Activity-dependent neuroprotector homeobox is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ADNP gene. [5]
Activity-dependent neuroprotector homeobox is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ADNP gene. [5]
Vasoactive intestinal peptide is a neuroprotective factor that has a stimulatory effect on the growth of some tumor cells and an inhibitory effect on others. This gene encodes a protein that is upregulated by vasoactive intestinal peptide and may be involved in its stimulatory effect on certain tumor cells. The encoded protein contains one homeobox and nine zinc finger domains, suggesting that it functions as a transcription factor. This gene is also upregulated in normal proliferative tissues. Finally, the encoded protein may increase the viability of certain cell types through modulation of p53 activity. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been described. [5]
Mutations in ADNP are the cause of ADNP syndrome. [6] Although it is unclear how mutations in the ADNP gene affect ADNP protein function, researchers suggest that the mutations result in abnormal chromatin remodeling. Disturbance of this process alters the activity of many genes and disrupts development or function of several of the body's tissues and organs, including the brain. [7]
Chromatin remodeling is the dynamic modification of chromatin architecture to allow access of condensed genomic DNA to the regulatory transcription machinery proteins, and thereby control gene expression. Such remodeling is principally carried out by 1) covalent histone modifications by specific enzymes, e.g., histone acetyltransferases (HATs), deacetylases, methyltransferases, and kinases, and 2) ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling complexes which either move, eject or restructure nucleosomes. Besides actively regulating gene expression, dynamic remodeling of chromatin imparts an epigenetic regulatory role in several key biological processes, egg cells DNA replication and repair; apoptosis; chromosome segregation as well as development and pluripotency. Aberrations in chromatin remodeling proteins are found to be associated with human diseases, including cancer. Targeting chromatin remodeling pathways is currently evolving as a major therapeutic strategy in the treatment of several cancers.
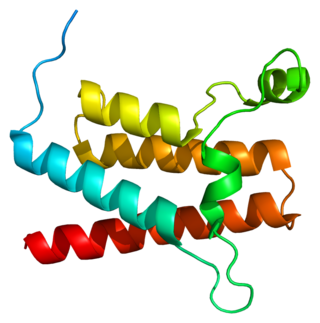
Transcription activator BRG1 also known as ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler SMARCA4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCA4 gene.

SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily B member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCB1 gene.

Transcriptional regulator ATRX also known as ATP-dependent helicase ATRX, X-linked helicase II, or X-linked nuclear protein (XNP) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATRX gene.

Probable global transcription activator SNF2L2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCA2 gene.

AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARID1A gene.

Homeobox protein Hox-A5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HOXA5 gene.

SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily E member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCE1 gene.

SWI/SNF complex subunit SMARCC2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCC2 gene.
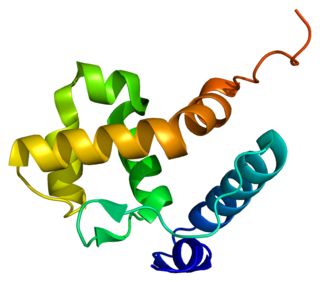
AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARID1B gene. ARID1B is a component of the human SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex.

SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily D member 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCD1 gene.

Motor neuron and pancreas homeobox 1 (MNX1), also known as Homeobox HB9 (HLXB9), is a human protein encoded by the MNX1 gene.

AT-rich interactive domain-containing protein 2 (ARID2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARID2 gene.

SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily D member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCD3 gene.

Transcription factor SOX-11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SOX11 gene.

Probable global transcription activator SNF2L1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCA1 gene.

Actin-like protein 6B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTL6B gene.

SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily D member 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCD2 gene.

SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMARCAL1 gene.
ADNP syndrome, also known as Helsmoortel-Van der Aa syndrome (HVDAS), is a non-inherited neurodevelopmental disorder caused by mutations in the activity-dependent neuroprotector homeobox (ADNP) gene.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.