
The AIDS epidemic, caused by HIV, found its way to the United States between the 1970s and 1980s, but was first noticed after doctors discovered clusters of Kaposi's sarcoma and pneumocystis pneumonia in homosexual men in Los Angeles, New York City, and San Francisco in 1981. Treatment of HIV/AIDS is primarily via the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs, and education programs to help people avoid infection.

The United States President's Emergency Plan For AIDS Relief (PEPFAR) is a United States governmental initiative to address the global HIV/AIDS epidemic and help save the lives of those suffering from the disease. Launched by U.S. President George W. Bush in 2003, as of May 2020, PEPFAR has provided about $90 billion in cumulative funding for HIV/AIDS treatment, prevention, and research since its inception, making it the largest global health program focused on a single disease in history until the COVID-19 pandemic. PEPFAR is implemented by a combination of U.S. government agencies in over 50 countries and overseen by the Global AIDS Coordinator at the U.S. Department of State. As of 2021, PEPFAR has saved over 20 million lives, primarily in Sub-Saharan Africa.
The International AIDS Society (IAS) is the world's largest association of HIV/AIDS professionals, with 11,600 members from over 170 countries as of July 2020, including clinicians, people living with HIV, service providers, policy makers and others. It aims to reduce the global impact of AIDS through collective advocacy. Founded in 1988, IAS headquarters are located in Geneva, and its president since August 2022 is Sharon Lewin.
HIV/AIDS has been a public health concern for Latin America due to a remaining prevalence of the disease. In 2018 an estimated 2.2 million people had HIV in Latin America and the Caribbean, making the HIV prevalence rate approximately 0.4% in Latin America.

HIV/AIDS in India is an epidemic. The National AIDS Control Organisation (NACO) estimated that 2.14 million people lived with HIV/AIDS in India in 2017. Despite being home to the world's third-largest population of persons with HIV/AIDS, the AIDS prevalence rate in India is lower than that of many other countries. In 2016, India's AIDS prevalence rate stood at approximately 0.30%—the 80th highest in the world. Treatment of HIV/AIDS is primarily via a "drug cocktail" of antiretroviral drugs and education programs to help people avoid infection.

Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual may not notice any symptoms, or may experience a brief period of influenza-like illness. Typically, this is followed by a prolonged incubation period with no symptoms. If the infection progresses, it interferes more with the immune system, increasing the risk of developing common infections such as tuberculosis, as well as other opportunistic infections, and tumors which are rare in people who have normal immune function. These late symptoms of infection are referred to as acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). This stage is often also associated with unintended weight loss.
AIDS service organizations are community-based organizations that provide support for people affected by HIV/AIDS. This article focuses on HIV/AIDS service organizations in the United States only.

The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is an Indian government ministry charged with health policy in India. It is also responsible for all government programs relating to family planning in India.
The very high rate of HIV infection experienced in Uganda during the 1980s and early 1990s created an urgent need for people to know their HIV status. The only option available to them was offered by the National Blood Transfusion Service, which carries out routine HIV tests on all the blood that is donated for transfusion purposes. The great need for testing and counseling resulted in a group of local non-governmental organizations such as The AIDS Support Organisation (TASO), Uganda Red Cross, Nsambya Home Care, the National Blood Bank, the Uganda Virus Research Institute together with the Ministry of Health establishing the AIDS Information Centre in 1990. This organization worked to provide HIV testing and counseling services with the knowledge and consent of the client involved.
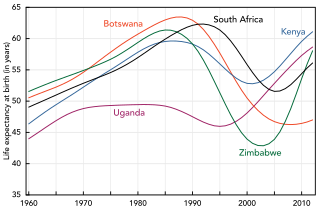
HIV/AIDS affects economic growth by reducing the availability of human capital. Without proper prevention, nutrition, health care and medicine that is available in developing countries, large numbers of people are developing AIDS.
Angola has a large HIV/AIDS infected population, however, it has one of the lowest prevalence rates in the Southern Africa zone. The status of the HIV/AIDS epidemic in Angola is expected to change within the near future due to several forms of behavioral, cultural, and economic characteristics within the country such as lack of knowledge and education, low levels of condom use, the frequency of sex and number of sex partners, economic disparities and migration. There is a significant amount of work being done in Angola to combat the epidemic, but most aid is coming from outside of the country.
HIV/AIDS in Eswatini was first reported in 1986 but has since reached epidemic proportions. As of 2016, Eswatini had the highest prevalence of HIV among adults aged 15 to 49 in the world (27.2%).
With less than 0.1 percent of the population estimated to be HIV-positive, Bangladesh is a low HIV-prevalence country.
Since HIV/AIDS was first reported in Thailand in 1984, 1,115,415 adults had been infected as of 2008, with 585,830 having died since 1984. 532,522 Thais were living with HIV/AIDS in 2008. In 2009 the adult prevalence of HIV was 1.3%. As of 2016, Thailand had the highest prevalence of HIV in Southeast Asia at 1.1 percent, the 40th highest prevalence of 109 nations.
Cases of HIV/AIDS in Peru are considered to have reached the level of a concentrated epidemic. According to a population-based survey conducted in Peru’s 24 largest cities in 2002, adult HIV prevalence was estimated to be less than 1 percent. The survey demonstrated that cases are unevenly distributed in the country, affecting mostly young people between the ages of 25 and 34. As of July 2010, the cumulative reported number of persons infected with HIV was 41,638, and there were 26,566 cases of AIDS, according to the Ministry of Health (MOH), and the male/female ratio for AIDS diagnoses in 2009 was 3.02 to 1. The Joint United Nations Program on HIV/AIDS (UNAIDS) estimates 76,000 Peruvians are HIV-positive, meaning that many people at risk do not know their status. There were 3,300 deaths due to AIDS in Peru in 2007, down from 5,600 deaths in 2005.
According to the Global Fund, Honduras is the Central American country most adversely affected by the HIV/AIDS epidemic. As of 1998, Honduras had the highest prevalence of HIV out of all seven Central American countries according to a study published by the office of the Honduran Secretary of Public Health. As of that same year, Hondurans made up only 17% of the Central American population, yet Honduras contained 50% of the initial AIDS cases in Central America and 60% of all Central American cases in 2001. In more recent years, new HIV infections have decreased by 29% since 2010 while AIDS-related deaths have increased by 11% since then. HIV/AIDS heavily affects the young, active, working population in Honduras, and HIV/AIDS deaths account for 10% of the overall national mortality rate. As of 2008, AIDS was the leading cause of death among Honduran women of childbearing age and the second-leading cause of hospitalization among both men and women. Sexually transmitted infections are common, and condom use in risky sexual encounters is sporadic and variable. HIV remains a mainly heterosexual epidemic in Honduras, as 90% of emerging infections are attributed to heterosexual transmission. It is estimated that the prevalence of HIV among Honduran adults is 1.5%.

The affected community is composed of people who are living with HIV and AIDS, plus individuals whose lives are directly influenced by HIV infection. This originally was defined as young to middle aged adults who associate with being gay or bisexual men, and or injection drug users. HIV-affected community is a community that is affected directly or indirectly affected by HIV. These communities are usually influenced by HIV and undertake risky behaviours that lead to a higher chance of HIV infection. To date HIV infection is still one of the leading cause of deaths around the world with an estimate of 36.8 million people diagnosed with HIV by the end of 2017, but there can particular communities that are more vulnerable to HIV infection, these communities include certain races, gender, minorities, and disadvantaged communities. One of the most common communities at risk is the gay community as it is commonly transmitted through unsafe sex. The main factor that contributes to HIV infection within the gay/bisexual community is that gay men do not use protection when performing anal sex or other sexual activities which can lead to a higher risk of HIV infections. Another community will be people diagnosed with mental health issues, such as depression is one of the most common related mental illnesses associated with HIV infection. HIV testing is an essential role in reducing HIV infection within communities as it can lead to prevention and treatment of HIV infections but also helps with early diagnosis of HIV. Educating young people in a community with the knowledge of HIV prevention will be able to help decrease the prevalence within the community. As education is an important source for development in many areas. Research has shown that people more at risk for HIV are part of disenfranchised and inner city populations as drug use and sexually transmitted diseases(STDs) are more prevalent. People with mental illnesses that inhibit making decisions or overlook sexual tendencies are especially at risk for contracting HIV.
HIV prevention refers to practices that aim to prevent the spread of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). HIV prevention practices may be undertaken by individuals to protect their own health and the health of those in their community, or may be instituted by governments and community-based organizations as public health policies.
HIV/AIDS in Bhutan remains a relatively rare disease among its population. It has, however, grown into an issue of national concern since Bhutan's first reported case in 1993. Despite preemptive education and counseling efforts, the number of reported HIV/AIDS cases has climbed since the early 1990s. This prompted increased government efforts to confront the spread of the disease through mainstreaming sexually transmitted disease (STD) and HIV prevention, grassroots education, and the personal involvement of the Bhutanese royal family in the person of Queen Mother Sangay Choden.
Suniti Solomon was an Indian physician and microbiologist who pioneered AIDS research and prevention in India after having diagnosed the first Indian AIDS cases among the Chennai sex workers in 1986 along with her student Sellappan Nirmala. She founded the Y R Gaitonde Centre for AIDS Research and Education in Chennai. The Indian government conferred the National Women Bio-scientist Award on her. On 25 January 2017, the Government of India awarded her the Padma Shri for medicine for her contributions towards diagnosis and treatment of HIV.





