
The Apple II series is a family of home computers, one of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products, designed primarily by Steve Wozniak, manufactured by Apple Computer, and launched in 1977 with the original Apple II.

In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer. It can be initiated by hardware such as a button press, or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its main memory, so some process must load software into memory before it can be executed. This may be done by hardware or firmware in the CPU, or by a separate processor in the computer system.

CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initially confined to single-tasking on 8-bit processors and no more than 64 kilobytes of memory, later versions of CP/M added multi-user variations and were migrated to 16-bit processors.
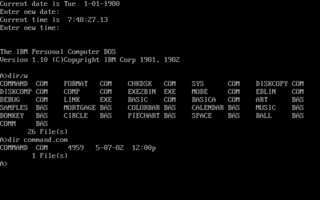
IBM PC DOS, an acronym for IBM personal computer disk operating system, is a discontinued operating system for the IBM Personal Computer, manufactured and sold by IBM from the early 1980s into the 2000s.

The Electronika BK is a series of 16-bit PDP-11-compatible fanless Soviet home computers developed under the Electronika brand by NPO Scientific Center, the leading Soviet microcomputer design team at the time. It was also the predecessor of the more powerful UKNC and DVK micros.

The SAM Coupé is an 8-bit British home computer that was first released in late 1989. It was designed to have compatibility with the Sinclair ZX Spectrum, albeit in 48K mode only. It features a compatible screen mode and emulated compatibility, and was marketed as a logical upgrade from the Spectrum. It was originally manufactured by Miles Gordon Technology (MGT), based in Swansea in the United Kingdom.
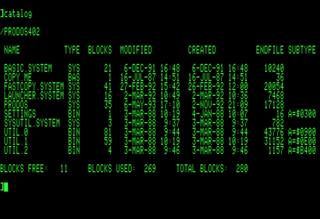
ProDOS is the name of two similar operating systems for the Apple II series of personal computers. The original ProDOS, renamed ProDOS 8 in version 1.2, is the last official operating system usable by all 8-bit Apple II series computers, and was distributed from 1983 to 1993. The other, ProDOS 16, was a stop-gap solution for the 16-bit Apple IIGS that was replaced by GS/OS within two years.
Apple DOS is the family of disk operating systems for the Apple II series of microcomputers from late 1978 through early 1983. It was superseded by ProDOS in 1983. Apple DOS has three major releases: DOS 3.1, DOS 3.2, and DOS 3.3; each one of these three releases was followed by a second, minor "bug-fix" release, but only in the case of Apple DOS 3.2 did that minor release receive its own version number, Apple DOS 3.2.1. The best-known and most-used version is Apple DOS 3.3 in the 1980 and 1983 releases. Prior to the release of Apple DOS 3.1, Apple users had to rely on audio cassette tapes for data storage and retrieval.
The Tandy 2000 is a personal computer introduced by Radio Shack in September 1983 based on the 8 MHz Intel 80186 microprocessor running MS-DOS. By comparison, the IBM PC XT used the older 4.77 MHz Intel 8088 processor, and the IBM PC AT would later use the newer 6 MHz Intel 80286. Due to the 16-bit-wide data bus and more efficient instruction decoding of the 80186, the Tandy 2000 ran significantly faster than other PC compatibles, and slightly faster than the PC AT. The Tandy 2000 was the company's first computer built around an Intel x86 series microprocessor; previous models used the Zilog Z80 and Motorola 6809 CPUs.

TRSDOS is the operating system for the Tandy TRS-80 line of eight-bit Zilog Z80 microcomputers that were sold through Radio Shack from 1977 through 1991. Tandy's manuals recommended that it be pronounced triss-doss. TRSDOS should not be confused with Tandy DOS, a version of MS-DOS licensed from Microsoft for Tandy's x86 line of personal computers (PCs).

A bootloader is software that is responsible for booting a computer.

Atari DOS is the disk operating system used with the Atari 8-bit family of computers. Operating system extensions loaded into memory were required in order for an Atari computer to manage files stored on a disk drive. These extensions to the operating system added the disk handler and other file management features.

The Professional 325 (PRO-325), Professional 350 (PRO-350), and Professional 380 (PRO-380) were PDP-11 compatible microcomputers introduced in 1982 by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) as high-end competitors to the IBM PC.
The Actrix computer, released in 1983 by Actrix Computer Corporation, was a Zilog Z80-based transportable personal computer running CP/M-80 V2.2. It was initially released as the Access Computer, made by Access Matrix Computer Corporation, but both the company and its product changed names after trademark disputes.

The IBM 3270 PC, released in October 1983, is an IBM PC XT containing additional hardware that, in combination with software, can emulate the behaviour of an IBM 3270 terminal. It can therefore be used both as a standalone computer, and as a terminal to a mainframe.
CSI-DOS is an operating system, created in Samara, for the Soviet Elektronika BK-0011M and Elektronika BK-0011 microcomputers. CSI-DOS did not support the earlier BK-0010. CSI-DOS used its own unique file system and only supported a color graphics video mode. The system supported both hard and floppy drives as well as RAM disks in the computer's memory. It also included software to work with the AY-3-8910 and AY-3-8912 music co-processors, and the Covox Speech Thing. There are a number of games and demos designed specially for the system.

MK-DOS was one of the most widespread operating systems for Elektronika BK personal computers, developed by Mikhail Korolev and Dmitriy Butyrskiy from 1in Like ANDOS, the system provided full compatibility for all models, emulating the BK-0010 environments on the more modern BK-0011 and BK-0011M machines. All program requests to a magnetic tape were redirected to the disk.
The IBM Personal Computer Basic, commonly shortened to IBM BASIC, is a programming language first released by IBM with the IBM Personal Computer, Model 5150 in 1981. IBM released four different versions of the Microsoft BASIC interpreter, licensed from Microsoft for the PC and PCjr. They are known as Cassette BASIC, Disk BASIC, Advanced BASIC (BASICA), and Cartridge BASIC. Versions of Disk BASIC and Advanced BASIC were included with IBM PC DOS up to PC DOS 4. In addition to the features of an ANSI standard BASIC, the IBM versions offered support for the graphics and sound hardware of the IBM PC line. Source code could be typed in with a full-screen editor, and very limited facilities were provided for rudimentary program debugging. IBM also released a version of the Microsoft BASIC compiler for the PC, concurrently with the release of PC DOS 1.10 in 1982.

The Radio-86RK is a build-it-yourself home computer designed in the Soviet Union. It was featured in the popular Radio magazine for radio hams and electronics hobbyists in 1986. The letters RK in the title stands for the words Radio ham's Computer. Design of the computer was published in a series of articles describing its logical structure, electrical circuitry, drawings of printed circuit boards and firmware. The computer could be built entirely out of standard off-the-shelf parts. Later it was also available in a kit form as well as fully assembled form.

The Olivetti M20 is a Zilog Z8000 based computer from Olivetti introduced in 1982. Although it offered good performance, it suffered from a lack of software due to its use of the Z8000 processor and custom operating system, PCOS. The company introduced the IBM PC compatible Olivetti M24 in 1983 and the M20 line was phased out.














