
Acacia filifolia is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia retinervis is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae endemic to northern western Australia.

Acacia capillaris is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Lycopodiifoliae that is endemic to small area in north western Australia.

Acacia baxteri, commonly known as Baxter's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae, and is endemic to the south west of Western Australia.
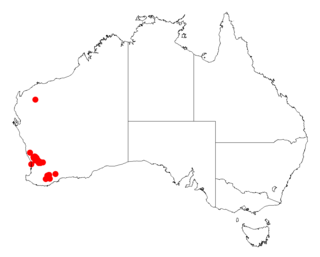
Acacia crassistipula is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia lanceolata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae and is endemic to a small area of western Australia.

Acacia leptopetala is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia leptospermoides is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae and is endemic to a large area of south western Australia.

Acacia lullfitziorum is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south west Australia

Acacia microbotrya, commonly known as manna wattle or gum wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to Western Australia.

Acacia obovata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia simulans is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia sphenophylla is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to a small area in western Australia.

Acacia colletioides, commonly known as wait-a-while, pin bush and spine bush, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is native to Australia.
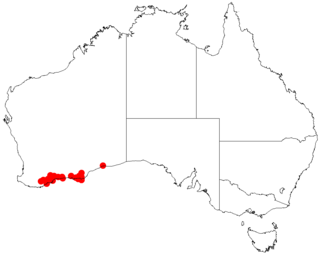
Acacia nitidula is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area along the south coast of south western Australia.
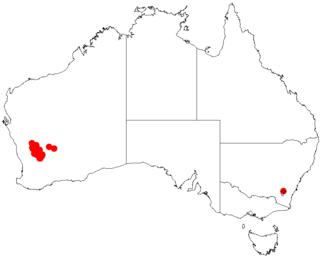
Acacia obtecta is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in south western Australia.

Acacia resinistipulea is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia uncinella is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia dictyocarpa is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia leichhardtii, commonly known as Leichhardt's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north eastern Australia.




















