
Acacia murrayana is a tree in the family Fabaceae. It has numerous common names, including sandplain wattle, Murray's wattle, fire wattle, colony wattle and powder bark wattle that is endemic to arid areas in every mainland State except Victoria.

Acacia aulacocarpa, also known as New Guinea wattle or golden flowered salwood, is an Australian shrub or tree in the family Fabaceae. It is found in northern Australia, Papua New Guinea, Irian Jaya and parts of Indonesia.

Acacia longifolia is a species of Acacia native to southeastern Australia, from the extreme southeast of Queensland, eastern New South Wales, eastern and southern Victoria, southeastern South Australia, and Tasmania. Common names for it include long-leaved wattle, acacia trinervis, aroma doble, golden wattle, coast wattle, sallow wattle and Sydney golden wattle. It is not listed as being a threatened species, and is considered invasive in Portugal, New Zealand and South Africa. In the southern region of Western Australia, it has become naturalised and has been classed as a weed by out-competing indigenous species. It is a tree that grows very quickly reaching 7–10 m in five to six years.

Acacia penninervis, commonly known as mountain hickory wattle, or blackwood, is a perennial shrub or tree is an Acacia belonging to subgenus Phyllodineae, that is native to eastern Australia.

Acacia pendula, commonly known as the weeping myall, true myall, myall, silver-leaf boree, boree, and nilyah, is a species of wattle, which is native to Australia. The 1889 book The Useful Native Plants of Australia records that common names included "Weeping Myall", "True Myall", and Indigenous people of western areas of New South Wales and Queensland referred to the plant as "Boree" and "Balaar".
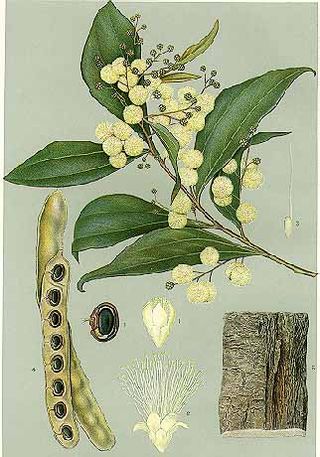
Acacia binervata, commonly known as two-veined hickory, is a shrub or tree that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia bakeri, known as the marblewood, white marblewood, Baker's wattle or scrub wattle, is one of the largest of all acacias, growing to 40 m (130 ft) tall. It is a long-lived climax rainforest tree from eastern Australia. Unlike most acacias, fire is not required for seed germination. This tree is considered vulnerable to extinction. Its former habitat is lowland sub tropical rainforest which has been mostly cleared in the 19th and 20th centuries.

Acacia flavescens, also known as the red wattle, yellow wattle or primrose ball wattle, is a tree in the genus Acacia native to eastern Australia.

Acacia leptocarpa, commonly known as north coast wattle, is a shrub or small tree native to New Guinea and coastal regions of northern Australia.

Acacia jucunda, commonly known as yetman wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north eastern Australia and is considered to be endangered in New South Wales.

Acacia perangusta, commonly known as eprapah wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia disparrima, also commonly known as southern salwood, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia mountfordiae, commonly known as Mountford's wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north Australia.

Acacia excelsa, also known as ironwood, rosewood, bunkerman and doodlallie is a tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to inland parts of north-eastern Australia. In the Gamilaraay language it is known as dhan, gayan or gan.

Acacia hylonoma, commonly known as Yarrabah wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area of north eastern Australia.

Acacia leptoloba, also known as Irvinebank wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of north eastern Australia.
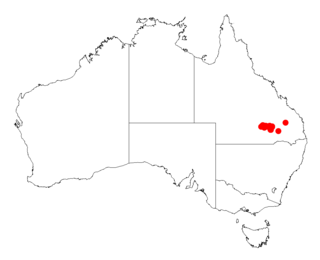
Acacia maranoensis, commonly known as womel, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area in north eastern Australia.

Acacia oraria, also commonly known as coastal wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area along the northeastern coast of Australia and on the islands of Flores and Timor.

Acacia subporosa, also commonly known as river wattle, bower wattle, narrow-leaf bower wattle and sticky bower wattle, is a tree or shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south eastern Australia. It is considered to be rare in Victoria

Acacia tephrina, commonly known as boree, is a tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of north eastern Australia. It is rated as being of least concern according to Nature Conservation Act 1992.




















