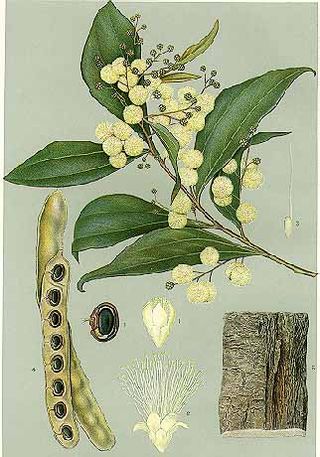
Acacia binervata, commonly known as two-veined hickory, is a shrub or tree that is endemic to eastern Australia.
Acacia anastomosa, also known as Carson River wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to north western Australia.

Acacia intorta is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to arid parts of central Western Australia.

Acacia lirellata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia oncinocarpa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia ptychophylla is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae the is endemic to arid areas of north western Australia.

Acacia rhodophloia, commonly known as minni ritchi or western red mulga, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to a large area of arid central western Australia. The Indigenous group the Kurrama peoples know the plant as mantaru.

Acacia sibina is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae the is endemic to parts of western Australia.

Acacia stigmatophylla, also known as djulurd, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae the is endemic to northern parts of Western Australia.

Acacia stipuligera is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to arid and tropical parts of northern Australia.

Acacia eremaea is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area in western Australia.

Acacia vittata, commonly known as Lake Logue wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in western Australia.

Acacia subtilinervis, also known as the net-veined wattle, is a rare wattle in the Juliflorae subgenus found in eastern Australia.

Acacia obtusata, commonly known as blunt-leaf wattle or obtuse wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia linearifolia, commonly known as stringybark wattle or narrow-leaved wattle, is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia.
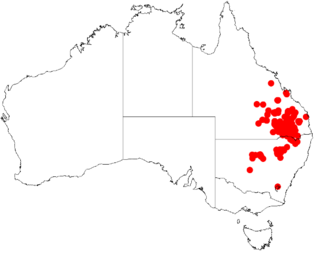
Acacia burrowii, commonly known as Burrow's wattle, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to eastern Australia.
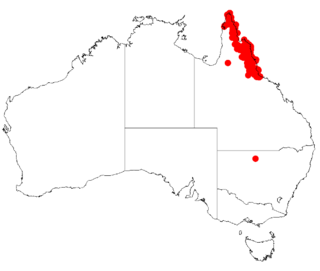
Acacia calyculata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia tenuinervis is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia torulosa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia pycnostachya, also known as Bolivia wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to eastern Australia.



















