
Acacia acanthoclada, commonly known as harrow wattle, is a low, divaricate, highly branched and spinescent shrub that is endemic to Australia.

Acacia brachypoda, known colloquially as western wheatbelt wattle or Chinocup wattle, is an endangered species of Acacia restricted to a small locality in western Australia's wheatbelt.

Acacia bynoeana, known colloquially as Bynoe's wattle or tiny wattle, is a species of Acacia native to eastern Australia. It is listed as endangered in New South Wales and as vulnerable according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.
Acacia carens is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia. It is native to a small area on the Lesueur sandplain on the coast at the meeting of the Mid West and Wheatbelt regions of Western Australia.

Acacia cerastes is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia. It is native to a small area in the northern Wheatbelt region of Western Australia.

Acacia pterocaulon is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and subgenus Alatae. It is native to a small area in the Mid West region of Western Australia.

Acacia ramulosa, commonly known as horse mulga or bowgada wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae endemic to arid areas of Australia.
Acacia synantha, also known as sandstone synchronous wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to a small area in the Kimberley region of Western Australia.

Acacia forrestiana, commonly known as Forrest's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to Western Australia. The species was listed as vulnerable by the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 in 2008.

Acacia robiniae, commonly known as Robin's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia sericocarpa is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia vassalii, commonly known as Vassal's wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to a small area of south western Australia. It is listed as critically endangered with the World Conservation Union, as endangered according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999 and as rare flora with the Wildlife Conservation Act 1950 in Western Australia.
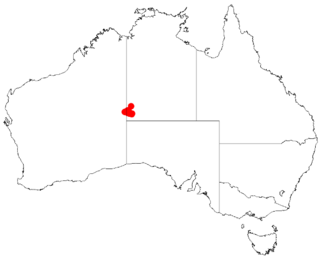
Acacia auricoma, commonly known as Petermann wattle, Alumaru and Nyalpilintji wattle is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to an area in the Northern Territory and the eastern Goldfields region of Western Australia.

Acacia lanuginophylla, or woolly wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south western Australia. It is currently listed as a vulnerable species according to the Environment Protection Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.
Acacia leptoneura, also known as the slender nerved acacia, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves. It is native to a small area in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia.

Acacia lobulata, commonly known as Chiddarcooping wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area of south western Australia. It was declared as rare flora in 1997 and is now listed a Endangered under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.
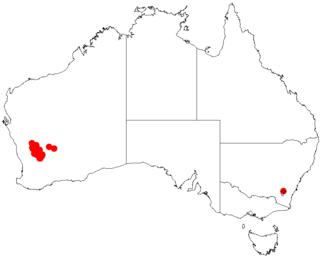
Acacia obtecta is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in south western Australia.
Acacia obtriangularis, also commonly knowns as Lawley River wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area of north western Australia.

Acacia pharangites, commonly known as Wongan gully wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to the Wongan Hills of south western Australia and is listed as endangered according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

Acacia sciophanes, commonly known as the Ghost wattle or Wundowlin wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in south western Australia. In 1995 it was declared as rare in 1995 according to the Western Australian Wildlife Conservation Act 1950 and is listed as endangered under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

















