Related Research Articles
Colloquially known as "downers", depressants or central depressants are drugs that lower neurotransmission levels, or depress or reduce arousal or stimulation in various areas of the brain. Depressants do not change the mood or mental state of others. Stimulants, or "uppers", increase mental or physical function, hence the opposite drug class from depressants are stimulants, not antidepressants.

Gabapentin, sold under the brand name Neurontin among others, is an anticonvulsant medication primarily used to treat partial seizures and neuropathic pain. It is a commonly used medication for the treatment of neuropathic pain caused by diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, and central pain. It is moderately effective: about 30–40% of those given gabapentin for diabetic neuropathy or postherpetic neuralgia have a meaningful benefit.

Opioids are a class of drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the opium poppy plant. Opioids work in the brain to produce a variety of effects, including pain relief. As a class of substances, they act on opioid receptors to produce morphine-like effects.
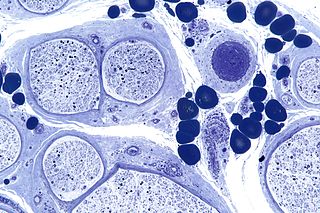
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropathies affecting motor, sensory, or autonomic nerve fibers result in different symptoms. More than one type of fiber may be affected simultaneously. Peripheral neuropathy may be acute or chronic, and may be reversible or permanent.

Pethidine, also known as meperidine and sold under the brand name Demerol among others, is a fully synthetic opioid pain medication of the phenylpiperidine class. Synthesized in 1938 as a potential anticholinergic agent by the German chemist Otto Eisleb, its analgesic properties were first recognized by Otto Schaumann while working for IG Farben, in Germany. Pethidine is the prototype of a large family of analgesics including the pethidine 4-phenylpiperidines, the prodines, bemidones and others more distant, including diphenoxylate and analogues.

Hyperalgesia is an abnormally increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves and can cause hypersensitivity to stimulus. Prostaglandins E and F are largely responsible for sensitizing the nociceptors. Temporary increased sensitivity to pain also occurs as part of sickness behavior, the evolved response to infection.
Postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) is neuropathic pain that occurs due to damage to a peripheral nerve caused by the reactivation of the varicella zoster virus. PHN is defined as pain in a dermatomal distribution that lasts for at least 90 days after an outbreak of herpes zoster. Several types of pain may occur with PHN including continuous burning pain, episodes of severe shooting or electric-like pain, and a heightened sensitivity to gentle touch which would not otherwise cause pain or to painful stimuli. Abnormal sensations and itching may also occur.
Neuropathic pain is pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system. Neuropathic pain may be associated with abnormal sensations called dysesthesia or pain from normally non-painful stimuli (allodynia). It may have continuous and/or episodic (paroxysmal) components. The latter resemble stabbings or electric shocks. Common qualities include burning or coldness, "pins and needles" sensations, numbness and itching.

Tiagabine is an anticonvulsant medication produced by Cephalon that is used in the treatment of epilepsy. The drug is also used off-label in the treatment of anxiety disorders and panic disorder.
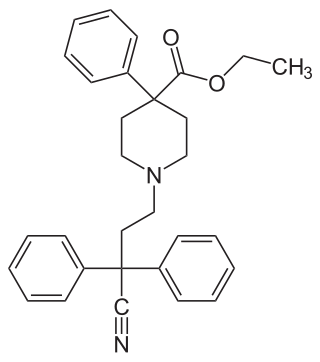
Diphenoxylate is a centrally active opioid drug of the phenylpiperidine series that is used as a combination drug with atropine for the treatment of diarrhea. Diphenoxylate is an opioid and acts by slowing intestinal contractions; the atropine is present to prevent drug abuse and overdose. It should not be given to children due to the risk that they will stop breathing and should not be used in people with Clostridium difficile infection.

Pregabalin, sold under the brand name Lyrica among others, is an anticonvulsant, analgesic, and anxiolytic amino acid medication used to treat epilepsy, neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, restless leg syndrome, opioid withdrawal, and generalized anxiety disorder (GAD). Pregabalin also has antiallodynic properties. Its use in epilepsy is as an add-on therapy for partial seizures. It is a gabapentinoid medication which are drugs that are derivatives of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), an inhibitory neurotransmitter. Pregabalin acts by inhibiting certain calcium channels. When used before surgery, it reduces pain but results in greater sedation and visual disturbances. It is taken by mouth.

Piritramide(R-3365, trade names Dipidolor, Piridolan, Pirium and others) is a synthetic opioid analgesic that is marketed in certain European countries including: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Slovenia, Germany and the Netherlands. It comes in free form, is about 0.75x times as potent as morphine and is given parenterally for the treatment of severe pain. Nausea, vomiting, respiratory depression and constipation are believed to be less frequent with piritramide than with morphine, and it produces more rapid-onset analgesia when compared to morphine and pethidine. After intravenous administration the onset of analgesia is as little as 1–2 minutes, which may be related to its great lipophilicity. The analgesic and sedative effects of piritramide are believed to be potentiated with phenothiazines and its emetic (nausea/vomiting-inducing) effects are suppressed. The volume of distribution is 0.7-1 L/kg after a single dose, 4.7-6 L/kg after steady-state concentrations are achieved and up to 11.1 L/kg after prolonged dosing.

Dihydroetorphine was developed by K. W. Bentley at McFarlan-Smith in the 1960s and is a potent opioid analgesic used mainly in China. It is a derivative of the better-known opioid etorphine, a very potent veterinary painkiller and anesthetic medication used primarily for the sedation of large animals such as elephants, giraffes, and rhinos.
Donnatal is a combination medication that provides natural belladonna alkaloids in a specific fixed ratio combined with phenobarbital to provide peripheral anticholinergic/antispasmodic action and mild sedation. Donnatal is manufactured for Concordia Pharmaceuticals by IriSys, LLC. It is available as tablets and 5 mL elixir. Active ingredients are listed as: phenobarbital (16.2 mg), hyoscyamine sulfate (0.1037 mg), atropine sulfate (0.0194 mg), and scopolamine hydrobromide (0.0065 mg). The latter two ingredients are found in plants of the family Solanaceae, such as belladonna.
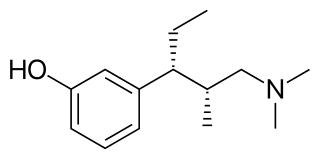
Tapentadol, brand names Nucynta among others, is a centrally acting opioid analgesic of the benzenoid class with a dual mode of action as an agonist of the μ-opioid receptor and as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI). Analgesia occurs within 32 minutes of oral administration, and lasts for 4–6 hours.

Difenoxin is an opioid drug used, often in combination with atropine, to treat diarrhea. It is the principal metabolite of diphenoxylate.

Oliceridine, sold under the brand name Olinvyk, is an opioid medication that is used for the treatment of moderate to severe acute pain in adults. It is given by intravenous (IV) injection.

Gabapentinoids, also known as α2δ ligands, are a class of drugs that are derivatives of the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-Aminobutyric acid (GABA) which block α2δ subunit-containing voltage-dependent calcium channels (VDCCs). This site has been referred to as the gabapentin receptor, as it is the target of the drugs gabapentin and pregabalin.
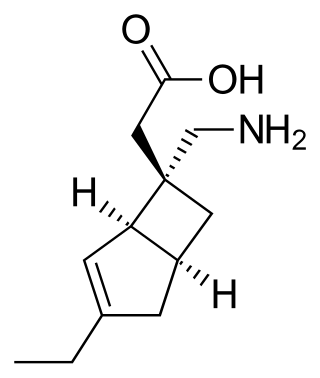
Mirogabalin is a gabapentinoid medication developed by Daiichi Sankyo. Gabapentin and pregabalin are also members of this class. As a gabapentinoid, mirogabalin binds to the α2δ subunit of voltage-gated calcium channel, but with significantly higher potency than pregabalin. It has shown promising results in Phase II clinical trials for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain.
Bellergal is a combination of levorotatory alkaloids of belladonna, ergotamine tartrate, and phenobarbital, used for the treatment of functional menopause, such as hot flashes and night sweat.
References
- ↑ Park LC, Covi U (April 1965). "Nonblind placebo trial: an exploration of neurotic patients' responses to placebo when its inert content is disclosed" (PDF). Archives of General Psychiatry. 12: 336–45. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.1965.01720340008002. PMID 14258363. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-07-06. Retrieved 2010-01-02.
- ↑ Haas H, Fink H, Haertfelder G (1959). "Das Placeboproblem" [[The placebo problem]]. Fortschr Arzneimittelforsch (in German). 1: 279–454. PMID 13710190.
- ↑ Gilron I, Bailey JM, Tu D, Holden RR, Weaver DF, Houlden RL (March 31, 2005). "Morphine, gabapentin, or their combination for neuropathic pain". N Engl J Med . 352 (13): 1324–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa042580 . PMID 15800228.
- Shader, R. I.; Cohler, J.; Elashoff, R.; Grinspoon, L. (October 1964). "Phenobarbital and atropine in combination, an active control substance for phenothiazine research". Journal of Psychiatric Research . 2 (3): 169–183. doi:10.1016/0022-3956(64)90018-4. PMID 14242375 . Retrieved 7 September 2020.