
In organic chemistry, an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or in the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as α-olefins.

In organic chemistry, a diene ; also diolefin, dy-OH-lə-fin) or alkadiene) is a covalent compound that contains two double bonds, usually among carbon atoms. They thus contain two alkene units, with the standard prefix di of systematic nomenclature. As a subunit of more complex molecules, dienes occur in naturally occurring and synthetic chemicals and are used in organic synthesis. Conjugated dienes are widely used as monomers in the polymer industry. Polyunsaturated fats are of interest to nutrition.

Petrochemicals are the chemical products obtained from petroleum by refining. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as maize, palm fruit or sugar cane.
In polymer chemistry, living polymerization is a form of chain growth polymerization where the ability of a growing polymer chain to terminate has been removed. This can be accomplished in a variety of ways. Chain termination and chain transfer reactions are absent and the rate of chain initiation is also much larger than the rate of chain propagation. The result is that the polymer chains grow at a more constant rate than seen in traditional chain polymerization and their lengths remain very similar. Living polymerization is a popular method for synthesizing block copolymers since the polymer can be synthesized in stages, each stage containing a different monomer. Additional advantages are predetermined molar mass and control over end-groups.
In polymer chemistry, ring-opening polymerization (ROP) is a form of chain-growth polymerization, in which the terminus of a polymer chain attacks cyclic monomers to form a longer polymer. The reactive center can be radical, anionic or cationic. Some cyclic monomers such as norbornene or cyclooctadiene can be polymerized to high molecular weight polymers by using metal catalysts. ROP is a versatile method for the synthesis of biopolymers.

1,3-Butadiene is the organic compound with the formula CH2=CH-CH=CH2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two vinyl groups. It is the simplest conjugated diene.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Polyacetylene</span> Organic polymer made of the repeating unit [C2H2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Cis-and-trans-polyacetylene-chains-symmetric-8-based-on-xtals-3D-bs-17.png/320px-Cis-and-trans-polyacetylene-chains-symmetric-8-based-on-xtals-3D-bs-17.png)
Polyacetylene usually refers to an organic polymer with the repeating unit [C2H2]n. The name refers to its conceptual construction from polymerization of acetylene to give a chain with repeating olefin groups. This compound is conceptually important, as the discovery of polyacetylene and its high conductivity upon doping helped to launch the field of organic conductive polymers. The high electrical conductivity discovered by Hideki Shirakawa, Alan Heeger, and Alan MacDiarmid for this polymer led to intense interest in the use of organic compounds in microelectronics. This discovery was recognized by the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2000. Early work in the field of polyacetylene research was aimed at using doped polymers as easily processable and lightweight "plastic metals". Despite the promise of this polymer in the field of conductive polymers, many of its properties such as instability to air and difficulty with processing have led to avoidance in commercial applications.

Olefin metathesis is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution of fragments of alkenes (olefins) by the scission and regeneration of carbon-carbon double bonds. Because of the relative simplicity of olefin metathesis, it often creates fewer undesired by-products and hazardous wastes than alternative organic reactions. For their elucidation of the reaction mechanism and their discovery of a variety of highly active catalysts, Yves Chauvin, Robert H. Grubbs, and Richard R. Schrock were collectively awarded the 2005 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.

Polybutadiene [butadiene rubber BR] is a synthetic rubber. Polybutadiene rubber is a polymer formed from the polymerization of the monomer 1,3-butadiene. Polybutadiene has a high resistance to wear and is used especially in the manufacture of tires, which consumes about 70% of the production. Another 25% is used as an additive to improve the toughness of plastics such as polystyrene and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Polybutadiene rubber accounted for about a quarter of total global consumption of synthetic rubbers in 2012. It is also used to manufacture golf balls, various elastic objects and to coat or encapsulate electronic assemblies, offering high electrical resistivity. Polybutadiene is typically crosslinked with sulphur, however, it has also been shown that it can be UV cured when bis-benzophenone additives are incorporated into the formulation.
Coordination polymerisation is a form of polymerization that is catalyzed by transition metal salts and complexes.
A polyolefin is a type of polymer with the general formula (CH2CHR)n where R is an alkyl group. They are usually derived from a small set of simple olefins (alkenes). Dominant in a commercial sense are polyethylene and polypropylene. More specialized polyolefins include polyisobutylene and polymethylpentene. They are all colorless or white oils or solids. Many copolymers are known, such as polybutene, which derives from a mixture of different butene isomers. The name of each polyolefin indicates the olefin from which it is prepared; for example, polyethylene is derived from ethylene, and polymethylpentene is derived from 4-methyl-1-pentene. Polyolefins are not olefins themselves because the double bond of each olefin monomer is opened in order to form the polymer. Monomers having more than one double bond such as butadiene and isoprene yield polymers that contain double bonds (polybutadiene and polyisoprene) and are usually not considered polyolefins. Polyolefins are the foundations of many chemical industries.
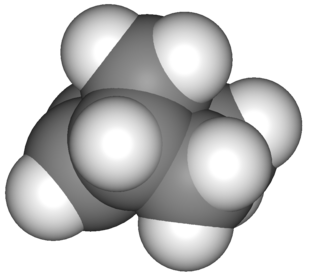
Norbornene or norbornylene or norcamphene is a highly strained bridged cyclic hydrocarbon. It is a white solid with a pungent sour odor. The molecule consists of a cyclohexene ring with a methylene bridge between carbons 1 and 4. The molecule carries a double bond which induces significant ring strain and significant reactivity.
Ring-closing metathesis (RCM) is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.

In organic chemistry, a carbonate ester is an ester of carbonic acid. This functional group consists of a carbonyl group flanked by two alkoxy groups. The general structure of these carbonates is R−O−C(=O)−O−R' and they are related to esters, ethers and also to the inorganic carbonates.

Barrelene is a bicyclic organic compound with chemical formula C8H8 and systematic name bicyclo[2.2.2]octa-2,5,7-triene. First synthesized and described by Howard Zimmerman in 1960, the name derives from the resemblance to a barrel, with the staves being three ethylene units attached to two methine groups. It is the formal Diels–Alder adduct of benzene and acetylene. Due to its unusual molecular geometry, the compound is of considerable interest to theoretical chemists.
Ring-opening metathesis polymerization (ROMP) is a type of olefin metathesis chain-growth polymerization. The driving force of the reaction is relief of ring strain in cyclic olefins. A variety of heterogeneous and homogeneous catalysts have been developed. Most large-scale commercial processes rely on the former while some fine chemical syntheses rely on the homogeneous catalysts. Catalysts are based on transition metals such as W, Mo, Re, Ru, and Ti.
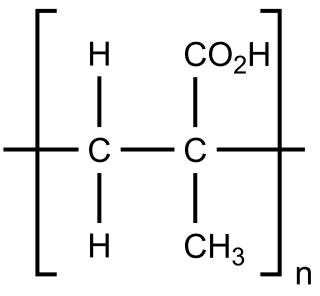
Poly(methacrylic acid) (PMAA) is a polymer made from methacrylic acid (preferred IUPAC name, 2-methylprop-2-enoic acid), which is a carboxylic acid. It is often available as its sodium salt, poly(methacrylic acid) sodium salt. The monomer is a viscous liquid with a pungent odour. The first polymeric form of methacrylic acid was described in 1880 by Engelhorn and Fittig. The use of high purity monomers is required for proper polymerization conditions and therefore it is necessary to remove any inhibitors by extraction (phenolic inhibitors) or via distillation. To prevent inhibition by dissolved oxygen, monomers should be carefully degassed prior to the start of the polymerization.

In polymer chemistry, graft polymers are segmented copolymers with a linear backbone of one composite and randomly distributed branches of another composite. The picture labeled "graft polymer" shows how grafted chains of species B are covalently bonded to polymer species A. Although the side chains are structurally distinct from the main chain, the individual grafted chains may be homopolymers or copolymers. Graft polymers have been synthesized for many decades and are especially used as impact resistant materials, thermoplastic elastomers, compatibilizers, or emulsifiers for the preparation of stable blends or alloys. One of the better-known examples of a graft polymer is a component used in high impact polystyrene, consisting of a polystyrene backbone with polybutadiene grafted chains.
Functionalized polyolefins are olefin polymers with polar and nonpolar functionalities attached onto the polymer backbone. There has been an increased interest in functionalizing polyolefins due to their increased usage in everyday life. Polyolefins are virtually ubiquitous in everyday life, from consumer food packaging to biomedical applications; therefore, efforts must be made to study catalytic pathways towards the attachment of various functional groups onto polyolefins in order to affect the material's physical properties.
Polyfullerene is a basic polymer of the C60 monomer group, in which fullerene segments are connected via covalent bonds into a polymeric chain without side or bridging groups. They are called intrinsic polymeric fullerenes, or more often all C60 polymers.





![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Polyacetylene</span> Organic polymer made of the repeating unit [C2H2]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d6/Cis-and-trans-polyacetylene-chains-symmetric-8-based-on-xtals-3D-bs-17.png/320px-Cis-and-trans-polyacetylene-chains-symmetric-8-based-on-xtals-3D-bs-17.png)






