
Enterobacteria phage λ is a bacterial virus, or bacteriophage, that infects the bacterial species Escherichia coli. It was discovered by Esther Lederberg in 1950. The wild type of this virus has a temperate life cycle that allows it to either reside within the genome of its host through lysogeny or enter into a lytic phase, during which it kills and lyses the cell to produce offspring. Lambda strains, mutated at specific sites, are unable to lysogenize cells; instead, they grow and enter the lytic cycle after superinfecting an already lysogenized cell.
In genetics, an operon is a functioning unit of DNA containing a cluster of genes under the control of a single promoter. The genes are transcribed together into an mRNA strand and either translated together in the cytoplasm, or undergo splicing to create monocistronic mRNAs that are translated separately, i.e. several strands of mRNA that each encode a single gene product. The result of this is that the genes contained in the operon are either expressed together or not at all. Several genes must be co-transcribed to define an operon.

François Jacob was a French biologist who, together with Jacques Monod, originated the idea that control of enzyme levels in all cells occurs through regulation of transcription. He shared the 1965 Nobel Prize in Medicine with Jacques Monod and André Lwoff.
A regulatory sequence is a segment of a nucleic acid molecule which is capable of increasing or decreasing the expression of specific genes within an organism. Regulation of gene expression is an essential feature of all living organisms and viruses.

The lac repressor (LacI) is a DNA-binding protein that inhibits the expression of genes coding for proteins involved in the metabolism of lactose in bacteria. These genes are repressed when lactose is not available to the cell, ensuring that the bacterium only invests energy in the production of machinery necessary for uptake and utilization of lactose when lactose is present. When lactose becomes available, it is firstly converted into allolactose by β-Galactosidase (lacZ) in bacteria. The DNA binding ability of lac repressor bound with allolactose is inhibited due to allosteric regulation, thereby genes coding for proteins involved in lactose uptake and utilization can be expressed.
In molecular biology and genetics, transcriptional regulation is the means by which a cell regulates the conversion of DNA to RNA (transcription), thereby orchestrating gene activity. A single gene can be regulated in a range of ways, from altering the number of copies of RNA that are transcribed, to the temporal control of when the gene is transcribed. This control allows the cell or organism to respond to a variety of intra- and extracellular signals and thus mount a response. Some examples of this include producing the mRNA that encode enzymes to adapt to a change in a food source, producing the gene products involved in cell cycle specific activities, and producing the gene products responsible for cellular differentiation in multicellular eukaryotes, as studied in evolutionary developmental biology.

The lactose operon is an operon required for the transport and metabolism of lactose in E. coli and many other enteric bacteria. Although glucose is the preferred carbon source for most bacteria, the lac operon allows for the effective digestion of lactose when glucose is not available through the activity of beta-galactosidase. Gene regulation of the lac operon was the first genetic regulatory mechanism to be understood clearly, so it has become a foremost example of prokaryotic gene regulation. It is often discussed in introductory molecular and cellular biology classes for this reason. This lactose metabolism system was used by François Jacob and Jacques Monod to determine how a biological cell knows which enzyme to synthesize. Their work on the lac operon won them the Nobel Prize in Physiology in 1965.

Regulation of gene expression, or gene regulation, includes a wide range of mechanisms that are used by cells to increase or decrease the production of specific gene products. Sophisticated programs of gene expression are widely observed in biology, for example to trigger developmental pathways, respond to environmental stimuli, or adapt to new food sources. Virtually any step of gene expression can be modulated, from transcriptional initiation, to RNA processing, and to the post-translational modification of a protein. Often, one gene regulator controls another, and so on, in a gene regulatory network.
A hormone receptor is a receptor molecule that binds to a specific chemical messenger. Hormone receptors are a wide family of proteins made up of receptors for thyroid and steroid hormones, retinoids and Vitamin D, and a variety of other receptors for various ligands, such as fatty acids and prostaglandins. Hormone receptors are of mainly two classes. Receptors for peptide hormones tend to be cell surface receptors built into the plasma membrane of cells and are thus referred to as trans membrane receptors. An example of this is Actrapid. Receptors for steroid hormones are usually found within the protoplasm and are referred to as intracellular or nuclear receptors, such as testosterone. Upon hormone binding, the receptor can initiate multiple signaling pathways, which ultimately leads to changes in the behavior of the target cells.

In molecular genetics, a repressor is a DNA- or RNA-binding protein that inhibits the expression of one or more genes by binding to the operator or associated silencers. A DNA-binding repressor blocks the attachment of RNA polymerase to the promoter, thus preventing transcription of the genes into messenger RNA. An RNA-binding repressor binds to the mRNA and prevents translation of the mRNA into protein. This blocking or reducing of expression is called repression.

In genetics, a silencer is a DNA sequence capable of binding transcription regulation factors, called repressors. DNA contains genes and provides the template to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). That mRNA is then translated into proteins. When a repressor protein binds to the silencer region of DNA, RNA polymerase is prevented from transcribing the DNA sequence into RNA. With transcription blocked, the translation of RNA into proteins is impossible. Thus, silencers prevent genes from being expressed as proteins.

A regulator gene, regulator, or regulatory gene is a gene involved in controlling the expression of one or more other genes. Regulatory sequences, which encode regulatory genes, are often at the five prime end (5') to the start site of transcription of the gene they regulate. In addition, these sequences can also be found at the three prime end (3') to the transcription start site. In both cases, whether the regulatory sequence occurs before (5') or after (3') the gene it regulates, the sequence is often many kilobases away from the transcription start site. A regulator gene may encode a protein, or it may work at the level of RNA, as in the case of genes encoding microRNAs. An example of a regulator gene is a gene that codes for a repressor protein that inhibits the activity of an operator.
In molecular biology, an inducer is a molecule that regulates gene expression. An inducer functions in two ways; namely:
Enzyme induction is a process in which a molecule induces the expression of an enzyme.
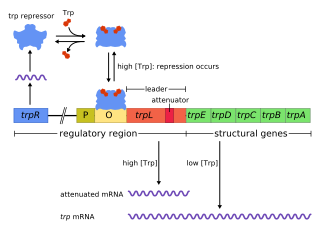
The trp operon is a group of genes that are transcribed together, encoding the enzymes that produce the amino acid tryptophan in bacteria. The trp operon was first characterized in Escherichia coli, and it has since been discovered in many other bacteria. The operon is regulated so that, when tryptophan is present in the environment, the genes for tryptophan synthesis are repressed.

Artificial transcription factors (ATFs) are engineered individual or multi molecule transcription factors that either activate or repress gene transcription (biology).

Amino acid synthesis is the set of biochemical processes by which the amino acids are produced. The substrates for these processes are various compounds in the organism's diet or growth media. Not all organisms are able to synthesize all amino acids. For example, humans can synthesize 11 of the 20 standard amino acids. These 11 are called the non-essential amino acids).
Serine dehydratase or L-serine ammonia lyase (SDH) is in the β-family of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent (PLP) enzymes. SDH is found widely in nature, but its structural and properties vary among species. SDH is found in yeast, bacteria, and the cytoplasm of mammalian hepatocytes. SDH catalyzes is the deamination of L-serine to yield pyruvate, with the release of ammonia.
The gal operon is a prokaryotic operon, which encodes enzymes necessary for galactose metabolism. Repression of gene expression for this operon works via binding of repressor molecules to two operators. These repressors dimerize, creating a loop in the DNA. The loop as well as hindrance from the external operator prevent RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter, and thus prevent transcription. Additionally, since the metabolism of galactose in the cell is involved in both anabolic and catabolic pathways, a novel regulatory system using two promoters for differential repression has been identified and characterized within the context of the gal operon.
Carbon catabolite repression, or simply catabolite repression, is an important part of global control system of various bacteria and other microorganisms. Catabolite repression allows microorganisms to adapt quickly to a preferred carbon and energy source first. This is usually achieved through inhibition of synthesis of enzymes involved in catabolism of carbon sources other than the preferred one. The catabolite repression was first shown to be initiated by glucose and therefore sometimes referred to as the glucose effect. However, the term "glucose effect" is actually a misnomer since other carbon sources are known to induce catabolite repression.










