Related Research Articles

The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic control, certification of personnel and aircraft, setting standards for airports, and protection of U.S. assets during the launch or re-entry of commercial space vehicles. Powers over neighboring international waters were delegated to the FAA by authority of the International Civil Aviation Organization.

The Mutual Security Act of 1951 launched a major American foreign aid program, 1951–61, of grants to numerous countries. It largely replaced the Marshall Plan. The main goal was to help poor countries develop and to contain the spread of communism. It was signed on October 10, 1951, by President Harry S. Truman. Annual authorizations were about $7.5 billion, out of a GDP of $340bn in 1951, for military, economic, and technical foreign aid to American allies. The aid was aimed primarily at shoring up Western Europe, as the Cold War developed. In 1961 it was replaced by a new foreign aid program, the Foreign Assistance Act of 1961, which created the Agency for International Development (AID), and focused more on Latin America.

The United States Department of Transportation is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is headed by the secretary of transportation, who reports directly to the president of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet.

Gainesville Regional Airport is a public airport three miles northeast of Gainesville, in Alachua County, Florida, United States. It is owned by Gainesville-Alachua Co. Auth. The National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2011–2015 categorized it as a primary commercial service airport.
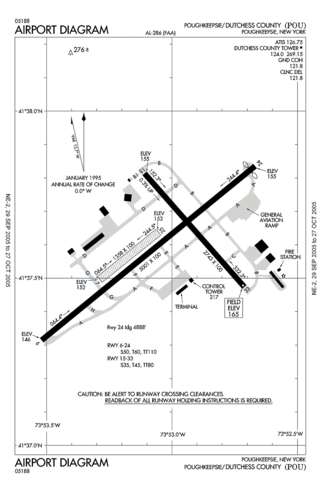
Hudson Valley Regional Airport, formerly known as Dutchess County Airport, is a county-owned public-use airport located on State Route 376 in the Town of Wappinger, Dutchess County, New York, United States, four miles (6 km) south of the central business district of Poughkeepsie. It is sometimes called Poughkeepsie Airport, which gives it the code POU. The airport provides corporate and general aviation transportation services.

Tri-State Airport is a public airport in Wayne County, West Virginia, United States, three miles south of Huntington, West Virginia, near Ceredo and Kenova. Owned by the Tri-State Airport Authority, it serves Huntington; Ashland, Kentucky; and Ironton, Ohio. It has heavy use for general aviation, and after the withdrawal of Delta Air Lines in June 2012, it was down to two airlines, one of which provides nationwide connecting service. In addition, there is one cargo airline flying to the airport, for a total of three commercial airlines serving it. On August 2, 2021, a federal subsidy was announced to subsidize flights to Washington-Dulles and Chicago-O'Hare airports. It is not yet known which airline will operate the flights.
East Texas Regional Airport is an airport located in Gregg County, Texas. The airport is just South of the city of Lakeport, and is 9 mi south of Longview. Its IATA identifier GGG comes from its prior name, Gregg County Airport. The airport is used for general aviation and military training; it has scheduled flights to Dallas/Fort Worth on American Airlines/American Eagle.
The United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has a system for categorizing public-use airports that is primarily based on the level of commercial passenger traffic through each facility. It is used to determine whether an airport is eligible for funding through the federal government's Airport Improvement Program (AIP). Fewer than 20% of airports in the U.S. qualify for the program, though most that don't qualify are private-use-only airports.
Anoka County–Blaine Airport, also known as Janes Field, is a public use airport in Anoka County, Minnesota, United States. Owned by Metropolitan Airports Commission, it is 10 nautical miles (19 km) north of the central business district of Minneapolis. The airport is located in the city of Blaine.

Atka Airport is a state-owned, public use airport located two nautical miles (4 km) north of the central business district of Atka, a city on Atka Island in the U.S. state of Alaska. Scheduled commercial airline passenger service is subsidized by the Essential Air Service program.
The Wendell H. Ford Aviation Investment and Reform Act for the 21st Century is a United States federal law, signed on 5 April 2000, seeking to improve airline safety. It is popularly called "AIR 21," and is also known as Public Law 106-181.

Seaside Municipal Airport is a general aviation airport located one mile (1.6 km) Northeast of Seaside in Clatsop County, Oregon, United States. It is owned and operated as a public airport by the city of Seaside. The airport has one asphalt runway, a parallel taxiway, a parking apron with space for up to 20 aircraft, and a five-bay hangar building. Seaside Municipal is the closest airport to Seaside, Gearhart, and Cannon Beach.

The Airport and Airway Development Act of 1970 was a United States federal law passed during the 91st Congress, and signed into law by President Richard Nixon in conjunction with the Airport and Airway Revenue Act on May 21, 1970. The act was meant to fill funding gaps in the airport and airway system, which had become inadequate due to the rapid growth of aviation. The legislation was estimated to generate greater than $11 billion in funds,
The National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems (NPIAS) is an inventory of U.S. aviation infrastructure assets. NPIAS was developed and now maintained by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).

Joseph A. Hardy Connellsville Airport is a public-use airport located four nautical miles southwest of Connellsville in Dunbar Township, Fayette County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is owned by the Fayette County Airport Authority and serves the south-eastern segment of the Pittsburgh metropolitan area. The airport serves the general aviation community with no scheduled commercial airline service.
Chignik Lagoon Airport is a state-owned, public-use airport serving Chignik Lagoon, in the Lake and Peninsula Borough of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is also known as Chignik Flats Airport. Scheduled airline service to King Salmon Airport is provided by Grant Aviation.
Mike Monroney Aeronautical Center is a regional office of the United States Federal Aviation Administration on the grounds of Will Rogers Airport in Oklahoma City. With around 7,500 direct federal employees, the Aeronautical Center is one of the Department of Transportation's largest facilities outside the Washington, DC area, and one of the 10 largest employers in the Oklahoma City metropolitan area. It is named for Senator Mike Monroney of Oklahoma, who wrote and sponsored the Federal Aviation Act of 1958.
The Surface and Air Transportation Program Extension Act of 2011 became a United States law when President Barack Obama signed the Act on September 16, 2011. The law extends taxes which fund federal highway expenditures through March and the Federal Aviation Administration through January. The Surface and Air Transportation Programs Extension Act of 2011 is a direct result of an agreement which was reached by the House and Senate majority leaders. This extension act was a top priority to Congress because federal highway and FAA funding was about to expire.
A passenger facility charge (PFC) is a fee that almost all airline travelers in the United States pay in their ticket price. The fee goes toward the upkeep and maintenance of airports, and is set up and capped according to US federal law.
This article lists the statutes amending the internal revenue laws of the United States.
References
- ↑ "Airport Improvement Program". Washington, D.C.: U.S. Federal Aviation Administration (FAA). 2020-02-28.
- ↑ "Overview: What is AIP?". FAA. 2017-11-15.
- 1 2 Airport Improvement Program Fiscal Year 2017 Report to Congress (PDF) (Report). FAA. February 2019. p. 6.
- ↑ "Airport and Airway Improvement Act of 1982 ~ P.L. 97-248" (PDF). 96 Stat. 671 ~ House Bill 4961. Legis★Works. September 3, 1982. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 5, 2018. Retrieved July 9, 2017.
- ↑ "H.R. 4961 ~ Tax Equity and Fiscal Responsibility Act of 1982". P.L. 97-248 ~ 96 Stat. 324. Congress.gov. November 13, 1981.
- ↑ "Harrison County Airport secures $310,000 in funding". timesleaderonline.com. Retrieved 2023-07-29.