Related Research Articles

Nvidia Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California, and incorporated in Delaware. It is a software and fabless company which designs and supplies graphics processing units (GPUs), application programming interfaces (APIs) for data science and high-performance computing as well as system on a chip units (SoCs) for the mobile computing and automotive market. Nvidia is also a dominant supplier of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware and software.

Jürgen Schmidhuber is a German computer scientist noted for his work in the field of artificial intelligence, specifically artificial neural networks. He is a scientific director of the Dalle Molle Institute for Artificial Intelligence Research in Switzerland. He is also director of the Artificial Intelligence Initiative and professor of the Computer Science program in the Computer, Electrical, and Mathematical Sciences and Engineering (CEMSE) division at the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) in Saudi Arabia.

Geoffrey Everest Hinton is a British-Canadian computer scientist and cognitive psychologist, most noted for his work on artificial neural networks. From 2013 to 2023, he divided his time working for Google and the University of Toronto, before publicly announcing his departure from Google in May 2023, citing concerns about the risks of artificial intelligence (AI) technology. In 2017, he co-founded and became the chief scientific advisor of the Vector Institute in Toronto.

Yann André LeCun is a Turing Award winning French-American computer scientist working primarily in the fields of machine learning, computer vision, mobile robotics and computational neuroscience. He is the Silver Professor of the Courant Institute of Mathematical Sciences at New York University and Vice-President, Chief AI Scientist at Meta.

Deep learning is the subset of machine learning methods based on neural networks with representation learning. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers in the network. Methods used can be either supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised.
Convolutional neural network (CNN) is a regularized type of feed-forward neural network that learns feature engineering by itself via filters optimization. Vanishing gradients and exploding gradients, seen during backpropagation in earlier neural networks, are prevented by using regularized weights over fewer connections. For example, for each neuron in the fully-connected layer, 10,000 weights would be required for processing an image sized 100 × 100 pixels. However, applying cascaded convolution kernels, only 25 neurons are required to process 5x5-sized tiles. Higher-layer features are extracted from wider context windows, compared to lower-layer features.
Google Brain was a deep learning artificial intelligence research team under the umbrella of Google AI, a research division at Google dedicated to artificial intelligence. Formed in 2011, it combined open-ended machine learning research with information systems and large-scale computing resources. It created tools such as TensorFlow, which allow neural networks to be used by the public, and multiple internal AI research projects, and aimed to create research opportunities in machine learning and natural language processing. It was merged into former Google sister company DeepMind to form Google DeepMind in April 2023.
Multimodal learning, in the context of machine learning, is a type of deep learning using a combination of various modalities of data, such as text, audio, or images, in order to create a more robust model of the real-world phenomena in question. In contrast, singular modal learning would analyze text or imaging data independently. Multimodal machine learning combines these fundamentally different statistical analyses using specialized modeling strategies and algorithms, resulting in a model that comes closer to representing the real world.
An AI accelerator, deep learning processor, or neural processing unit (NPU) is a class of specialized hardware accelerator or computer system designed to accelerate artificial intelligence and machine learning applications, including artificial neural networks and machine vision. Typical applications include algorithms for robotics, Internet of Things, and other data-intensive or sensor-driven tasks. They are often manycore designs and generally focus on low-precision arithmetic, novel dataflow architectures or in-memory computing capability. As of 2024, a typical AI integrated circuit chip contains tens of billions of MOSFETs.
The ImageNet project is a large visual database designed for use in visual object recognition software research. More than 14 million images have been hand-annotated by the project to indicate what objects are pictured and in at least one million of the images, bounding boxes are also provided. ImageNet contains more than 20,000 categories, with a typical category, such as "balloon" or "strawberry", consisting of several hundred images. The database of annotations of third-party image URLs is freely available directly from ImageNet, though the actual images are not owned by ImageNet. Since 2010, the ImageNet project runs an annual software contest, the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge, where software programs compete to correctly classify and detect objects and scenes. The challenge uses a "trimmed" list of one thousand non-overlapping classes.
Ilya Sutskever is a Russian-born computer scientist working in machine learning. Sutskever is a co-founder and former Chief Scientist at OpenAI. He holds citizenship in Russia, Israel, and Canada.
Wojciech Zaremba is a Polish computer scientist, a founding team member of OpenAI (2016–present), where he leads both the Codex research and language teams. The teams actively work on AI that writes computer code and creating successors to GPT-3 respectively.
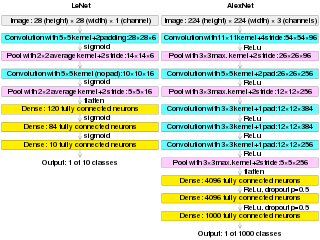
AlexNet is the name of a convolutional neural network (CNN) architecture, designed by Alex Krizhevsky in collaboration with Ilya Sutskever and Geoffrey Hinton, who was Krizhevsky's Ph.D. advisor at the University of Toronto.
Chainer is an open source deep learning framework written purely in Python on top of NumPy and CuPy Python libraries. The development is led by Japanese venture company Preferred Networks in partnership with IBM, Intel, Microsoft, and Nvidia.

A residual neural network is a seminal deep learning model in which the weight layers learn residual functions with reference to the layer inputs. It was developed in 2015 for image recognition and won that year's ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge.
The CIFAR-10 dataset is a collection of images that are commonly used to train machine learning and computer vision algorithms. It is one of the most widely used datasets for machine learning research. The CIFAR-10 dataset contains 60,000 32x32 color images in 10 different classes. The 10 different classes represent airplanes, cars, birds, cats, deer, dogs, frogs, horses, ships, and trucks. There are 6,000 images of each class.
DeepScale, Inc. was an American technology company headquartered in Mountain View, California, that developed perceptual system technologies for automated vehicles. On October 1, 2019, the company was acquired by Tesla, Inc.
Artificial neural networks (ANNs) are models created using machine learning to perform a number of tasks. Their creation was inspired by neural circuitry. While some of the computational implementations ANNs relate to earlier discoveries in mathematics, the first implementation of ANNs was by psychologist Frank Rosenblatt, who developed the perceptron. Little research was conducted on ANNs in the 1970s and 1980s, with the AAAI calling that period an "AI winter".
Nvidia GTC is a global artificial intelligence (AI) conference for developers that brings together developers, engineers, researchers, inventors, and IT professionals. Topics focus on AI, computer graphics, data science, machine learning and autonomous machines. Each conference begins with a keynote from Nvidia CEO and founder Jensen Huang, followed by a variety of sessions and talks with experts from around the world.
Specialized computer hardware is often used to execute artificial intelligence (AI) programs faster, and with less energy, such as Lisp machines, neuromorphic engineering, event cameras, and physical neural networks. As of 2023, the market for AI hardware is dominated by GPUs.
References
- 1 2 Gershgorn, Dave (18 June 2018). "The inside story of how AI got good enough to dominate Silicon Valley". Quartz. Retrieved 23 February 2021.
- 1 2 Witt, Stephen (27 November 2023). "How Jensen Huang's Nvidia Is Powering the A.I. Revolution". The New Yorker. Retrieved 24 December 2023.
- ↑ "Alex Krizhevsky". Google Scholar Citations.
- ↑ "CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets" . Retrieved 7 March 2021.
- ↑ Krizhevsky, Alex (2009), Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images (PDF), CiteSeerX 10.1.1.222.9220 , S2CID 18268744