In chemistry, an alkali is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline is commonly, and alkalescent less often, used in English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases.
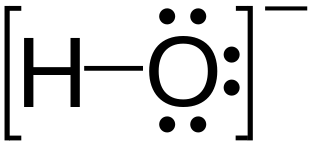
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and hydrogen atom held together by a single covalent bond, and carries a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile, and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate in aqueous solution, liberating solvated hydroxide ions. Sodium hydroxide is a multi-million-ton per annum commodity chemical. The corresponding electrically neutral compound HO• is the hydroxyl radical. The corresponding covalently bound group –OH of atoms is the hydroxy group. Hydroxide ion and hydroxy group are nucleophiles and can act as catalysts in organic chemistry.

Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, is an inorganic compound with the formula NaOH. It is a white solid ionic compound consisting of sodium cations Na+
and hydroxide anions OH−
.

In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis bases. All definitions agree that bases are substances which react with acids as originally proposed by G.-F. Rouelle in the mid-18th century.

Sodium carbonate, Na2CO3·10H2O, (also known as washing soda, soda ash and soda crystals) is the inorganic compound with the formula Na2CO3 and its various hydrates. All forms are white, odourless, water-soluble salts that yield moderately alkaline solutions in water. Historically, it was extracted from the ashes of plants growing in sodium-rich soils. Because the ashes of these sodium-rich plants were noticeably different from ashes of wood (once used to produce potash), sodium carbonate became known as "soda ash". It is produced in large quantities from sodium chloride and limestone by the Solvay process.

Sodium hypochlorite is a chemical compound with the formula NaOCl or NaClO, comprising a sodium cation and a hypochlorite anion. It may also be viewed as the sodium salt of hypochlorous acid. The anhydrous compound is unstable and may decompose explosively. It can be crystallized as a pentahydrate NaOCl·5H
2O, a pale greenish-yellow solid which is not explosive and is stable if kept refrigerated.
The compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula HCl and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colourless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hydrogen chloride gas and hydrochloric acid are important in technology and industry. Hydrochloric acid, the aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride, is also commonly given the formula HCl.

A corrosive substance is one that will damage or destroy other substances with which it comes into contact by means of a chemical reaction.

Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca(OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed or slaked with water. It has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide.

In chemistry, neutralization or neutralisation is a chemical reaction in which acid and a base react quantitatively with each other. In a reaction in water, neutralization results in there being no excess of hydrogen or hydroxide ions present in the solution. The pH of the neutralized solution depends on the acid strength of the reactants.
The Leblanc process was an early industrial process for making soda ash used throughout the 19th century, named after its inventor, Nicolas Leblanc. It involved two stages: making sodium sulfate from sodium chloride, followed by reacting the sodium sulfate with coal and calcium carbonate to make sodium carbonate. The process gradually became obsolete after the development of the Solvay process.
The Solvay process or ammonia-soda process is the major industrial process for the production of sodium carbonate (soda ash, Na2CO3). The ammonia-soda process was developed into its modern form by the Belgian chemist Ernest Solvay during the 1860s. The ingredients for this are readily available and inexpensive: salt brine (from inland sources or from the sea) and limestone (from quarries). The worldwide production of soda ash in 2005 was estimated at 42 million tonnes, which is more than six kilograms (13 lb) per year for each person on Earth. Solvay-based chemical plants now produce roughly three-quarters of this supply, with the remaining being mined from natural deposits. This method superseded the Leblanc process.

Sodium sulfate (also known as sodium sulphate or sulfate of soda) is the inorganic compound with formula Na2SO4 as well as several related hydrates. All forms are white solids that are highly soluble in water. With an annual production of 6 million tonnes, the decahydrate is a major commodity chemical product. It is mainly used as a filler in the manufacture of powdered home laundry detergents and in the Kraft process of paper pulping for making highly alkaline sulfides.
The chloralkali process is an industrial process for the electrolysis of sodium chloride solutions. It is the technology used to produce chlorine and sodium hydroxide, which are commodity chemicals required by industry. 35 million tons of chlorine were prepared by this process in 1987. The chlorine and sodium hydroxide produced in this process are widely used in the chemical industry.
Basic oxides are oxides that show basic properties in opposition to acidic oxides and that either
Calcium chlorate is the calcium salt of chloric acid, with the chemical formula Ca(ClO3)2. Like other chlorates, it is a strong oxidizer.

Alkali, or Alkaline, soils are clay soils with high pH, a poor soil structure and a low infiltration capacity. Often they have a hard calcareous layer at 0.5 to 1 metre depth. Alkali soils owe their unfavorable physico-chemical properties mainly to the dominating presence of sodium carbonate, which causes the soil to swell and difficult to clarify/settle. They derive their name from the alkali metal group of elements, to which sodium belongs, and which can induce basicity. Sometimes these soils are also referred to as alkaline sodic soils.
Alkaline soils are basic, but not all basic soils are alkaline.
Chlorine gas can be produced by extracting from natural materials, including the electrolysis of a sodium chloride solution (brine) and other ways.

Hydrochloric acid [H+(aq) Cl−(aq) or H3O+ Cl−], also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride (chemical formula:HCl). It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid. It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical.











