Related Research Articles

George Ord, Jr. was an American zoologist who specialized in North American ornithology and mammalogy. Based in part on specimens collected by Lewis and Clark in the North American interior, Ord's article "Zoology of North America" (1815), which was published in the second American edition of William Guthrie's Geographical, Historical, and Commercial Grammar, has been recognized as the "first systematic zoology of America by an American".

John Obadiah Westwood was an English entomologist and archaeologist also noted for his artistic talents. He published several illustrated works on insects and antiquities. He was among the first entomologists with an academic position at Oxford University. He was a natural theologian, staunchly anti-Darwinian, and sometimes adopted a quinarian viewpoint. Although he never travelled widely, he described species from around the world on the basis of specimens, especially of the larger, curious, and colourful species, obtained by naturalists and collectors in England.

Thomas Say was an American entomologist, conchologist, and herpetologist. His studies of insects and shells, numerous contributions to scientific journals, and scientific expeditions to Florida, Georgia, the Rocky Mountains, Mexico, and elsewhere made him an internationally known naturalist. Say has been called the father of American descriptive entomology and American conchology. He served as librarian for the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, curator at the American Philosophical Society, and professor of natural history at the University of Pennsylvania.

The Academy of Natural Sciences of Drexel University, formerly the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, is the oldest natural science research institution and museum in the Americas. It was founded in 1812, by many of the leading naturalists of the young American republic with an expressed mission of "the encouragement and cultivation of the sciences". It has sponsored expeditions, conducted original environmental and systematics research, and amassed natural history collections containing more than 17 million specimens. The Academy also organizes public exhibits and educational programs for both schools and the general public.

George Vernon Hudson FRSNZ was a British-born New Zealand entomologist credited with proposing the modern daylight saving time. He was awarded the Hector Memorial Medal in 1923.

The National Intelligence Service is the chief intelligence agency of South Korea. The agency was officially established in 1961 as the Korean Central Intelligence Agency, during the rule of President Park Chung-hee's military Supreme Council for National Reconstruction, which displaced the Second Republic of Korea. The original duties of the KCIA were to supervise and coordinate both international and domestic intelligence activities and criminal investigations by all government intelligence agencies, including that of the military. The agency's broad powers allowed it to actively intervene in politics. Agents undergo years of training and checks before they are officially inducted and receive their first assignments.
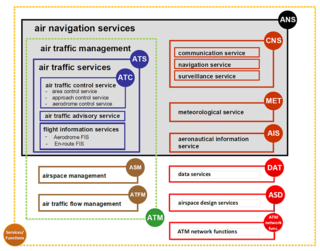
Air traffic management (ATM) aims at ensuring the safe and efficient flow or air traffic. It encompasses three types of services:

Carl Robert Osten-Sacken or Carl-Robert Romanovich, Baron von der Osten-Sacken, Baron Osten Sacken was a Russian diplomat and entomologist. He served as the Russian consul general in New York City during the American Civil War, living in the United States from 1856 to 1877. He worked on the taxonomy of flies in general and particularly of the family Tipulidae.

Xiphydriidae are a family of wood wasps that includes around 150 species. They are located all over the world including North and South America, Australia, Europe, and others. Xiphydriidae larvae are wood borers in dead trees or branches of a range of trees. They are characterized as having long and skinny necks with dome-shaped heads. The oldest fossils of the group are from the mid Cretaceous.

The Cixiidae are a family of fulgoroid insects, one of many families commonly known as planthoppers, distributed worldwide and comprising more than 2,000 species from over 150 genera. The genera are placed into three subfamilies, Borystheninae, Bothriocerinae and Cixiinae with sixteen tribes currently accepted in Cixiinae.

The Heptageniidae are a family of mayflies with over 500 described species mainly distributed in the Holarctic, Oriental, and Afrotropical regions, and also present in the Central American Tropics and extreme northern South America. The group is sometimes referred to as flat-headed mayflies or stream mayflies. These are generally rather small mayflies with three long tails. The wings are usually clear with prominent venation although species with variegated wings are known. As in most mayflies, the males have large compound eyes, but not divided into upper and lower parts.

May Roberta Berenbaum is an American entomologist whose research focuses on the chemical interactions between herbivorous insects and their host plants, and the implications of these interactions on the organization of natural communities and the evolution of species. She is particularly interested in nectar, plant phytochemicals, honey and bees, and her research has important implications for beekeeping.

George Henry Horn was a U.S. entomologist who specialized in the study of beetles.

Argyractis is a genus of moths of the family Crambidae.
Paradidyma is a genus of flies in the family Tachinidae.
The IEEE Power & Energy Society, formerly the IEEE Power Engineering Society, is the oldest society of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) focused on the scientific and engineering knowledge about electric power and energy.

Lucy Way Sistare Say was an American naturalist and scientific artist. Say illustrated and colored 66 of 68 plates included in American Conchology, a depiction of the North American mollusks collected by her husband, Thomas Say, during his expeditions in North America. Lucy Say became the first female member of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia (ANSP) on October 26, 1841.
Coleman Townsend Robinson was an American entomologist who specialised in Lepidoptera.

Howard Radclyffe Roberts Jr. was an American entomologist known for his work on grasshoppers. His 1941 University of Pennsylvania Ph.D. dissertation was an early work highlighting the role phallic structures could play in grasshopper taxonomy. While serving in World War II, he and Edward Shearman Ross cowrote The Mosquito Atlas, used by the armed forces to identify malaria-transmitting mosquitos. Roberts worked for the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia (ANSP), serving as its managing director from 1947 to 1972. He described dozens of grasshopper species from North and South America, and also is the eponym of several taxa named in his honor.
References
- ↑ "The American Entomological Society – About Us". ansp.org. 2011. Retrieved October 19, 2011.
- ↑ "American Entomologial Society – Publications". ansp.org. 2011. Retrieved October 19, 2011.