
The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) is a United States government corporation supplying deposit insurance to depositors in American commercial banks and savings banks. The FDIC was created by the Banking Act of 1933, enacted during the Great Depression to restore trust in the American banking system. More than one-third of banks failed in the years before the FDIC's creation, and bank runs were common. The insurance limit was initially US$2,500 per ownership category, and this has been increased several times over the years. Since the enactment of the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act in 2010, the FDIC insures deposits in member banks up to $250,000 per ownership category. FDIC insurance is backed by the full faith and credit of the government of the United States, and according to the FDIC, "since its start in 1933 no depositor has ever lost a penny of FDIC-insured funds".
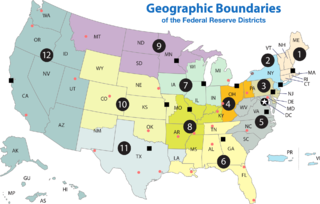
A Federal Reserve Bank is a regional bank of the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States. There are twelve in total, one for each of the twelve Federal Reserve Districts that were created by the Federal Reserve Act of 1913. The banks are jointly responsible for implementing the monetary policy set forth by the Federal Open Market Committee, and are divided as follows:

A credit union is a member-owned nonprofit cooperative financial institution. They may offer financial services equivalent to those of commercial banks, such as share accounts, share draft accounts, credit cards, credit, share term certificates, and online banking. Normally, only a member of a credit union may deposit or borrow money. In several African countries, credit unions are commonly referred to as SACCOs.

The National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) is an American government-backed insurer of credit unions in the United States, one of two agencies that provide deposit insurance to depositors in U.S. depository institutions, the other being the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, which insures commercial banks and savings institutions. The NCUA is an independent federal agency created by the United States Congress to regulate, charter, and supervise federal credit unions. With the backing of the full faith and credit of the U.S. government, the NCUA operates and manages the National Credit Union Share Insurance Fund, insuring the deposits of more than 124 million account holders in all federal credit unions and the overwhelming majority of state-chartered credit unions. Besides the Share Insurance Fund, the NCUA operates three other funds: the NCUA Operating Fund, the Central Liquidity Facility (CLF), and the Community Development Revolving Loan Fund (CDRLF). The NCUA Operating Fund, with the Share Insurance Fund, finances the agency's operations.

A savings and loan association (S&L), or thrift institution, is a financial institution that specializes in accepting savings deposits and making mortgage and other loans. The terms "S&L" and "thrift" are mainly used in the United States; similar institutions in the United Kingdom, Ireland and some Commonwealth countries include building societies and trustee savings banks. They are often mutually held, meaning that the depositors and borrowers are members with voting rights, and have the ability to direct the financial and managerial goals of the organization like the members of a credit union or the policyholders of a mutual insurance company. While it is possible for an S&L to be a joint-stock company, and even publicly traded, in such instances it is no longer truly a mutual association, and depositors and borrowers no longer have membership rights and managerial control. By law, thrifts can have no more than 20 percent of their lending in commercial loans—their focus on mortgage and consumer loans makes them particularly vulnerable to housing downturns such as the deep one the U.S. experienced in 2007.

The savings and loan crisis of the 1980s and 1990s was the failure of 32% of savings and loan associations (S&Ls) in the United States from 1986 to 1995. An S&L or "thrift" is a financial institution that accepts savings deposits and makes mortgage, car and other personal loans to individual members.

Louise McCarren Herring, was an Ohio native, recognized as one of the pioneer leaders of the not-for-profit cooperative credit union movement in the United States. Herring is universally regarded in the United States credit union movement as being the “Mother of Credit Unions” for her work with the movement since its earliest days.

The Canada Deposit Insurance Corporation is a Canadian federal Crown Corporation created by Parliament in 1967 to provide deposit insurance to depositors in Canadian commercial banks and savings institutions. CDIC insures Canadians' deposits held at Canadian banks up to C$100,000 in case of a bank failure. CDIC automatically insures many types of savings against the failure of a financial institution. However, the bank must be a CDIC member and not all savings are insured. CDIC is also Canada's resolution authority for banks, federally regulated credit unions, trust and loan companies as well as associations governed by the Cooperative Credit Associations Act that take deposits.
Deposit insurance or deposit protection is a measure implemented in many countries to protect bank depositors, in full or in part, from losses caused by a bank's inability to pay its debts when due. Deposit insurance systems are one component of a financial system safety net that promotes financial stability.
The Expedited Funds Availability Act was enacted in 1987 by the United States Congress for the purpose of standardizing hold periods on deposits made to commercial banks and to regulate institutions' use of deposit holds. It is also referred to as Regulation CC or Reg CC, after the Federal Reserve regulation that implements the act. The law is codified in Title 12, Chapter 41 of the US Code and Title 12, Part 229 of the Code of Federal Regulations.
Dual chartering refers to the system by which credit unions in the United States can be chartered under either of two governmental authorities; by either the federal government or by the state government. This system exists because of the Federal Credit Union Act, which Congress passed in 1934.

Flow of funds accounts are a system of interrelated balance sheets for a nation, calculated periodically. There are two types of balance sheets: those showing
Deposit Insurance Agency (DIA) is a Russian state corporation established in January 2004 to manage operation of the deposit insurance system in the Russian Federation. DIA pays insurance compensations to depositors of failed banks. DIA also exercises bankruptcy administrator functions of insolvent banks, non–governmental pension funds and insurance companies, it is responsible for resolution of banks and managing the system of guaranteeing the rights of insured persons in the mandatory pension insurance system.
The National Credit Union Share Insurance Fund provides deposit insurance to protect the accounts of credit union members at federally insured institutions in the United States. Created in 1970, the Share Insurance Fund is administered by the National Credit Union Administration, an independent federal financial regulator. The Share Insurance Fund is funded completely by participating credit unions, and not one penny of insured savings has ever been lost by a member of a federally insured credit union. The Share Insurance Fund is backed by the full faith and credit of the United States government.
Bank regulation in the United States is highly fragmented compared with other G10 countries, where most countries have only one bank regulator. In the U.S., banking is regulated at both the federal and state level. Depending on the type of charter a banking organization has and on its organizational structure, it may be subject to numerous federal and state banking regulations. Apart from the bank regulatory agencies the U.S. maintains separate securities, commodities, and insurance regulatory agencies at the federal and state level, unlike Japan and the United Kingdom. Bank examiners are generally employed to supervise banks and to ensure compliance with regulations.

Credit unions in the United States served 100 million members, comprising 43.7% of the economically active population, in 2014. U.S. credit unions are not-for-profit, cooperative, tax-exempt organizations. The clients of the credit unions become partners of the financial institution and their presence focuses in certain neighborhoods because they center their services in one specific community. As of March 2020, the largest American credit union was Navy Federal Credit Union, serving U.S. Department of Defense employees, contractors, and families of servicepeople, with over $125 billion in assets and over 9.1 million members. Total credit union assets in the U.S. reached $1 trillion as of March 2012. Approximately 236,000 people were directly employed by credit unions per data derived from the 2012 National Credit Union Administration (NCUA) Credit Union Directory. As of 2019, there were 5,236 federally insured credit unions with 120.4 million members, and deposits of $1.22 trillion.

Hawaii State Federal Credit Union (HSFCU) is a federally chartered credit union headquartered in Honolulu, Hawaii and regulated under the authority of the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA). HSFCU is the largest credit union in Hawaii. As of September 2013, HSFCU had $1.3 billion in assets, approximately 77,000 members, and 8 branches.
This article details the history of banking in the United States. Banking in the United States is regulated by both the federal and state governments.

The Credit Union Share Insurance Fund Parity Act is a bill that would expand federal deposit insurance to include Interest on Lawyer Trust Accounts (IOLTAs) and similar escrow accounts housed within credit unions.

Telhio Credit Union or Telhio is a US Credit union or financial cooperative headquartered in Columbus, Ohio. Telhio is registered as a state-chartered type credit union and is the fifth largest credit union in Central Ohio. As of December 2020, Telhio has approximately $947Mil in assets, and 52,569 members. Telhio is federally insured by the National Credit Union Administration (NCUA), which insures accounts in federal and most state-chartered credit unions in the United States up to $250,000. Additionally, Telhio carries ESI Insurance, which insures personal accounts an additional $250,000, for a total of $500,000 in deposit insurance.











