
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor. Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist.
Radiology is the medical discipline that uses medical imaging to diagnose and treat diseases within the bodies of animals and humans.
Medical physics is a profession which deals with the application of the concepts and methods of physics to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of human diseases with a specific goal of improving human health and well-being. Since 2008, medical physics has been included as a health profession according to International Standard Classification of Occupation of the International Labour Organization.
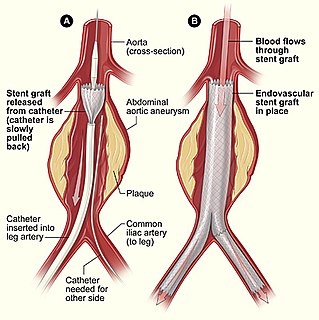
Minimally invasive procedures encompass surgical techniques that limit the size of incisions needed and so lessen wound healing time, associated pain and risk of infection. Surgery by definition is invasive and many operations requiring incisions of some size are referred to as open surgery, in which incisions made can sometimes leave large wounds that are painful and take a long time to heal. Minimally invasive procedures have been enabled by the advance of various medical technologies. An endovascular aneurysm repair as an example of minimally invasive surgery is much less invasive in that it involves much smaller incisions than the corresponding open surgery procedure of open aortic surgery. This minimally invasive surgery became the most common method of repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in 2003 in the United States.
The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists (RANZCR) is the leading professional organisation for the promotion of the science and practice of the medical specialties of clinical radiology and radiation oncology in Australia and New Zealand. The College has members throughout the world. RANZCR provides the educational curricula for medical graduates training to enter the specialties.
The American College of Radiology (ACR), founded in 1923, is a professional medical society representing nearly 40,000 diagnostic radiologists, radiation oncologists, interventional radiologists, nuclear medicine physicians and medical physicists.

Radiographers, also known as radiologic technologists, diagnostic radiographers and medical radiation technologists are healthcare professionals who specialise in the imaging of human anatomy for the diagnosis and treatment of pathology. Radiographers are infrequently, and almost always erroneously, known as x-ray technicians. In countries that use the title radiologic technologist they are often informally referred to as techs in the clinical environment; this phrase has emerged in popular culture such as television programmes. The term radiographer can also refer to a therapeutic radiographer, also known as a radiation therapist.

The Society of Radiographers (SoR) is a professional body and trade union that represents more than 90 percent of the diagnostic and therapeutic radiographers in the United Kingdom. The College of Radiographers (CoR) is a charitable subsidiary of the Society, they are collectively known as the Society and College of Radiographers (SCoR).

The Royal College of Radiologists (RCR) is the professional body responsible for the specialty of clinical oncology and clinical radiology throughout the United Kingdom. Its role is to advance the science and practice of radiology and oncology, further public education and set appropriate professional standards of practice. The College also sets and monitors the educational curriculum for those training to enter the profession. It is a registered charity in the United Kingdom.
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology is the official journal of the Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists. It is a bimonthly medical journal covering radiological practice and research in Australasia. It is published by Wiley-Blackwell and was established in 1957.
The American Society of Radiologic Technologists (ASRT), located in Albuquerque, New Mexico, is a professional membership association for medical imaging technologists, radiation therapists and radiologic science students.
Carlos A. Pérez is an American radiation oncologist. He is well known for his contributions to the clinical management of patients, especially those with gynecologic tumors and carcinoma of the prostate, the breast and head and neck.
Ann Barrett OBE, is Emeritus Professor of Oncology in the University of East Anglia, England, and formerly deputy dean of the School of Medicine and lead clinician for oncology at the Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital NHS Trust. She was awarded an OBE in 2010 for services to medicine. She is also a fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland.
Simon N. Powell is a British cancer researcher and radiation oncologist residing in New York City.

The American Osteopathic Board of Radiology (AOBR) is an organization that provides board certification to qualified Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) who specialize in the use of imaging in the diagnosis and treatment of disease (radiologists). The board is one 18 medical specialty certifying boards of the American Osteopathic Association Bureau of Osteopathic Specialists approved by the American Osteopathic Association (AOA), and was established in 1939. The American Osteopathic Board of Radiology and the American Board of Radiology are the two certifying boards for radiologists in the United States. As of December 2011, 732 osteopathic radiologists held active certification with the AOBR. Radiologists board certified by the AOBR are eligible for membership in the American College of Radiology.

Julian C. Josey Jr. is a radiation oncologist at the Gibbs Cancer Center & Research Institute in Spartanburg, South Carolina. A native of Spartanburg, he has been a leader in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer for more than 40 years.

Ferenc Andras Jolesz was a Hungarian-American physician and scientist best known for his research on image guided therapy, the process by which information derived from diagnostic imaging is used to improve the localization and targeting of diseased tissue to monitor and control treatment during surgical and interventional procedures. He pioneered the field of Magnetic Resonance Imaging-guided interventions and introduced of a variety of new medical procedures based on novel combinations of imaging and therapy delivery.
Interventional oncology is a subspecialty field of interventional radiology that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer and cancer-related problems using targeted minimally invasive procedures performed under image guidance. Interventional oncology has developed to a separate pillar of modern oncology and it employs X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help guide miniaturized instruments to allow targeted and precise treatment of solid tumours located in various organs of the human body, including but not limited to the liver, kidneys, lungs, and bones. Interventional oncology treatments are routinely carried out by interventional radiologists in appropriate settings and facilities.
Walter "Wally" J. Curran, Jr. is an American radiation oncologist specializing in the treatment of malignant brain tumors and locally advanced lung cancer. He is the global chief medical officer of GenesisCare, a provider of cancer and cardiovascular care that serves communities in 440 locations across the world.
Eleanor D. Montague was an American radiologist and educator who established breast-conserving therapy in the United States and improved radiation therapy techniques. She became a member of the Texas Women's Hall of Fame in 1993.








