
In organic chemistry, the ene reaction is a chemical reaction between an alkene with an allylic hydrogen and a compound containing a multiple bond, in order to form a new σ-bond with migration of the ene double bond and 1,5 hydrogen shift. The product is a substituted alkene with the double bond shifted to the allylic position.

Grubbs catalysts are a series of transition metal carbene complexes used as catalysts for olefin metathesis. They are named after Robert H. Grubbs, the chemist who supervised their synthesis. Several generations of the catalyst have been developed. Grubbs catalysts tolerate many functional groups in the alkene substrates, are air-tolerant, and are compatible with a wide range of solvents. For these reasons, Grubbs catalysts have become popular in synthetic organic chemistry. Grubbs, together with Richard R. Schrock and Yves Chauvin, won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in recognition of their contributions to the development of olefin metathesis.

Olefin metathesis is an organic reaction that entails the redistribution of fragments of alkenes (olefins) by the scission and regeneration of carbon-carbon double bonds. Because of the relative simplicity of olefin metathesis, it often creates fewer undesired by-products and hazardous wastes than alternative organic reactions. For their elucidation of the reaction mechanism and their discovery of a variety of highly active catalysts, Yves Chauvin, Robert H. Grubbs, and Richard R. Schrock were collectively awarded the 2005 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
A transition metal carbene complex is an organometallic compound featuring a divalent organic ligand. The divalent organic ligand coordinated to the metal center is called a carbene. Carbene complexes for almost all transition metals have been reported. Many methods for synthesizing them and reactions utilizing them have been reported. The term carbene ligand is a formalism since many are not derived from carbenes and almost none exhibit the reactivity characteristic of carbenes. Described often as M=CR2, they represent a class of organic ligands intermediate between alkyls (−CR3) and carbynes (≡CR). They feature in some catalytic reactions, especially alkene metathesis, and are of value in the preparation of some fine chemicals.
Ring-closing metathesis (RCM) is a widely used variation of olefin metathesis in organic chemistry for the synthesis of various unsaturated rings via the intramolecular metathesis of two terminal alkenes, which forms the cycloalkene as the E- or Z- isomers and volatile ethylene.
In organic chemistry, kinetic resolution is a means of differentiating two enantiomers in a racemic mixture. In kinetic resolution, two enantiomers react with different reaction rates in a chemical reaction with a chiral catalyst or reagent, resulting in an enantioenriched sample of the less reactive enantiomer. As opposed to chiral resolution, kinetic resolution does not rely on different physical properties of diastereomeric products, but rather on the different chemical properties of the racemic starting materials. The enantiomeric excess (ee) of the unreacted starting material continually rises as more product is formed, reaching 100% just before full completion of the reaction. Kinetic resolution relies upon differences in reactivity between enantiomers or enantiomeric complexes.

In organic chemistry, organocatalysis is a form of catalysis in which the rate of a chemical reaction is increased by an organic catalyst. This "organocatalyst" consists of carbon, hydrogen, sulfur and other nonmetal elements found in organic compounds. Because of their similarity in composition and description, they are often mistaken as a misnomer for enzymes due to their comparable effects on reaction rates and forms of catalysis involved.
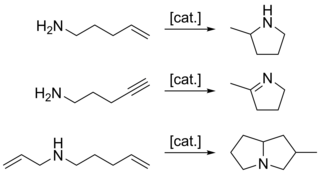
In organic chemistry, hydroamination is the addition of an N−H bond of an amine across a carbon-carbon multiple bond of an alkene, alkyne, diene, or allene. In the ideal case, hydroamination is atom economical and green. Amines are common in fine-chemical, pharmaceutical, and agricultural industries. Hydroamination can be used intramolecularly to create heterocycles or intermolecularly with a separate amine and unsaturated compound. The development of catalysts for hydroamination remains an active area, especially for alkenes. Although practical hydroamination reactions can be effected for dienes and electrophilic alkenes, the term hydroamination often implies reactions metal-catalyzed processes.
Asymmetric hydrogenation is a chemical reaction that adds two atoms of hydrogen to a target (substrate) molecule with three-dimensional spatial selectivity. Critically, this selectivity does not come from the target molecule itself, but from other reagents or catalysts present in the reaction. This allows spatial information to transfer from one molecule to the target, forming the product as a single enantiomer. The chiral information is most commonly contained in a catalyst and, in this case, the information in a single molecule of catalyst may be transferred to many substrate molecules, amplifying the amount of chiral information present. Similar processes occur in nature, where a chiral molecule like an enzyme can catalyse the introduction of a chiral centre to give a product as a single enantiomer, such as amino acids, that a cell needs to function. By imitating this process, chemists can generate many novel synthetic molecules that interact with biological systems in specific ways, leading to new pharmaceutical agents and agrochemicals. The importance of asymmetric hydrogenation in both academia and industry contributed to two of its pioneers — William Standish Knowles and Ryōji Noyori — being awarded one half of the 2001 Nobel Prize in Chemistry.
Metal-catalyzed intermolecular carbenoid cyclopropanations are organic reactions that result in the formation of a cyclopropane ring from a metal carbenoid species and an alkene. In the Simmons–Smith reaction the metal involved is zinc.
The White catalyst is a transition metal coordination complex named after the chemist by whom it was first synthesized, M. Christina White, a professor at the University of Illinois. The catalyst has been used in a variety of allylic C-H functionalization reactions of α-olefins. In addition, it has been shown to catalyze oxidative Heck reactions.
The Tsuji–Trost reaction is a palladium-catalysed substitution reaction involving a substrate that contains a leaving group in an allylic position. The palladium catalyst first coordinates with the allyl group and then undergoes oxidative addition, forming the π-allyl complex. This allyl complex can then be attacked by a nucleophile, resulting in the substituted product.

The Doyle–Kirmse reaction is an organic reaction in which a metal carbene reacts with an allyl compound with transposition of the alkene and transfer of the electronegative group from the allyl onto the carbene carbon.

Phosphinooxazolines are a class of chiral ligands used in asymmetric catalysis. Their complexes are particularly effective at generating single enatiomers in reactions involving highly symmetric transition states, such as allylic substitutions, which are typically difficult to perform stereoselectively. The ligands are bidentate and have been shown to be hemilabile with the softer P‑donor being more firmly bound than the harder N‑donor.
In organic chemistry, the Keck asymmetric allylation is a chemical reaction that involves the nucleophilic addition of an allyl group to an aldehyde. The catalyst is a chiral complex that contains titanium as a Lewis acid. The chirality of the catalyst induces a stereoselective addition, so the secondary alcohol of the product has a predictable absolute stereochemistry based on the choice of catalyst. This name reaction is named for Gary Keck.
In organic chemistry, carbonyl allylation describes methods for adding an allyl anion to an aldehyde or ketone to produce a homoallylic alcohol. The carbonyl allylation was first reported in 1876 by Alexander Zaitsev and employed an allylzinc reagent.
Cobalt(II)–porphyrin catalysis is a process in which a Co(II) porphyrin complex acts as a catalyst, inducing and accelerating a chemical reaction.

A Zhan catalyst is a type of ruthenium-based organometallic complex used in olefin metathesis. This class of chemicals is named after the chemist who first synthesized them, Zheng-Yun J. Zhan.
In organic chemistry, hydrovinylation is the formal insertion of an alkene into the C-H bond of ethylene. The more general reaction, hydroalkenylation, is the formal insertion of an alkene into the C-H bond of any terminal alkene. The reaction is catalyzed by metal complexes. A representative reaction is the conversion of styrene and ethylene to 3-phenybutene:
The ketimine Mannich reaction is an asymmetric synthetic technique using differences in starting material to push a Mannich reaction to create an enantiomeric product with steric and electronic effects, through the creation of a ketimine group. Typically, this is done with a reaction with proline or another nitrogen-containing heterocycle, which control chirality with that of the catalyst. This has been theorized to be caused by the restriction of undesired (E)-isomer by preventing the ketone from accessing non-reactive tautomers. Generally, a Mannich reaction is the combination of an amine, a ketone with a β-acidic proton and aldehyde to create a condensed product in a β-addition to the ketone. This occurs through an attack on the ketone with a suitable catalytic-amine unto its electron-starved carbon, from which an imine is created. This then undergoes electrophilic addition with a compound containing an acidic proton. It is theoretically possible for either of the carbonyl-containing molecules to create diastereomers, but with the addition of catalysts which restrict addition as of the enamine creation, it is possible to extract a single product with limited purification steps and in some cases as reported by List et al.; practical one-pot syntheses are possible. The process of selecting a carbonyl-group gives the reaction a direct versus indirect distinction, wherein the latter case represents pre-formed products restricting the reaction's pathway and the other does not. Ketimines selects a reaction group, and circumvent a requirement for indirect pathways.









