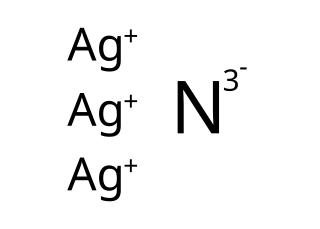Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula NH3. A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous waste, particularly among aquatic organisms, and it contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to 45 percent of the world's food and fertilizers. Around 70% of ammonia is used to make fertilisers in various forms and composition, such as urea and Diammonium phosphate. Ammonia in pure form is also applied directly into the soil.

Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation. Dry distillation is the heating of solid materials to produce gaseous products. Dry distillation may involve chemical changes such as destructive distillation or cracking and is not discussed under this article. Distillation may result in essentially complete separation, or it may be a partial separation that increases the concentration of selected components in the mixture. In either case, the process exploits differences in the relative volatility of the mixture's components. In industrial applications, distillation is a unit operation of practically universal importance, but it is a physical separation process, not a chemical reaction.

A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions at which thermodynamically distinct phases occur and coexist at equilibrium.
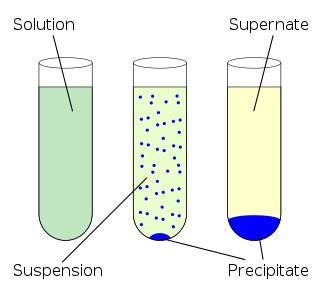
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
In physical chemistry, supersaturation occurs with a solution when the concentration of a solute exceeds the concentration specified by the value of solubility at equilibrium. Most commonly the term is applied to a solution of a solid in a liquid. A supersaturated solution is in a metastable state; it may be brought to equilibrium by forcing the excess of solute to separate from the solution. The term can also be applied to a mixture of gases.
In physical chemistry, Henry's law is a gas law that states that the amount of dissolved gas in a liquid is proportional to its partial pressure above the liquid. The proportionality factor is called Henry's law constant. It was formulated by the English chemist William Henry, who studied the topic in the early 19th century.

Dinitrogen pentoxide is the chemical compound with the formula N2O5, also known as nitrogen pentoxide or nitric anhydride. It is one of the binary nitrogen oxides, a family of compounds that only contain nitrogen and oxygen. It exists as colourless crystals that melt at 41 °C. Its boiling point is 47 °C, and sublimes slightly above room temperature, yielding a colorless gas.
Ammonia solution, also known as ammonia water, ammonium hydroxide, ammoniacal liquor, ammonia liquor, aqua ammonia, aqueous ammonia, or (inaccurately) ammonia, is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH3(aq). Although the name ammonium hydroxide suggests an alkali with composition [NH+
4][OH−
], it is actually impossible to isolate samples of NH4OH. The ions NH+
4 and OH− do not account for a significant fraction of the total amount of ammonia except in extremely dilute solutions.

Lead(II) iodide or lead iodide is a salt with the formula PbI
2. At room temperature, it is a bright yellow odorless crystalline solid, that becomes orange and red when heated. It was formerly called plumbous iodide.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on carbon dioxide.
A solubility chart is a chart with a list of ions and how, when mixed with other ions, they can become precipitates or remain aqueous.

Ammonium dichromate is an inorganic compound with the formula (NH4)2Cr2O7. In this compound, as in all chromates and dichromates, chromium is in a +6 oxidation state, commonly known as hexavalent chromium. It is a salt consisting of ammonium ions and dichromate ions.

A Diet Coke and Mentos eruption is a reaction between the carbonated beverage Diet Coke and Mentos mints that causes the beverage to be expelled from its container. The candies catalyze the release of gas from the beverage, which creates an eruption that pushes most of the liquid up and out of the bottle. Lee Marek and "Marek's Kid Scientists" were the first to publicly demonstrate the experiment on the Late Show with David Letterman in 1999. Steve Spangler's televised demonstration of the eruption in 2005 became popular on YouTube, launching a chain of several other Diet Coke and Mentos experiment viral videos. Experiments carried out at altitudes ranging from below sea level in Death Valley to the summit of Pikes Peak have demonstrated that the reaction works better at higher elevations.
Volatiles are the group of chemical elements and chemical compounds that can be readily vaporized. In contrast with volatiles, elements and compounds that are not readily vaporized are known as refractory substances.

In chemistry, a condenser is laboratory apparatus used to condense vapors – that is, turn them into liquids – by cooling them down.

Superheated water is liquid water under pressure at temperatures between the usual boiling point, 100 °C (212 °F) and the critical temperature, 374 °C (705 °F). It is also known as "subcritical water" or "pressurized hot water". Superheated water is stable because of overpressure that raises the boiling point, or by heating it in a sealed vessel with a headspace, where the liquid water is in equilibrium with vapour at the saturated vapor pressure. This is distinct from the use of the term superheating to refer to water at atmospheric pressure above its normal boiling point, which has not boiled due to a lack of nucleation sites.
An air separation plant separates atmospheric air into its primary components, typically nitrogen and oxygen, and sometimes also argon and other rare inert gases.
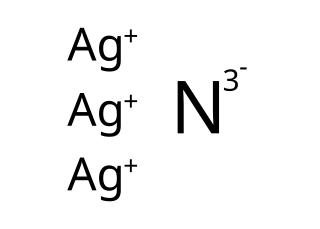
Silver nitride is an explosive chemical compound with symbol Ag3N. It is a black, metallic-looking solid which is formed when silver oxide or silver nitrate is dissolved in concentrated solutions of ammonia, causing formation of the diammine silver complex which subsequently breaks down to Ag3N. The standard free energy of the compound is about +315 kJ/mol, making it an endothermic compound which decomposes explosively to metallic silver and nitrogen gas.
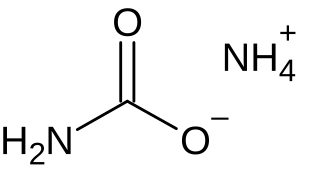
Ammonium carbamate is a chemical compound with the formula [NH4][H2NCO2] consisting of ammonium cation NH+4 and carbamate anion NH2COO−. It is a white solid that is extremely soluble in water, less so in alcohol. Ammonium carbamate can be formed by the reaction of ammonia NH3 with carbon dioxide CO2, and will slowly decompose to those gases at ordinary temperatures and pressures. It is an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of urea (NH2)2CO, an important fertilizer.
The use of ionic liquids in carbon capture is a potential application of ionic liquids as absorbents for use in carbon capture and sequestration. Ionic liquids, which are salts that exist as liquids near room temperature, are polar, nonvolatile materials that have been considered for many applications. The urgency of climate change has spurred research into their use in energy-related applications such as carbon capture and storage.