
Cymbidium, commonly known as boat orchids, is a genus of evergreen flowering plants in the orchid family Orchidaceae. Orchids in this genus are epiphytic, lithophytic, terrestrial or rarely leafless saprophytic herbs usually with pseudobulbs. There are usually between three and twelve leaves arranged in two ranks on each pseudobulb or shoot and lasting for several years. From one to a large number of flowers are arranged on an unbranched flowering stem arising from the base of the pseudobulb. The sepals and petals are all free from and similar to each other. The labellum is significantly different from the other petals and the sepals and has three lobes. There are about fifty-five species and sixteen further natural hybrids occurring in the wild from tropical and subtropical Asia to Australia. Cymbidiums are well known in horticulture and many cultivars have been developed.

Gomphotherium is an extinct genus of gomphothere proboscidean from the Neogene of Eurasia, Africa and North America. The genus is probably paraphyletic.
Sinocyclocheilus is a genus of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae endemic to China, only found in Guangxi, Guizhou and Yunnan. Almost all of its species live in or around caves and most of these have adaptions typical of cavefish such as a lack of scales, lack of pigmentation and reduced eyes. Several species have an unusual hunchbacked appearance and some of the cave-dwellers have a "horn" on the back, the function of which is unclear. In contrast, the Sinocyclocheilus species that live aboveground, as well as a few found underground, show no clear cavefish adaptions. They are relatively small fish reaching up to 23 cm (9.1 in) in length. The individual species have small ranges and populations, leading to the status of most of the evaluated species as threatened. Many species populations in the genus have yet to be evaluated by the IUCN.

Oreonectes is a genus of fish in the family Nemacheilidae found in the rivers and caves of Asia. Many of these species are troglobitic.

Triplophysa is a genus of fish in the family Nemacheilidae found mainly in and around the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China. Currently, the genus is a mixed assemblage of species. Some lineages have been identified and treated as subgenera, but as Wikipedia follows Fishbase for fish species all but Hedinichthys have been treated as subgenera in Wikipedia, although Kottelat in his revision of the loaches did recognise them as valid. FishBase, however, includes these in Triplophysa without specifying subgenera and treats the names given by Kottelat as synonyms.

Phanerochaete is a genus of crust fungi in the family Phanerochaetaceae.

As baicalin is a flavone glycoside, it is a flavonoid. It is the glucuronide of baicalein.
Sinoleontopodium is a genus of Tibetan plants in the tribe Gnaphalieae within the family Asteraceae.

Nerita balteata is a species of sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Neritidae.

Pestalotiopsis is a genus of ascomycete fungi in the Sporocadaceae family.
Huwentoxins (HWTX) are a group of neurotoxic peptides found in the venom of the Chinese bird spider Haplopelma schmidti. The species was formerly known as Haplopelma huwenum, Ornithoctonus huwena and Selenocosmia huwena. While structural similarity can be found among several of these toxins, HWTX as a group possess high functional diversity.

Qianzhousaurus is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period. There is currently only one species named, the type species Qianzhousaurus sinensis which is a member of the tribe Alioramini within the group, and most closely related to Alioramus, another alioramin.
Parafossarulus striatulus is a species of freshwater snail with gills and an operculum, an aquatic prosobranch gastropod mollusk in the family Bithyniidae.

Forcipomyia is a genus of biting midges in the subfamily Forcipomyiinae. Species of the subgenus Lasiohelea suck vertebrate blood. Some species are ectoparasites on larger insects. Other species in the genus are important pollinators of the cacao tree. There are at least 1,000 described species in Forcipomyia.

Zhejiang Agricultural University (ZAU) is a former public university in Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China. Founded as the Zhejiang College of Agriculture in 1952, the university was merged into Zhejiang University in 1998. Its campus now becomes the Huajiachi Campus of Zhejiang University.

Taiwanofungus is a fungal genus of unknown familial placement in the order Polyporales. The genus contains two species: the type, Taiwanofungus camphoratus, and T. salmoneus. Taiwanofungus was circumscribed by Chinese mycologists in 2004. T. camphoratus is a medicinal fungus that is found in Taiwan, where it grows on the endemic tree species Cinnamomum kanehirae. It was first described in 1990 by Mu Zang and Ching-Hua Su as a species of Ganoderma. T. salmoneus, originally placed in Antrodia, was validly added to the genus in 2012.

Luperini is a tribe of skeletonizing leaf beetles in the family Chrysomelidae. There are more than 30 genera and 500 described species in Luperini.
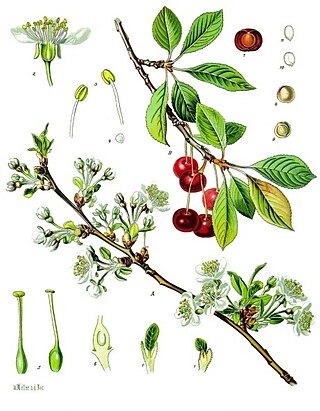
Prunus subg. Cerasus is a subgenus of Prunus. Species of the subgenus have a single winter bud per axil. The flowers are usually in small corymbs or umbels of several together, but some species have short racemes. The fruit is a drupe and has no obvious groove along the side. The subgenus is native to the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, with two species in North America, four in Europe, two in North Africa, and the remainder in Asia.

Longan witches broom-associated virus is a species of positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that has not been assigned to a genus within the family Potyviridae. It is thought to be the cause of witch's broom in longan, a large tropical tree from southeastern Asia of economic value. Longan witches broom disease is a condition that was first described in 1941. The virus was found in symptomatic plants and absent in healthy plants, but not all of Koch's postulates have been fulfilled.

Agriotypus is a genus of insect belonging to the family Ichneumonidae first described by John Curtis in 1832.















