Grand Canyon Village is a census-designated place (CDP) located on the South Rim of the Grand Canyon, in Coconino County, Arizona, United States. Its population was 2,004 at the 2010 Census. Located in Grand Canyon National Park, it is wholly focused on accommodating tourists visiting the canyon. Its origins trace back to the railroad completed from Williams, to the canyon's South Rim by the Santa Fe Railroad in 1901. Many of the structures in use today date from that period. The village contains numerous landmark buildings, and its historic core is a National Historic Landmark District, designated for its outstanding implementation of town design.

Williams is a city in Coconino County, Arizona, United States, located west of Flagstaff. Its population was 3,023 at the 2010 census. It lies on the routes of Historic Route 66 and Interstate 40. It is also the southern terminus of the Grand Canyon Railway, which takes visitors to Grand Canyon Village. There are numerous inns, motels, restaurants and gas stations catering to the large influx of tourists rather than local residents, especially during the summer and holiday seasons.

Ash Fork is a census-designated place in Yavapai County, Arizona, United States. Its population was 396 at the 2010 U.S. Census, down from 457 in 2000.

Clarkdale is a town in Yavapai County, Arizona, United States. The Verde River flows through the town as does Bitter Creek, an intermittent tributary of the river. According to the 2010 census, the population of the town was 4,097.

The known human history of the Grand Canyon area stretches back 10,500 years, when the first evidence of human presence in the area is found. Native Americans have inhabited the Grand Canyon and the area now covered by Grand Canyon National Park for at least the last 4,000 of those years. Ancestral Pueblo peoples, first as the Basketmaker culture and later as the more familiar Pueblo people, developed from the Desert Culture as they became less nomadic and more dependent on agriculture. A similar culture, the Cochimi also lived in the canyon area. Drought in the late 13th century likely caused both groups to move on. Other people followed, including the Paiute, Cerbat, and the Navajo, only to be later forced onto reservations by the United States Government.

The Fred Harvey Company was the owner of the Harvey House chain of restaurants, hotels and other hospitality industry businesses alongside railroads in the Western United States. It was founded in 1876 by Fred Harvey to cater to the growing number of train passengers.

The Grand Canyon Railway is a heritage railroad which carries passengers between Williams, Arizona, and the South Rim of Grand Canyon National Park.
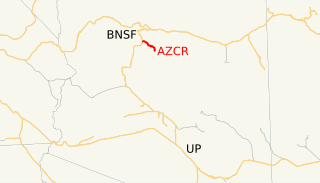
The Clarkdale Arizona Central Railroad is an Arizona short-line railroad that operates from a connection with the BNSF Railway at Drake, Arizona. The AZCR runs 37.8 miles (60.8 km) from Drake to Clarkdale, Arizona. An excursion train also runs on the line through Verde Canyon and is operated by the same owners under the Verde Canyon Railroad. The AZCR is owned by David L. Durbano.
The Santa Fe and Grand Canyon Railroad (SF&GC) was a 56-mile railroad that ran from Williams, Arizona to take mining supplies and people to the copper mines near Anita. In 1901, the SF&GC was sold at foreclosure and became the Grand Canyon Railway, a subsidiary of the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway. Today the line is a heritage railway owned by the Grand Canyon Railway providing excursions to the Grand Canyon.

Williams Depot is a privately owned train station in Williams, Arizona. It is the southern terminus of the Grand Canyon Railway line.

Grand Canyon Depot, also known as Grand Canyon Railroad Station, was constructed in 1909–10 for the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway at the South Rim of the Grand Canyon, in what is now Grand Canyon National Park. It is one of three remaining railroad depots in the United States built with logs as the primary structural material. The station is within 330 feet (100 m) of the rim of the canyon, opposite the El Tovar Hotel, also built by the railroad. The depot is designated a National Historic Landmark, is listed the National Register of Historic Places, and is included in the Grand Canyon Village National Historic Landmark District.

Forest City is a ghost town in Utah County, Utah, United States. It is located in the valley of Dutchman Flat in the upper part of American Fork Canyon, in the Uinta National Forest. A silver mining town just over the mountain from Alta, Forest City was inhabited about 1871–1880. The town grew up around the smelter that was built to process ore from the canyon's mines. The American Fork Railroad, which was intended to serve Forest City and the smelter, stopped short of its destination due to engineering difficulties. Transportation costs rose too high for the mines to continue operating profitably. As the smelter, mines, and railroad closed down, Forest City was abandoned.

Sego is a ghost town in Grand County, Utah, United States. It lies in the narrow, winding Sego Canyon, in the Book Cliffs some 5 miles (8.0 km) north of Thompson Springs. Formerly an important eastern Utah coal mining town, Sego was inhabited about 1910–1955. The town is accessed via the grade of the Ballard & Thompson Railroad, a spur from the Denver and Rio Grande Western built by the founders of the town to transport the coal.
The El Paso and Southwestern Railroad began in 1888 as the Arizona and South Eastern Railroad, a short line serving copper mines in southern Arizona. Over the next few decades, it grew into a 1200-mile system that stretched from Tucumcari, New Mexico, southward to El Paso, Texas, and westward to Tucson, Arizona, with several branch lines, including one to Nacozari, Mexico. The railroad was bought by the Southern Pacific Railroad in 1924 and fully merged into its parent company in 1955. The EP&SW was a major link in the transcontinental route of the Golden State Limited.

Robert Brewster Stanton was a United States civil and mining engineer. He was chief engineer of an expedition investigating the Grand Canyon for a possible railroad line in 1889-90, and investigated many mining properties.
Apex was a lumber town on the Grand Canyon Railway situated in Coconino County, Arizona.

Joseph Mayer was an American businessman, gold prospector and pioneer who founded the town of Mayer, Arizona.