Related Research Articles
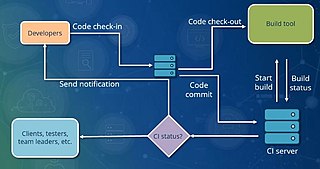
In software engineering, continuous integration (CI) is the practice of merging all developers' working copies to a shared mainline several times a day. Nowadays it is typically implemented in such a way that it triggers an automated build with testing. Grady Booch first proposed the term CI in his 1991 method, although he did not advocate integrating several times a day. Extreme programming (XP) adopted the concept of CI and did advocate integrating more than once per day – perhaps as many as tens of times per day.
Release engineering, frequently abbreviated as RE or as the clipped compound Releng, is a sub-discipline in software engineering concerned with the compilation, assembly, and delivery of source code into finished products or other software components. Associated with the software release life cycle, it was said by Boris Debic of Google Inc. that release engineering is to software engineering as manufacturing is to an industrial process:
Release engineering is the difference between manufacturing software in small teams or startups and manufacturing software in an industrial way that is repeatable, gives predictable results, and scales well. These industrial style practices not only contribute to the growth of a company but also are key factors in enabling growth.
Application lifecycle management (ALM) is the product lifecycle management of computer programs. It encompasses requirements management, software architecture, computer programming, software testing, software maintenance, change management, continuous integration, project management, and release management.
Build automation is the process of automating the creation of a software build and the associated processes including: compiling computer source code into binary code, packaging binary code, and running automated tests.
Azure DevOps Server is a Microsoft product that provides version control, reporting, requirements management, project management, automated builds, testing and release management capabilities. It covers the entire application lifecycle and enables DevOps capabilities. Azure DevOps can be used as a back-end to numerous integrated development environments (IDEs) but is tailored for Microsoft Visual Studio and Eclipse on all platforms.
Aldon is a business unit of Rocket Software. It develops, manufactures, licenses and supports software change management products for the enterprise application lifecycle management (ALM) and software change management (SCM) markets.

Parasoft is an independent software vendor specializing in automated software testing and application security with headquarters in Monrovia, California. It was founded in 1987 by four graduates of the California Institute of Technology who planned to commercialize the parallel computing software tools they had been working on for the Caltech Cosmic Cube, which was the first working hypercube computer built.
Multi-stage continuous integration is a software development technique intended to achieve highly integrated parallel development activity while reducing the scope of integration problems.
Release management is the process of managing, planning, scheduling and controlling a software build through different stages and environments; it includes testing and deploying software releases.
PTC IntegrityLifecycle Manager is a software system lifecycle management (SSLM) and application lifecycle management (ALM) platform developed by MKS Inc. and was first released in 2001. The software is client/server, with both desktop (java/swing) and web client interfaces. It provides software development organizations with a collaborative environment in which they can manage the end-to-end processes of development, from requirements management, engineering change management, revision control, and build management to test management and software deployment, as well as associated reports and metrics.
Micro Focus Application Lifecycle Management (ALM) is a set of software tools developed and marketed by Micro Focus (previously Hewlett-Packard and Hewlett Packard Enterprise) for application development and testing. It includes tools for requirements management, test planning and functional testing, performance testing (when used with Performance Center), developer management (through integration with developer environments such as Collabnet, TeamForge and Microsoft Visual Studio), and defect management.
Continuous testing is the process of executing automated tests as part of the software delivery pipeline to obtain immediate feedback on the business risks associated with a software release candidate. Continuous testing was originally proposed as a way of reducing waiting time for feedback to developers by introducing development environment-triggered tests as well as more traditional developer/tester-triggered tests.
Continuous delivery (CD) is a software engineering approach in which teams produce software in short cycles, ensuring that the software can be reliably released at any time and, following a pipeline through a "production-like environment", without doing so manually. It aims at building, testing, and releasing software with greater speed and frequency. The approach helps reduce the cost, time, and risk of delivering changes by allowing for more incremental updates to applications in production. A straightforward and repeatable deployment process is important for continuous delivery.
Parasoft Virtualize is a service virtualization product that can create, deploy, and manage simulated test environments for software development and software testing purposes. These environments simulate the behavior of dependent resources that are unavailable, difficult to access, or difficult to configure for development or testing. It simulates the behavior of dependent resources such as mainframes, ERP systems, databases, web services, third-party information systems, or other systems that are out of direct developer/tester control. The product is used in conjunction with hardware/OS virtualization to provide developers and testers with the resources they need to execute their development and testing tasks earlier, faster, or more completely. Its technologies for automating continuous testing are used as part of continuous delivery, continuous integration, and continuous release.
Perforce Software, Inc. is an American developer of software used for developing and running applications, including version control software, web-based repository management, developer collaboration, application lifecycle management, web application servers, debugging tools and Agile planning software.
In software deployment, an environment or tier is a computer system or set of systems in which a computer program or software component is deployed and executed. In simple cases, such as developing and immediately executing a program on the same machine, there may be a single environment, but in industrial use, the development environment and production environment are separated, often with several stages in between. This structured release management process allows phased deployment (rollout), testing, and rollback in case of problems.
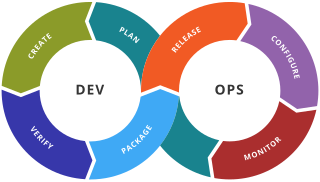
A DevOps toolchain is a set or combination of tools that aid in the delivery, development, and management of software applications throughout the systems development life cycle, as coordinated by an organisation that uses DevOps practices.
TestOps refers to the discipline of managing the operational aspects of testing within the software delivery lifecycle.
References
- ↑ Fredrick, Jeffrey; Minick, Eric (2011). "Enterprise Continuous Delivery Maturity Model" (PDF). UrbanCode. p. 14. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-02-22. Retrieved February 17, 2012.
- ↑ Julius, Paul (September 11, 2009). "Enterprise CI Cultural Maturity". UrbanCode Blogs. UrbanCode. Retrieved February 17, 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 Humble, Jez; Farley, David (2010). Continuous Delivery: Reliable Software Releases Through Build, Test, and Deployment Automation (3rd ed.). Addison Wesley. p. 463. ISBN 978-0-321-60191-9.
- ↑ Ellis Agência Web (July 19, 2018). "True Application Lifecycle Management With Urbancode" Retrieved July 19, 2022.
- ↑ "UrbanCode DevOps platform™". UrbanCode. Archived from the original on February 25, 2013. Retrieved February 11, 2013.
- ↑ "Urbancode's AnthillPro Reaches Milestone 400th Customer in Company's Strongest Quarter" (Press release). Cleveland, Ohio: UrbanCode. December 7, 2009. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- ↑ "IBM Acquires UrbanCode to Help Businesses Rapidly Deliver Mobile, Cloud, Big Data and Social Software". www-03.ibm.com. IBM. Retrieved 6 August 2014.
- ↑ "Retirement of AnthillPro". Urbancode.com. Archived from the original on June 17, 2020. Retrieved June 17, 2020.
- ↑ MSDN (January 18, 2007). "PRJ: Microsoft Project for Windows Version History". Article ID: 98026 - Last Review: January 18, 2007 - Revision: 3.1. MSDN. Retrieved March 14, 2012.
- ↑ "Nightly Builds: the bleeding edge". mozilla. mozilla.org. February 1, 2011. Archived from the original on February 18, 2012. Retrieved March 1, 2012.
- ↑ "Iteration Activities Rolling and Nightly Builds". MSDN Library. February 7, 2008. Archived from the original on January 28, 2013. Retrieved March 1, 2012.
- 1 2 3 4 Duvall, Paul M.; Matyas, Steve; Glover, Andrew (June 2007). Continuous Integration: Improving Software Quality and Reducing Risk . Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Addison-Wesley. p. 283. ISBN 978-0-321-33638-5.
- ↑ Hatcher, Erik; Loughran, Steve (2003). Java Development with Ant: How to automate your build, test and deployment processes . Greenwich, CT: Manning. pp. 634. ISBN 1-930110-58-8.
- ↑ Larman, Craig (2004). Agile & Iterative Development: A Managers Guide. Boston, MA: Addison-Wesley. p. 342. ISBN 0-13-111155-8.
- ↑ Clark, Mike (July 1, 2004). Pragmatic Project Automation: How to Build, Deploy, and Monitor Java Applications. USA: Pragmatic Bookshelf. p. 176. ISBN 978-0-9745140-3-1.
- ↑ Bradley Holt (August 8, 2011). "The Case For Rapid Release Cycles". Bradley-Holt. Retrieved March 14, 2012.
- 1 2 Minick, Eric (October 26, 2006). "Urbancode announces AnthillPro 3.0, lifecycle automation server". TheServerSide.com. Retrieved February 22, 2012.
- 1 2 Dr. Dobb's Journal (January 27, 2008). "Urbancode Releases Continuous Integration Tool Upgrade". Dr. Dobb's. Retrieved February 14, 2012.
- ↑ "Release Management". Wikibooks. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- ↑ Wyser, Della; Kurz, Jon (March 13, 2007). "Jolts 2007: Change and Configuration Management". Dr. Dobb's Journal. Retrieved February 13, 2012.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ Colville, Ronni J.; Brittain, Kris; Scott, Donna (2011). "Cool Vendors in Release Management, 2011". Gartner. Gartner. Retrieved February 23, 2012.[ dead link ]
- ↑ Sayko, Michael (September 15, 2008). "Using a Commercial Tool to Automate a Build and Deployment Process". CM Crossroads. Retrieved February 3, 2012.
- 1 2 Feinman, Jeff (October 9, 2009). "Command-line features added to AnthillPro". SD Times. Archived from the original on January 31, 2010. Retrieved February 14, 2012.
- ↑ Rubinstein, David (November 4, 2011). "Agile processes adopted widely, study shows". SD Times. Retrieved February 11, 2012.
- ↑ Dr. Dobb's Journal (October 28, 2008). "UrbanCode Adds PreFlight Builds". Dr. Dobb's. Retrieved February 10, 2012.
- ↑ "AnthillPro 3.7 Released". Agile Journal. October 5, 2009. Retrieved February 14, 2012.