Related Research Articles

The United States Food and Drug Administration is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, dietary supplements, prescription and over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, animal foods & feed and veterinary products.

Anthrax is an infection caused by the bacterium Bacillus anthracis. It can occur in four forms: skin, lungs, intestinal, and injection. Symptom onset occurs between one day and more than two months after the infection is contracted. The skin form presents with a small blister with surrounding swelling that often turns into a painless ulcer with a black center. The inhalation form presents with fever, chest pain and shortness of breath. The intestinal form presents with diarrhea, abdominal pains, nausea and vomiting. The injection form presents with fever and an abscess at the site of drug injection.

Infliximab, a chimeric monoclonal antibody, sold under the brand name Remicade among others, is a medication used to treat a number of autoimmune diseases. This includes Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and Behçet's disease. It is given by slow injection into a vein, typically at six- to eight-week intervals.

Hyaluronidases are a family of enzymes that catalyse the degradation of hyaluronic acid (HA). Karl Meyer classified these enzymes in 1971, into three distinct groups, a scheme based on the enzyme reaction products. The three main types of hyaluronidases are two classes of eukaryotic endoglycosidase hydrolases and a prokaryotic lyase-type of glycosidase.
Rintatolimod, sold under the tradename Ampligen, is a medication intended for treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS). There is some evidence it may improve some CFS symptoms.
Raxibacumab is a human monoclonal antibody intended for the prophylaxis and treatment of inhaled anthrax. Its efficacy has been proven in rabbits and monkeys. In December 2012 raxibacumab was approved in the United States for the treatment of inhalational anthrax due to Bacillus anthracis in combination with appropriate antibacterial drugs, and for prophylaxis of inhalational anthrax when alternative therapies are not available or are not appropriate.

Enrofloxacin (ENR) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic sold by the Bayer Corporation under the trade name Baytril. It is sold by in a generic form by Bimeda Inc. under the name EnroMed 100. Enrofloxacin is currently approved by the FDA for the treatment of individual pets and domestic animals in the United States. In September 2005, the FDA withdrew approval of Baytril for use in water to treat flocks of poultry, as this practice was noted to promote the evolution of fluoroquinolone-resistant strains of the bacterium Campylobacter, a human pathogen.
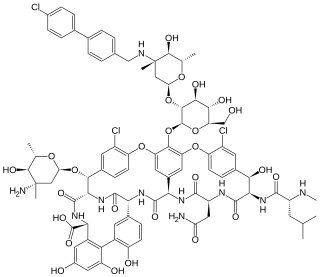
Oritavancin, sold under the brand name Orbactiv among others, is a semisynthetic glycopeptide antibiotic medication for the treatment of serious Gram-positive bacterial infections. Its chemical structure as a lipoglycopeptide is similar to vancomycin.

The Project Bioshield Act was an act passed by the United States Congress in 2004 calling for $5 billion for purchasing vaccines that would be used in the event of a bioterrorist attack. This was a ten-year program to acquire medical countermeasures to biological, chemical, radiological, and nuclear agents for civilian use. A key element of the Act was to allow stockpiling and distribution of vaccines which had not been tested for safety or efficacy in humans, due to ethical concerns. Efficacy of such agents cannot be directly tested in humans without also exposing humans to the chemical, biological, or radioactive threat being treated, so testing follows the FDA Animal Rule for pivotal animal efficacy.

Dalbavancin, sold under the brand names Dalvance in the US and Xydalba in the EU among others, is a second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic medication. It belongs to the same class as vancomycin, the most widely used and one of the treatments available to people infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) is a human immunoglobulin that is used to prevent the development of hepatitis B and is used for the treatment of acute exposure to HBsAg.

Nivolumab, sold under the brand name Opdivo, is a medication used to treat a number of types of cancer. This includes melanoma, lung cancer, malignant pleural mesothelioma, renal cell carcinoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, head and neck cancer, urothelial carcinoma, colon cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, liver cancer, gastric cancer, and esophageal or gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) cancer. It is used by slow injection into a vein.

Anthrax vaccine adsorbed (AVA) is the only FDA-licensed human anthrax vaccine in the United States. It is produced under the trade name BioThrax by the Emergent BioDefense Corporation in Lansing, Michigan. The parent company of Emergent BioDefense is Emergent BioSolutions of Rockville, Maryland. It is sometimes called MDPH-PA or MDPH-AVA after the former Michigan Department of Public Health, which formerly was involved in its production.

Oliceridine, sold under the brand name Olinvyk, is an opioid medication that is used for the treatment of moderate to severe acute pain in adults. It is given by intravenous (IV) injection.

Finafloxacin (Xtoro) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic. In the United States, it is approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat acute otitis externa caused by the bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus.

Ceftazidime/avibactam, sold under the brand name Avycaz among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication composed of ceftazidime, a cephalosporin antibiotic, and avibactam, a β-lactamase inhibitor. It is used to treat complicated intra-abdominal infections, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia. It is only recommended when other options are not appropriate. It is given by injection into a vein.
Elusys Therapeutics is a biopharmaceutical company founded in Pine Brook, New Jersey in 1998. The company specializes in the development of antibodies for the treatment infectious diseases. The antibodies are developed from protein complexes called heteropolymers which can bind to specific pathogens on one side and red blood cells on the other side.

Lefamulin, sold under the brand name Xenleta, is an antibiotic medication used it to treat adults with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.
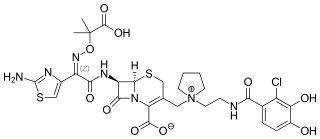
Cefiderocol, sold under the brand name Fetroja among others, is an antibiotic used to treat complicated urinary tract infections when no other options are available. It is indicated for the treatment of multi-drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria including Pseudomonas aeruginosa. It is given by injection into a vein.
Antibiotics in poultry farming in America is the controversial prophylactic use of antibiotics in the country's poultry farming industry. This does not represent the position in other countries.
References
- ↑ Savransky V, Ionin B, Reece J (May 2020). "Current Status and Trends in Prophylaxis and Management of Anthrax Disease". Pathogens (Basel, Switzerland). 9 (5): 370. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9050370 . PMC 7281134 . PMID 32408493.
- ↑ "FDA approves treatment for inhalation anthrax". United States Food and Drug Administration. 25 March 2015.
- ↑ "Anthrasil Approval History". Drugs.com. Retrieved 26 March 2015.