A disk image, in computing, is a computer file containing the contents and structure of a disk volume or of an entire data storage device, such as a hard disk drive, tape drive, floppy disk, optical disc, or USB flash drive. A disk image is usually made by creating a sector-by-sector copy of the source medium, thereby perfectly replicating the structure and contents of a storage device independent of the file system. Depending on the disk image format, a disk image may span one or more computer files.

The Macintosh Plus computer is the third model in the Macintosh line, introduced on January 16, 1986, two years after the original Macintosh and a little more than a year after the Macintosh 512K, with a price tag of US$2599. As an evolutionary improvement over the 512K, it shipped with 1 MB of RAM standard, expandable to 4 MB, and an external SCSI peripheral bus, among smaller improvements. Originally, the computer's case was the same beige color as the original Macintosh, Pantone 453, however in 1987, the case color was changed to the long-lived, warm gray "Platinum" color. It is the earliest Macintosh model able to run System 7.

The Power Macintosh G3 is a series of personal computers designed, manufactured, and sold by Apple Computer, Inc. from November 1997 to August 1999. It represented Apple's first step towards eliminating redundancy and complexity in the product line by replacing eight Power Macintosh models with three: Desktop and Mini Tower models for professional and home use, and an All-In-One model for education. The introduction of the Desktop and Mini Tower models coincided with Apple starting to sell build-to-order Macs directly from its web site in an online store, which was unusual for the time as Dell was the only major computer manufacturer doing this. Apple's move to build-to-order sales of the Power Macintosh G3 also coincided with the acquisition of Power Computing Corporation, which had been providing telephone sales of Macintosh clones for more than two years.
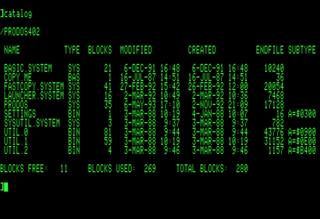
ProDOS is the name of two similar operating systems for the Apple II series of personal computers. The original ProDOS, renamed ProDOS 8 in version 1.2, is the last official operating system usable by all 8-bit Apple II series computers, and was distributed from 1983 to 1993. The other, ProDOS 16, was a stop-gap solution for the 16-bit Apple IIGS that was replaced by GS/OS within two years.
Disk formatting is the process of preparing a data storage device such as a hard disk drive, solid-state drive, floppy disk or USB flash drive for initial use. In some cases, the formatting operation may also create one or more new file systems. The first part of the formatting process that performs basic medium preparation is often referred to as "low-level formatting". Partitioning is the common term for the second part of the process, making the data storage device visible to an operating system. The third part of the process, usually termed "high-level formatting" most often refers to the process of generating a new file system. In some operating systems all or parts of these three processes can be combined or repeated at different levels and the term "format" is understood to mean an operation in which a new disk medium is fully prepared to store files. Some formatting utilities allow distinguishing between a quick format, which does not erase all existing data and a long option that does erase all existing data.

System 7, codenamed "Big Bang", and also known as Mac OS 7, is a graphical user interface-based operating system for Macintosh computers and is part of the classic Mac OS series of operating systems. It was introduced on May 13, 1991, by Apple Computer, Inc. It succeeded System 6, and was the main Macintosh operating system until it was succeeded by Mac OS 8 in 1997. Features added with the System 7 release included virtual memory, personal file sharing, QuickTime, QuickDraw 3D, and an improved user interface.

In computing, the fdisk command-line utility provides disk-partitioning functions - for example: preparatory to defining file systems. fdisk features in the DOS, DR FlexOS, IBM OS/2, and Microsoft Windows operating systems, and in certain ports of FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, DragonFly BSD and macOS for compatibility reasons. In versions of the Windows NT operating-system line from Windows 2000 onwards, fdisk is replaced by a more advanced tool called diskpart. Similar utilities exist for Unix-like systems, for example, BSD disklabel.

The Macintosh 512Kenhanced (512Ke) was introduced in April 1986 as a cheaper alternative to the top-of-the-line Macintosh Plus, which had debuted three months previously. It is the same as the Macintosh 512K but with the 800K disk drive and 128K of ROM used in the Macintosh Plus. Like its predecessors, it has little room for expansion. Some companies did create memory upgrades that brought the machine up to 2 MB or more. It is the earliest Macintosh model able to run System Software 6. It is also the earliest that can be used as an AppleShare server and, with a bridge Mac, communicate with modern devices.

Multi-booting is the act of installing multiple operating systems on a single computer, and being able to choose which one to boot. The term dual-booting refers to the common configuration of specifically two operating systems. Multi-booting may require a custom boot loader.

The USB mass storage device class is a set of computing communications protocols, specifically a USB Device Class, defined by the USB Implementers Forum that makes a USB device accessible to a host computing device and enables file transfers between the host and the USB device. To a host, the USB device acts as an external hard drive; the protocol set interfaces with a number of storage devices.

Disk Utility is a system utility for performing disk and disk volume-related tasks on the macOS operating system by Apple Inc.

Boot Camp Assistant is a multi boot utility included with Apple Inc.'s macOS that assists users in installing Microsoft Windows operating systems on Intel-based Macintosh computers. The utility guides users through non-destructive disk partitioning of their hard disk drive or solid state drive and installation of Windows device drivers for the Apple hardware. The utility also installs a Windows Control Panel applet for selecting the default boot operating system.

Time Machine is a backup software application distributed as part of macOS, the desktop operating system developed by Apple. The software is designed to work with external storage devices and most commonly used with external disk drives. It was first introduced in Mac OS X Leopard.

Target Disk Mode is a boot mode unique to Macintosh computers.

Oracle VM VirtualBox is a free and open-source hosted hypervisor for x86 virtualization, developed by Oracle Corporation. Created by Innotek, it was acquired by Sun Microsystems in 2008, which was in turn acquired by Oracle in 2010.

The Macintosh Hard Disk 20 was the first hard drive developed by Apple Computer specifically for use with the Macintosh 512K. Introduced on September 17, 1985, it was part of Apple's long-awaited solution toward completing the Macintosh Office announced in January 1985. It would be over a year more before Apple would release the file server software AppleShare that would link all of the hardware together. By that time the SCSI interface introduced on the Macintosh Plus in January 1986, would accommodate far faster and more efficient hard drives, rendering the Hard Disk 20 virtually obsolete.

The Apple Tape Backup 40SC is an external, SCSI-interfaced, 1⁄4-inch (6.35 mm) QIC, mini-cartridge tape drive. It was first introduced by Apple, Inc. in 1987 and discontinued in 1994. The drive came bundled with Retrospect backup software. The drive is also compatible with the tape software included with A/UX.

The classic Mac OS is the series of operating systems developed for the Macintosh family of personal computers by Apple Inc. from 1984 to 2001, starting with System 1 and ending with Mac OS 9. The Macintosh operating system is credited with having popularized the graphical user interface concept. It was included with every Macintosh that was sold during the era in which it was developed, and many updates to the system software were done in conjunction with the introduction of new Macintosh systems.















