Sextus Julius Frontinus was a prominent Roman civil engineer, author, soldier and senator of the late 1st century AD. He was a successful general under Domitian, commanding forces in Roman Britain, and on the Rhine and Danube frontiers. A novus homo, he was consul three times. Frontinus ably discharged several important administrative duties for Nerva and Trajan. However, he is best known to the post-Classical world as an author of technical treatises, especially De aquaeductu, dealing with the aqueducts of Rome.
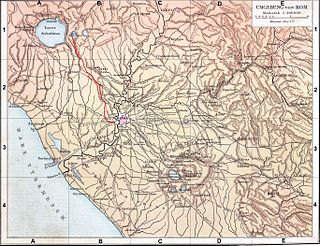
The Aniene, formerly known as the Teverone, is a 99-kilometer (62 mi) river in Lazio, Italy. It originates in the Apennines at Trevi nel Lazio and flows westward past Subiaco, Vicovaro, and Tivoli to join the Tiber in northern Rome. It formed the principal valley east of ancient Rome and became an important water source as the city's population expanded. The falls at Tivoli were noted for their beauty. Historic bridges across the river include the Ponte Nomentano, Ponte Mammolo, Ponte Salario, and Ponte di San Francesco, all of which were originally fortified with towers.

The Aqua Appia was the first Roman aqueduct, constructed in 312 BC by the co-censors Gaius Plautius Venox and Appius Claudius Caecus, the same Roman censor who also built the important Via Appia.
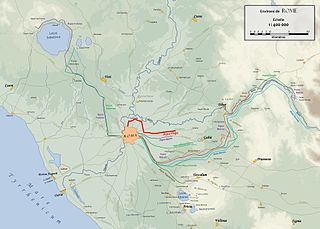
The Aqua Virgo was one of the eleven Roman aqueducts that supplied the city of ancient Rome. It was completed in 19 BC by Marcus Agrippa, during the reign of the emperor Augustus and was built mainly to supply the contemporaneous Baths of Agrippa in the Campus Martius.

The Aqua Augusta, or Serino Aqueduct, was one of the largest, most complex and costliest aqueduct systems in the Roman world; it supplied water to at least eight ancient cities in the Bay of Naples including Pompeii and Herculaneum. This aqueduct was unlike any other of its time, being a regional network rather than being focused on one urban centre.

The Romans constructed aqueducts throughout their Republic and later Empire, to bring water from outside sources into cities and towns. Aqueduct water supplied public baths, latrines, fountains, and private households; it also supported mining operations, milling, farms, and gardens.

Aqua Anio Novus was an ancient Roman aqueduct supplying the city of Rome. Like the Aqua Claudia, it was begun by emperor Caligula in 38 AD and completed in 52 AD by Claudius, who dedicated them both on August 1.

Aqua Claudia was an ancient Roman aqueduct that, like the Aqua Anio Novus, was begun by Emperor Caligula in 38 AD and finished by Emperor Claudius in 52 AD.
Sanitation in ancient Rome, acquired from the Etruscans, was very advanced compared to other ancient cities and provided water supply and sanitation services to residents of Rome. Although there were many sewers, public latrines, baths and other sanitation infrastructure, disease was still rampant. The baths are known to symbolise the "great hygiene of Rome".

The Aqua Julia is a Roman aqueduct built in 33 BC by Agrippa under Augustus to supply the city of Rome. It was repaired and expanded by Augustus from 11–4 BC.

The Acqua Felice is one of the aqueducts of Rome, completed in 1586 by Pope Sixtus V, whose birth name, which he never fully abandoned, was Felice Peretti. The first new aqueduct of early modern Rome, its source is at the springs at Pantano Borghese, off Via Casilina. Its length is fifteen miles (24 km), running underground for eight miles (13 km) from its source, first in the channel of Aqua Alexandrina, then alternating on the arches of the Aqua Claudia and the Aqua Marcia for seven miles (11 km) to its terminus at the Fontana dell'Acqua Felice on the Quirinal Hill, standing to one side of the Strada Pia, so as to form a piazza in this still new part of Rome. The engineer was Giovanni Fontana, brother of Sixtus' engineer-architect Domenico Fontana, who recorded that the very day the new pope entered the Lateran, he decided that he would bring water once again to the hills of Rome, which had remained waterless and sparsely inhabited, largely by monasteries, since the original ancient aqueducts had been destroyed in the sixth century. From the source, which Sixtus purchased, there was only a very small fall, and the work required an underground conduit as well as an aqueduct carried on arches.
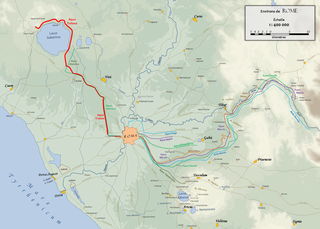
The Aqua Traiana was a 1st-century Roman aqueduct built by Emperor Trajan and inaugurated in 109 AD. It channelled water from sources around Lake Bracciano, 40 km (25 mi) north-west of Rome, to ancient Rome. It joined the earlier Aqua Alsietina to share a common lower route into Rome.

In Ancient Rome, the Aqua Alsietina was the earlier of the two western Roman aqueducts, erected sometime around 2 BC, during the reign of emperor Augustus. It was the only water supply for the Transtiberine region, on the right bank of the river Tiber until the Aqua Traiana was built.
De aquaeductu is a two-book official report given to the emperor Nerva or Trajan on the state of the aqueducts of Rome, and was written by Sextus Julius Frontinus at the end of the 1st century AD. It is also known as De Aquis or De Aqueductibus Urbis Romae. It is the earliest official report of an investigation made by a distinguished citizen on Roman engineering works to have survived. Frontinus had been appointed Water Commissioner by the emperor Nerva in AD 96.

The Aqua Marcia is one of the longest of the eleven aqueducts that supplied the city of Rome. The aqueduct was built between 144–140 BC, during the Roman Republic. The still-functioning Acqua Felice from 1586 runs on long stretches along the route of the Aqua Marcia.

Aqueducts are bridges constructed to convey watercourses across gaps such as valleys or ravines. The term aqueduct may also be used to refer to the entire watercourse, as well as the bridge. Large navigable aqueducts are used as transport links for boats or ships. Aqueducts must span a crossing at the same level as the watercourses on each end. The word is derived from the Latin aqua ("water") and ducere, therefore meaning "to lead water". A modern version of an aqueduct is a pipeline bridge. They may take the form of tunnels, networks of surface channels and canals, covered clay pipes or monumental bridges.

The Appian Way Regional Park is the second-largest urban park of Europe, after Losiny Ostrov National Park in Moscow. It is a protected area of around 4580 hectares, established by the Italian region of Latium. It falls primarily within the territory of Rome but parts also extend into the neighbouring towns of Ciampino and Marino.

The Aqua Anio Vetus was an ancient Roman aqueduct, and the second oldest after the Aqua Appia.

The Curator Aquarum was a Roman official responsible for managing Rome's water supply and distributing free grain. Curators were appointed by the emperor. The first curator was Agrippa. Another notable Curator Aquarum was Frontinus, a Roman engineer.


















