
Gadiformes, also called the Anacanthini, are an order of ray-finned fish that include the cod, hakes, pollock, haddock, burbot, rocklings and moras, many of which are food fish of major commercial value. They are mostly marine fish found throughout the world and the vast majority are found in temperate or colder regions while a few species may enter brackish estuaries. Pacific tomcods, one of the two species that makes up the genus Microgadus, are able to enter freshwater, but there is no evidence that they breed there. Some populations of landlocked Atlantic tomcod on the other hand, complete their entire life cycle in freshwater. Yet only one species, the burbot, is a true freshwater fish.

The Gonorynchiformes are an order of ray-finned fish that includes the important food source, the milkfish, and a number of lesser-known types, both marine and freshwater.

Neopterygii is a subclass of ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii). Neopterygii includes the Holostei and the Teleostei, of which the latter comprise the vast majority of extant fishes, and over half of all living vertebrate species. While living holosteans include only freshwater taxa, teleosts are diverse in both freshwater and marine environments. Many new species of teleosts are scientifically described each year.

The Osmeriformes are an order of ray-finned fish that includes the true or freshwater smelts and allies, such as the galaxiids and noodlefishes; they are also collectively called osmeriforms. They belong to the teleost superorder Protacanthopterygii, which also includes pike and salmon, among others. The order's name means "smelt-shaped", from Osmerus + the standard fish order suffix "-formes". It ultimately derives from Ancient Greek osmé + Latin forma, the former in reference to the characteristic aroma of the flesh of Osmerus.

Aulopiformes is a diverse order of marine ray-finned fish consisting of some 15 extant and several prehistoric families with about 45 genera and over 230 species. The common names grinners, lizardfishes and allies, or aulopiforms are sometimes used for this group. The scientific name means "Aulopus-shaped", from Aulopus + the standard fish order suffix "-formes". It ultimately derives from Ancient Greek aulós + Latin forma, the former in reference to the elongated shape of many aulopiforms.

The herring smelts or argentines are a family, Argentinidae, of marine smelts. They are similar in appearance to smelts but have much smaller mouths.

Paraulopus is the only genus in the family Paraulopidae, a family of grinners in the order Aulopiformes. They are commonly known as cucumberfishes, but locally some other Teleostei are also known by that name. They were considered in the Chlorophthalmidae or greeneye family until 2001.

Protacanthopterygii is a ray-finned fish taxon ranked as a superorder of the infraclass Teleostei. They inhabit both marine and freshwater habitats. They appear to have evolved in the Cretaceous or perhaps late Jurassic, originating probably roughly 150 million years ago; fossils of them and the closely related Otocephala are known from throughout the Cretaceous.

Apateodus is a genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish which was described by Woodward in 1901. It was a relative of modern lizardfish and lancetfish in the order Aulopiformes, and one of a number of prominent nektonic aulopiforms of Cretaceous marine ecosystems.

The Heterenchelyidae or mud eels are a small family of eels native to the Atlantic, Mediterranean, and eastern Pacific.
Casierius is an extinct genus of marine ray-finned fish that lived during the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous epoch. It was a relative of the modern bonefish in the extinct family Phyllodontidae, although some authorities consider it either a true albulid or a very early eel. It contains a single species, C. heckeli, known from the Glen Rose Formation near Hood County, Texas.
Ampheristus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish. It was a basal or stem member of the family Ophidiidae, which contains modern cusk-eels. Fossils are known from worldwide from the Late Cretaceous to the late Paleogene, making it a rather successful survivor of the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event.

Stenopterygii are a superorder of ray-finned fish in the infraclass Teleostei. Their validity is somewhat doubtful, as the group was established to separate, out of a large group of closely related Teleostei, a mere two rather peculiarly autapomorphic orders at best. In some treatments, it is even monotypic.
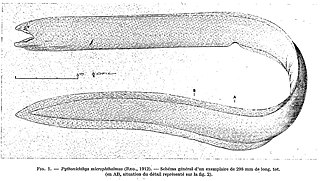
Pythonichthys is a genus of eels of the family Heterenchelyidae that occur in tropical waters of the eastern Pacific Ocean off of Panama and in the Atlantic Ocean near the Caribbean Sea and the west coast of Africa. It contains the following described species:

Argentina is a genus of fishes in the family Argentinidae.

Plethodidae is an extinct family of teleost fish that existed during the Late Cretaceous period. Fossils are known from North America, North Africa, and Europe.

Alepocephaliformes is an order of marine deep-sea teleost fishes. It was previously classified as the suborder Alepocephaloidei of the order Argentiniformes.

Otocephala is a clade of ray-finned fishes within the infraclass Teleostei that evolved some 230 million years ago. It is named for the presence of a hearing (otophysic) link from the swimbladder to the inner ear. Other names proposed for the group include Ostarioclupeomorpha and Otomorpha.

Teleosteomorpha is a clade of ray-finned fishes containing all teleost fish and their closest extinct relatives. Also in this group are two diverse Mesozoic fish orders, the Aspidorhynchiformes and the Pachycormiformes. Several other non-teleostomorph teleosteans existed throughout the Mesozoic, although not as dominant as the two main clades in the group.

Dortokidae is an extinct family of freshwater pan-pleurodiran turtles, known from the Cretaceous and Paleocene of Europe. Only four species have been named, but indeterminate fossils show that they were abundant across western and eastern-central Europe during the Cretaceous. The family is only known from postcranial remains.



















