Blowfish is a symmetric-key block cipher, designed in 1993 by Bruce Schneier and included in many cipher suites and encryption products. Blowfish provides a good encryption rate in software, and no effective cryptanalysis of it has been found to date. However, the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) now receives more attention, and Schneier recommends Twofish for modern applications.

Arabidopsis thaliana, the thale cress, mouse-ear cress or arabidopsis, is a small plant from the mustard family (Brassicaceae), native to Eurasia and Africa. Commonly found along the shoulders of roads and in disturbed land, it is generally considered a weed.

JPEG 2000 (JP2) is an image compression standard and coding system. It was developed from 1997 to 2000 by a Joint Photographic Experts Group committee chaired by Touradj Ebrahimi, with the intention of superseding their original JPEG standard, which is based on a discrete cosine transform (DCT), with a newly designed, wavelet-based method. The standardized filename extension is .jp2 for ISO/IEC 15444-1 conforming files and .jpx for the extended part-2 specifications, published as ISO/IEC 15444-2. The registered MIME types are defined in RFC 3745. For ISO/IEC 15444-1 it is image/jp2.

Squaring the square is the problem of tiling an integral square using only other integral squares. The name was coined in a humorous analogy with squaring the circle. Squaring the square is an easy task unless additional conditions are set. The most studied restriction is that the squaring be perfect, meaning the sizes of the smaller squares are all different. A related problem is squaring the plane, which can be done even with the restriction that each natural number occurs exactly once as a size of a square in the tiling. The order of a squared square is its number of constituent squares.

The Westerbork Synthesis Radio Telescope (WSRT) is an aperture synthesis interferometer built on the site of the former World War II Nazi detention and transit camp Westerbork, north of the village of Westerbork, Midden-Drenthe, in the northeastern Netherlands.
The Combined Array for Research in Millimeter-wave Astronomy (CARMA) was an astronomical instrument comprising 23 radio telescopes, dedicated in 2006. These telescopes formed an astronomical interferometer where all the signals are combined in a purpose-built computer to produce high-resolution astronomical images. The telescopes ceased operation in April 2015 and were relocated to the Owens Valley Radio Observatory for storage.

A primordium in embryology, is an organ or tissue in its earliest recognizable stage of development. Cells of the primordium are called primordial cells. A primordium is the simplest set of cells capable of triggering growth of the would-be organ and the initial foundation from which an organ is able to grow. In flowering plants, a floral primordium gives rise to a flower.

The Nottingham Arabidopsis Stock Centre (NASC) provides seed and information resources to the International Arabidopsis Genome Project and the wider research community. It is based in the School of Biosciences at the University of Nottingham's Sutton Bonington Campus, in the English county of Nottinghamshire.

The Murchison Widefield Array (MWA) is a joint project between an international consortium of organisations to construct and operate a low-frequency radio array. 'Widefield' refers to its very large field of view. Operating in the frequency range 70–300 MHz, the main scientific goals of the MWA are to detect neutral atomic Hydrogen emission from the cosmological Epoch of Reionization (EoR), to study the Sun, the heliosphere, the Earth's ionosphere, and radio transient phenomena, as well as map the extragalactic radio sky. It is located at the Murchison Radio-astronomy Observatory (MRO).
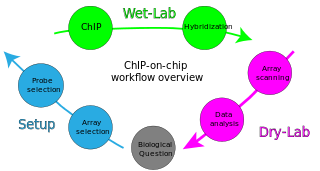
ChIP-on-chip is a technology that combines chromatin immunoprecipitation ('ChIP') with DNA microarray ("chip"). Like regular ChIP, ChIP-on-chip is used to investigate interactions between proteins and DNA in vivo. Specifically, it allows the identification of the cistrome, the sum of binding sites, for DNA-binding proteins on a genome-wide basis. Whole-genome analysis can be performed to determine the locations of binding sites for almost any protein of interest. As the name of the technique suggests, such proteins are generally those operating in the context of chromatin. The most prominent representatives of this class are transcription factors, replication-related proteins, like origin recognition complex protein (ORC), histones, their variants, and histone modifications.
XLDB is a yearly conference about databases, data management and analytics. The definition of extremely large refers to data sets that are too big in terms of volume, and/or velocity, and/or variety to be handled using conventional solutions. This conference deals with the high-end of very large databases (VLDB). It was conceived and it is chaired by Jacek Becla.

Anant Agarwal is an Indian computer architecture researcher. He is a professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), where he led the development of Alewife, an early cache coherent multiprocessor, and also has served as director of the MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory. He is the founder and CTO of Tilera, a fabless semiconductor company focusing on scalable multicore embedded processor design. He also serves as the CEO of edX, a joint partnership between MIT and Harvard University that offers free online learning.

Tiling arrays are a subtype of microarray chips. Like traditional microarrays, they function by hybridizing labeled DNA or RNA target molecules to probes fixed onto a solid surface.
In computer science, fringe search is a graph search algorithm that finds the least-cost path from a given initial node to one goal node.
HOTHEAD is an Arabidopsis thaliana gene that encodes a flavin adenine dinucleotide-containing oxidoreductase. This gene has a role in the creation of the carpel during the formation of flowers through the fusion of epidermal cells. Observations of reversion of the hothead phenotype and genotype led to the suggestion that the plants were able to "remember" the sequences of genes present in their ancestors, possibly through a cache of complementary RNA. This report attracted broad attention, and alternative explanations were suggested. Later research suggested that the supposed reversion phenomenon was due to the plants having a pronounced bias towards outcrossing, rather than self-fertilizing at high rates, as is typical for A. thaliana.
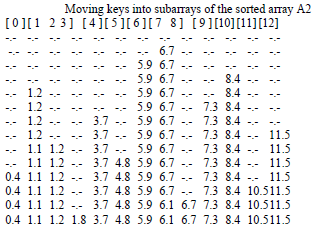
ProxmapSort, or Proxmap sort, is a sorting algorithm that works by partitioning an array of data items, or keys, into a number of "subarrays". The name is short for computing a "proximity map," which indicates for each key K the beginning of a subarray where K will reside in the final sorted order. Keys are placed into each subarray using insertion sort. If keys are "well distributed" among the subarrays, sorting occurs in linear time. The computational complexity estimates involve the number of subarrays and the proximity mapping function, the "map key," used. It is a form of bucket and radix sort.

rasdaman is an Array DBMS, that is: a Database Management System which adds capabilities for storage and retrieval of massive multi-dimensional arrays, such as sensor, image, simulation, and statistics data. A frequently used synonym to arrays is raster data, such as in 2-D raster graphics; this actually has motivated the name rasdaman. However, rasdaman has no limitation in the number of dimensions - it can serve, for example, 1-D measurement data, 2-D satellite imagery, 3-D x/y/t image time series and x/y/z exploration data, 4-D ocean and climate data, and even beyond spatio-temporal dimensions.

An array database management system or array DBMS provides database services specifically for arrays, that is: homogeneous collections of data items, sitting on a regular grid of one, two, or more dimensions. Often arrays are used to represent sensor, simulation, image, or statistics data. Such arrays tend to be Big Data, with single objects frequently ranging into Terabyte and soon Petabyte sizes; for example, today's earth and space observation archives typically grow by Terabytes a day. Array databases aim at offering flexible, scalable storage and retrieval on this information category.
LUX or Phytoclock1 (PCL1) is a gene that codes for LUX ARRHYTHMO, a protein necessary for circadian rhythms in Arabidopsis thaliana. LUX protein associates with Early Flowering 3 (ELF3) and Early Flowering 4 (ELF4) to form the Evening Complex (EC), a core component of the Arabidopsis repressilator model of the plant circadian clock. The LUX protein functions as a transcription factor that negatively regulates Pseudo-Response Regulator 9 (PRR9), a core gene of the Midday Complex, another component of the Arabidopsis repressilator model. LUX is also associated with circadian control of hypocotyl growth factor genes PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 4 (PIF4) and PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTOR 5 (PIF5).











