
Alexandria is the second largest city in Egypt and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile River delta. Founded in c. 331 BC by Alexander the Great, Alexandria grew rapidly and became a major centre of Hellenic civilization, eventually replacing Memphis, in present-day Greater Cairo, as Egypt's capital. Called the "Bride of the Mediterranean" internationally, Alexandria is a popular tourist destination and an important industrial centre due to its natural gas and oil pipelines from Suez.

Cairo is the capital of Egypt and the city-state Cairo Governorate, and is the country's largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metropolitan area is the 12th-largest in the world by population with a population of over 22.1 million.

The Great Pyramid of Giza is the largest Egyptian pyramid and served as the tomb of pharaoh Khufu, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom. Built in the early 26th century BC, over a period of about 27 years, the pyramid is the oldest of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, and the only wonder that has remained largely intact. It is the most famous monument of the Giza pyramid complex, which is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Memphis and its Necropolis". It is situated at the northern end of the line of the three pyramids at Giza.

The Nile is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer. Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About 6,650 km (4,130 mi) long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt, Sudan and South Sudan. Additionally, the Nile is an important economic river, supporting agriculture and fishing.

The Red Sea is a seawater inlet of the Indian Ocean, lying between Africa and Asia. Its connection to the ocean is in the south, through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait and the Gulf of Aden. To its north lie the Sinai Peninsula, the Gulf of Aqaba, and the Gulf of Suez. It is underlain by the Red Sea Rift, which is part of the Great Rift Valley.

The Rosetta Stone is a stele of granodiorite inscribed with three versions of a decree issued in Memphis, Egypt, in 196 BC during the Ptolemaic dynasty on behalf of King Ptolemy V Epiphanes. The top and middle texts are in Ancient Egyptian using hieroglyphic and Demotic scripts, respectively, while the bottom is in Ancient Greek. The decree has only minor differences between the three versions, making the Rosetta Stone key to deciphering the Egyptian scripts.

The Fatimid Caliphate was a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD under the rule of the Fatimids, an Isma'ili Shi'a dynasty. Spanning a large area of North Africa and West Asia, it ranged from the western Mediterranean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids trace their ancestry to the Islamic prophet Muhammad's daughter Fatima and her husband, ‘Ali ibn Abi Talib, the first Shi‘a imam. The Fatimids were acknowledged as the rightful imams by different Isma‘ili communities as well as by denominations in many other Muslim lands and adjacent regions. Originating during the Abbasid Caliphate, the Fatimids conquered Ifriqiya and established the city of al-Mahdiyya. The Fatimid dynasty ruled territories across the Mediterranean coast and ultimately made Egypt the center of the caliphate. At its height, the caliphate included—in addition to Egypt—varying areas of the Maghreb, Sicily, the Levant, and the Hejaz.

Mamluk were non-Arab, ethnically diverse enslaved mercenaries, slave-soldiers, and freed slaves who were assigned high-ranking military and administrative duties, serving the ruling Arab and Ottoman dynasties in the Muslim world.

Luxor is a city in Upper Egypt, which includes the site of the Ancient Egyptian city of Thebes. Luxor had a population of 1,333,309 in 2020, with an area of approximately 417 km2 (161 sq mi) and is the capital of the Luxor Governorate. It is among the oldest inhabited cities in the world.

Port Said is a city that lies in northeast Egypt extending about 30 km (19 mi) along the coast of the Mediterranean Sea, straddling the west bank of the northern mouth of the Suez Canal. It forms the majority of the Port Said governorate, where its seven districts comprise seven of the governorate's eight regions. The city was established in 1859 during the building of the Suez Canal, and at the beginning of 2023 had a population of 680,375 people.

The Ayyubid dynasty, also known as the Ayyubid Sultanate, was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurdish origin, Saladin had originally served the Zengid ruler Nur ad-Din, leading Nur ad-Din's army in battle against the Crusaders in Fatimid Egypt, where he was made Vizier. Following Nur ad-Din's death, Saladin was proclaimed as the first Sultan of Egypt by the Abbasid Caliphate, and rapidly expanded the new sultanate beyond the frontiers of Egypt to encompass most of the Levant, in addition to Hijaz, Yemen, northern Nubia, Tarabulus, Cyrenaica, southern Anatolia, and northern Iraq, the homeland of his Kurdish family. By virtue of his sultanate including Hijaz, the location of the Islamic holy cities of Mecca and Medina, he was the first ruler to be hailed as the Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques, a title that would be held by all subsequent sultans of Egypt until the Ottoman conquest of 1517. Saladin's military campaigns in the first decade of his rule, aimed at uniting the various Arab and Muslim states in the region against the Crusaders, set the general borders and sphere of influence of the sultanate of Egypt for the almost three and a half centuries of its existence. Most of the Crusader states, including the Kingdom of Jerusalem, fell to Saladin after his victory at the Battle of Hattin in 1187. However, the Crusaders reconquered the coast of Palestine in the 1190s.

Egyptian Arabic, locally known as Colloquial Egyptian, or simply Masri (مَصرى), is the most widely spoken vernacular Arabic dialect in Egypt. It is part of the Afro-Asiatic language family, and originated in the Nile Delta in Lower Egypt. The estimated 100 million Egyptians speak a continuum of dialects, among which Cairene is the most prominent. It is also understood across most of the Arabic-speaking countries due to broad Egyptian influence in the region, including through Egyptian cinema and Egyptian music. These factors help to make it the most widely spoken and by far the most widely studied variety of Arabic.

Fustat, also Fostat, was the first capital of Egypt under Muslim rule, and the historical centre of modern Cairo. It was built adjacent to what is now known as Old Cairo by the Rashidun Muslim general 'Amr ibn al-'As immediately after the Muslim conquest of Egypt in AD 641, and featured the Mosque of Amr, the first mosque built in Egypt.

Abū Tamīm Maʿad al-Mustanṣir biʾllāh was the eighth Fatimid Caliph from 1036 until 1094. He was one of the longest reigning Muslim rulers. His reign was the twilight of the Fatimid state. The start of his reign saw the continuation of competent administrators running the Fatamid state, overseeing the state's prosperity in the first two decades of al-Mustansir's reign. However, the break out of court infighting between the Turkish and Berber/Sudanese court factions following al-Yazuri's assassination, coinciding with natural disasters in Egypt and the gradual loss of administrative control over Fatamid possessions outside of Egypt, almost resulted in the total collapse of the Fatamid state in the 1060s, before the appointment of the Armenian general Badr al-Jamali, who assumed power as vizier in 1073, and became the de facto dictator of the country under the nominal rule of al-Mustansir.

Shajar al-Durr, also Shajarat al-Durr, whose royal name was al-Malika ʿAṣmat ad-Dīn ʾUmm-Khalīl Shajar ad-Durr, was a ruler of Egypt. She was the wife of As-Salih Ayyub, and later of Izz al-Din Aybak, the first sultan of the Mamluk Bahri dynasty. Prior to becoming Ayyub's wife, she was a child slave and Ayyub's concubine.

The General Intelligence Service, often referred to as the Mukhabarat is an Egyptian intelligence agency responsible for providing national security intelligence, both domestically and internationally. The GIS is part of the Egyptian intelligence community, together with the Office of Military Intelligence Services and Reconnaissance and National Security Agency.

Al Masry Sporting Club is an Egyptian sports club based in Port Said, Egypt. The club is mainly known for its professional football team, that competes in the Egyptian Premier League, the highest division of the Egyptian football league system.

Egypt, officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and the Sinai Peninsula in the southwest corner of Asia. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world, and the third-most populated in Africa, behind Nigeria and Ethiopia.
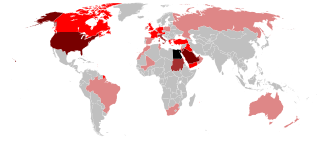
Egyptians are an ethnic group originating in the Nile Valley in Egypt. Egyptian identity is closely tied to geography. The population is concentrated in the Nile Valley, a small strip of cultivable land stretching from the First Cataract to the Mediterranean and enclosed by desert both to the east and to the west. This unique geography has been the basis of the development of Egyptian society since antiquity.

Muhammad Ali was the Ottoman Albanian governor and de facto ruler of Egypt from 1805 to 1848, considered the founder of modern Egypt. At the height of his rule, he controlled Egypt, Sudan, Hejaz, Najd, the Levant, Crete and parts of Greece.