Organization
The trade zone is promoted by the Atlantic Institute for Market Studies in Halifax, Nova Scotia, with U.S. representatives in Bangor, Maine.
Atlantica has also been promoted by the Atlantic Growth Network, also based in Halifax, with the support of the Atlantic Canada Opportunities Agency, which sponsored a 2002 conference.
A conference on these issues was held at Saint John, New Brunswick June 8–10, 2006. Another conference was held in Halifax, Nova Scotia June 11–16, 2007.
This effort has also been supported by the Atlantic Provinces Chamber of Commerce and Vermont Economic Development. A trade and networking conference was held October 4–6, 2008, in Stowe, Vermont at Smugglers Notch resort as part of the RTC Congress Conference.
Regional justification
The boundaries defined by the Atlantic Institute for Market Studies broadly echo the Atlantic Northeast, incorporating Upstate New York roughly north of I-90 (or the Erie Canal), Vermont, New Hampshire, Maine, New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Prince Edward Island, the island of Newfoundland, and Quebec on the south shore of the Saint Lawrence Seaway. The inclusion of Labrador, and thus the entirety of Newfoundland and Labrador, is unsettled. Some organization maps also include the region of Quebec directly south of Labrador, but this has not been elaborated on.
The proponents of Atlantica believe this region has common geography, demographics, economics, and environment. In particular, proponents believe that the region has seen declining political influence in both countries, and would do well to pool its resources.
Supporters believe that state, provincial, and international borders, as well as tariffs and regulatory differences, disrupt the economic potential of the region, and that a common strategy would maximize the region's opportunities in the globalization era. The goal of the institute seems to be further reduction of tariff and regulatory barriers under NAFTA and development of cross-border infrastructure to facilitate shipping. The benefit to New England is access to the port of Halifax, while the benefit to the Atlantic provinces is direct overland access to U.S. markets.
Opposition
Opponents of the nascent Atlantica project see it having a neo-liberal agenda that would harm worker pay and rights, benefit corporations at the expense of consumers, and undermine social services through reduced taxation. Protesters were seen at the June 2006 conference , and large-scale demonstrations occurred in Halifax, Nova Scotia from June 14–16 in opposition to the accord. One of these protests turned into a small scale riot, when the Black Bloc, which included perhaps 150 protesters, moved off the planned route and ran towards the business district of Spring Garden Road, likely planning to attack or demonstrate outside the many outlets of large corporations there. Police cars and buildings were pelted with rocks and water balloons filled with paint, but police quickly quelled most of the violence. Three people were seriously injured. Twenty protesters were arrested and were released on bail after the conference ended.
Additional protests have been held with concerns over the proposed privately funded $1 Billion super-highway planned to cut across New Brunswick and Maine with corridors into Vermont and northern New Hampshire.

The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces or the Canadian Maritimes, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island (PEI). The Maritimes had a population of 1,813,606 in 2016. Together with Canada's easternmost province, Newfoundland and Labrador, the Maritime provinces make up the region of Atlantic Canada.
Land Force Atlantic Area (LFAA) was a formation responsible for Canadian Army operations in the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick, Newfoundland and Labrador, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. LFAA is headquartered at Canadian Forces Base Halifax. The command was formed in 1992 and renamed in 2013 to become the 5th Canadian Division.

The Canadian Federation of Engineering Students (CFES) is the national association of undergraduate engineering student societies in Canada and exists to organize activities, provide services and interact with professional and other bodies at the national and international level for the benefit of Canadian engineering students. The organization is a bilingual non-profit corporation based in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada, managed by a volunteer team of engineering students and recent graduates from across Canada.

The Intercolonial Railway of Canada, also referred to as the Intercolonial Railway (ICR), was a historic Canadian railway that operated from 1872 to 1918, when it became part of Canadian National Railways. As the railway was also completely owned and controlled by the federal government, the Intercolonial was also one of Canada's first Crown corporations.

Marine Atlantic Inc. is an independent Canadian federal Crown corporation which is mandated to operate ferry services between the provinces of Newfoundland and Labrador and Nova Scotia.

The Atlantic Time Zone is a geographical region that keeps standard time—called Atlantic Standard Time (AST)—by subtracting four hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), resulting in UTC−04:00. During part of the year, some portions of the zone observe daylight saving time, referred to as Atlantic Daylight Time (ADT), by moving their clocks forward one hour to result in UTC−03:00. The clock time in this zone is based on the mean solar time of the 60th meridian west of the Greenwich Observatory.
The Atlantic Canada Opportunities Agency is the Government of Canada's agency responsible for helping to create opportunities for economic growth in the Atlantic Provinces by working with the people of the region. Planned spending for 2015-2016 consisted of 171 million dollars for enterprise development, 89 million dollars for community development, 25 million dollars for internal services and 11 million dollars for policy, advocacy and coordination.

Eastern Provincial Airways, also known as EPA, was the backbone of air travel in the eastern atlantic provinces of Canada in the 1970s. At its peak, the carrier operated jet service with Boeing 737-200 aircraft connecting many communities that today only have scheduled passenger flights provided by 18-seat commuter turboprop aircraft. The airline traces its history from Maritime Central Airways (MCA) from 1961. It merged with CP Air to form Canadian Pacific Airlines in 1986.

Maritime Union is a proposed political union of the three Maritime provinces of Canada – New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island – to form a single new province. This vision has sometimes been expanded to a proposed Atlantic Union, which would also include the province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
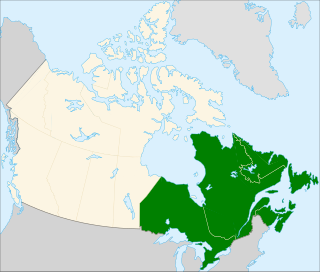
Eastern Canada is generally considered to be the region of Canada east of Manitoba, consisting of the following provinces:
The European and North American Railway (E&NA) is the name for three historic Canadian and American railways which were built in New Brunswick and Maine.

UTC−04:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of −04:00. It is observed in the Eastern Time Zone during the warm months of daylight saving time, as Eastern Daylight Time. The Atlantic Time Zone observes it during standard time . It is observed all year in the Eastern Caribbean.

The Atlantic Northeast is a region of North America which includes the U.S. states of Connecticut, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, New Hampshire, Vermont, and Maine, and the Canadian provinces of Québec, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland and Labrador.

New Brunswick, is one of the three Maritime provinces in Canada, and the only officially bilingual province (English-French) in the country. The history of New Brunswick can be viewed according to four periods: pre-European contact, French colonization, British colonization and finally, New Brunswick since Confederation.

The New England Governors and Eastern Canadian Premiers (NEG-ECP) Climate Change Action Plan 2001 is a resolution adopted on August 28, 2001, by the New England Governors and the Eastern Canadian Premiers. The resolution calls for a reduction in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions to 1990 levels by 2010, at least 10% below 1990 levels by 2020, 35-45% below 1990 levels by 2030, and a 75-85% reduction of 2001 levels by 2050.

Western Local Escort Force (WLEF) referred to the organization of anti-submarine escorts for World War II trade convoys from North American port cities to the Western Ocean Meeting Point near Newfoundland where ships of the Mid-Ocean Escort Force (MOEF) assumed responsibility for safely delivering the convoys to the British Isles.

The East Coast Music Association is a non-profit association that hosts an annual awards ceremony based in Atlantic Canada for music appreciation on the East Coast of Canada. Since its beginning in 1989 when it was launched as the Maritime Music Awards by Halifax music industry promoter Rob Cohn, it has grown from the original five categories to over 40 categories for artist, industry and honorary awards.
Fibe is the brand name used by Bell Aliant for its suite of fiber to the home (FTTH) unified communication services, including Internet access, IPTV, and home telephone service, available in much of Atlantic Canada and previously in some regions of Ontario and Quebec. The Fibe service covers an entire urban area with a fibre optic network.

The New England Governors and Eastern Canadian Premiers' Annual Conference is an annual international meeting of the American governors of the six New England states of Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont as well as the Canadian premiers of Quebec, Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland and Labrador. According to the Council of Atlantic Premiers, the meeting is meant to "advance the interests" of the states and provinces as well as to encourage "cooperation" built on the "historic ties" between them The first conference was held in 1973. In 2014, the 38th annual conference was held at Bretton Woods in northern New Hampshire.

McInnes Cooper is a full-service Canadian law firm with nearly 200 lawyers. It is centrally located in Atlantic Canada, with offices in Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland and Labrador.















