
The Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party (DFL) is the Minnesota affiliate of the U.S. Democratic Party. As of 2023, it controls four of Minnesota's eight U.S. House seats, both of its U.S. Senate seats, the Minnesota House of Representatives and Senate, and all other statewide offices, including the governorship, making it the dominant party in the state.

The governor of Minnesota is the head of government of the U.S. state of Minnesota, leading the state's executive branch. Forty people have been governor of Minnesota, though historically there were also three governors of Minnesota Territory. Alexander Ramsey, the first territorial governor, also served as state governor several years later. State governors are elected to office by popular vote, but territorial governors were appointed to the office by the United States president. The current governor of Minnesota is Tim Walz of the Democratic-Farmer-Labor Party (DFL).

The Minnesota Legislature is the bicameral legislature of the U.S. state of Minnesota consisting of two houses: the Senate and the House of Representatives. Senators are elected from 67 single-member districts. In order to account for decennial redistricting, members run for one two-year term and two four-year terms each decade. They are elected for four-year terms in years ending in 2 and 6, and for two-year terms in years ending in 0. Representatives are elected for two-year terms from 134 single-member districts formed by dividing the 67 senate districts in half.

The lieutenant governor of Minnesota is a constitutional officer in the executive branch of the U.S. state of Minnesota. Fifty individuals have held the office of lieutenant governor since statehood. The incumbent is Peggy Flanagan, a DFLer and the first Native American elected to a statewide executive office in Minnesota's history.

The 2006 Minnesota gubernatorial election took place on November 7, 2006. Incumbent Tim Pawlenty was endorsed by the state Republican convention on June 2, 2006, while the state Democratic–Farmer–Labor convention endorsed Mike Hatch on June 10, 2006. The party primaries took place on September 12, 2006, with Hatch defeating DFL challengers Becky Lourey and Ole Savior and incumbent Pawlenty defeating Sue Jeffers. In the November 7 general election, Pawlenty received a plurality of the votes, defeating Hatch by a margin of 1%. As a result, this election was the closest race of the 2006 gubernatorial election cycle.

John J. Marty is a member of the Minnesota Senate, representing District 40, which includes parts of Ramsey County in the northern Twin Cities metropolitan area. As a young state senator, he ran for governor of Minnesota in 1994. He won the DFL nomination and the Democratic primary but lost the general election to the incumbent governor, Arne Carlson. Marty ran for governor again in 2010, but withdrew from the race after failing to win his party's endorsement.

The secretary of state of Minnesota is a constitutional officer in the executive branch of government of the U.S. state of Minnesota. Twenty-two individuals have held the office of secretary of state since statehood. The incumbent is Steve Simon, a DFLer.

The state auditor of Minnesota is a constitutional officer in the executive branch of the U.S. state of Minnesota. Nineteen individuals have held the office of state auditor since statehood. The incumbent is Julie Blaha, a DFLer.

The state treasurer of Minnesota was a constitutional officer in the executive branch of the U.S. state of Minnesota. Twenty-six individuals occupied the office of state treasurer from 1858 until the office's abolition in 2003. The final state treasurer was Carol C. Johnson, a DFLer.

Minnesota is known for a politically active citizenry, with populism being a longstanding force among the state's political parties. Minnesota has consistently high voter turnout; in the 2008 U.S. presidential election, 77.8% of eligible Minnesotans voted – the highest percentage of any U.S. state or territory – versus the national average of 61.7%. This was due in part to its same day voter registration laws; previously unregistered voters can register on election day, at their polls, with evidence of residency.

John Lesch is a Minnesota politician and former member of the Minnesota House of Representatives. A member of the Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party (DFL), he last represented 66B, which included portions of Saint Paul in Ramsey County, in the Twin Cities metropolitan area. He is a prosecuting attorney for Saint Paul.

The 2010 Minnesota Attorney General election was held on Tuesday, November 2, 2010, to elect the Minnesota Attorney General for a four-year term. Primary elections were held on August 10, 2010. Incumbent Lori Swanson of the Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party (DFL) won reelection to a second term.

Ken Martin is an American political figure from Minnesota. He is currently Chairman of the Minnesota Democratic-Farmer-Labor (DFL) Party, President of the Association of State Democratic Committees, and a Vice Chair of the Democratic National Committee.

Raymond Howard Dehn is a Minnesota politician and community organizer who served in the Minnesota House of Representatives. A member of the Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party (DFL), he last represented District 59B in Minneapolis. He was a candidate for mayor of Minneapolis in 2017.

A general election was held in the U.S. state of Minnesota on November 4, 2014. All of Minnesota's executive officers were up for election as well as all the seats in the Minnesota House of Representatives, several state judicial seats, a United States Senate seat, all of Minnesota's eight seats in the United States House of Representatives, and several seats for local offices. A primary election was held on August 12, 2014, to nominate major political party candidates for partisan offices and candidates for nonpartisan offices.

The 2014 Minnesota Attorney General election was held on November 4, 2014, to elect the Minnesota Attorney General.

The 2006 Minnesota Attorney General election was held on Tuesday, November 7, 2006 to elect the Minnesota Attorney General for a four-year term. DFL incumbent Mike Hatch chose to run for governor instead of reelection. Lori Swanson of the Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party (DFL) won election to her first term.
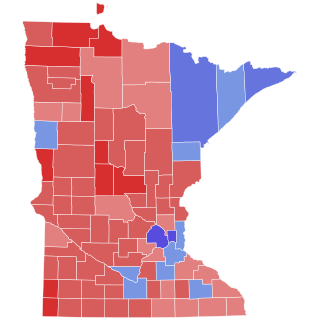
The 2022 Minnesota Secretary of State election was held on November 8, 2022, to elect the Secretary of State of Minnesota. Incumbent DFLer Steve Simon won re-election to a third term.

The 2022 Minnesota State Auditor election was held on November 8, 2022, to elect the state auditor of the U.S. state of Minnesota. Incumbent DFLer Julie Blaha won re-election to a second term.







































