
Mining is the extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agricultural processes, or feasibly created artificially in a laboratory or factory. Ores recovered by mining include metals, coal, oil shale, gemstones, limestone, chalk, dimension stone, rock salt, potash, gravel, and clay. The ore must be a rock or mineral that contains valuable constituent, can be extracted or mined and sold for profit. Mining in a wider sense includes extraction of any non-renewable resource such as petroleum, natural gas, or even water.

A slurry pipeline is a specially engineered pipeline used to move ores, such as coal or iron, or mining waste, called tailings, over long distances. A mixture of the ore concentrate and water, called slurry, is pumped to its destination and the water is filtered out. Due to the abrasive properties of slurry, the pipelines can be lined with high-density polyethylene (HDPE), or manufactured completely from HDPE Pipe, although this requires a very thick pipe wall. Slurry pipelines are used as an alternative to railroad transportation when mines are located in remote, inaccessible areas.

The Athabasca oil sands, also known as the Athabasca tar sands, are large deposits of bitumen, a heavy and viscous form of petroleum, located in northeastern Alberta, Canada. These reserves are one of the largest sources of unconventional oil in the world, making Canada a significant player in the global energy market.
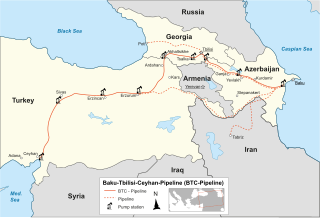
The Baku–Tbilisi–Ceyhan (BTC) pipeline is a 1,768 kilometres (1,099 mi) long crude oil pipeline from the Azeri–Chirag–Gunashli oil field in the Caspian Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. It connects Baku, the capital of Azerbaijan and Ceyhan, a port on the south-eastern Mediterranean coast of Turkey, via Tbilisi, the capital of Georgia. It is the second-longest oil pipeline in the former Soviet Union, after the Druzhba pipeline. The first oil that was pumped from the Baku end of the pipeline reached Ceyhan on 28 May 2006.

Teck Resources Limited, known as Teck Cominco until late 2008, is a diversified natural resources company headquartered in Vancouver, British Columbia, that is engaged in mining and mineral development, including coal for the steelmaking industry, copper, zinc, and energy. Secondary products include lead, silver, gold, molybdenum, germanium, indium and cadmium. Teck Resources was formed from the amalgamation of Teck and Cominco in 2001.
Fluor Corporation is an American multinational engineering and construction firm, headquartered in Irving, Texas. It is a holding company that provides services through its subsidiaries in three main areas: oil and gas, industrial and infrastructure, government and power. It is the largest publicly traded engineering and construction company in the Fortune 500 rankings and is listed as 259th overall.

Worley Limited is an Australian engineering professional services company which provides project delivery and consulting services to the resources and energy sectors, and complex process industries.

The Kearl Oil Sands Project is an oil sands mine in the Athabasca Oil Sands region at the Kearl Lake area, about 70 kilometres (43 mi) north of Fort McMurray in Alberta, Canada that is operated by the 143-year old Calgary, Alberta-headquartered Imperial Oil Limited—one of the largest integrated oil companies in Canada. Kearl is owned by Imperial Oil and is controlled by Imperial's parent company, ExxonMobil—an American multinational that is one of the largest in the world.

Mitsui & Co., Ltd. is one of the largest sogo shosha in Japan; it is part of the Mitsui Group.

China Minmetals Corporation is a Chinese metals and mineral trading company headquartered in Beijing. It is a state-owned corporation under direct supervision of the State-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission (SASAC). China Minmetals is engaged in the production and trading of metals and minerals, including copper, aluminum, tungsten, tin, antimony, lead, zinc, and nickel.
Xtract Resources plc is a diversified metals and minerals producer based in London, United Kingdom. The company's shares are traded on London Stock Exchange Alternative Investment Market. Its CEO is Colin Bird. The primary focus of the company is gold and copper exploration and mining. The company's main assets are located in Chile, Mozambique, and South Africa.

ALTEN is a French multinational engineering and technology consulting company founded in 1988, it has offices in 30 countries. ALTEN's stock is listed in compartment B of the Euronext Paris market ; it is part of the SBF 120, the IT CAC 50 index and MIDCAP 100, and is eligible for the Deferred Settlement Service (SRD).

Although there are numerous oil companies operating in Canada, as of 2009, the majority of production, refining and marketing was done by fewer than 20 of them. According to the 2013 edition of Forbes Global 2000, canoils.com and any other list that emphasizes market capitalization and revenue when sizing up companies, as of March 31, 2014 these are the largest Canada-based oil and gas companies.

Mineral industry of Colombia refers to the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials in Colombia. Colombia is well-endowed with minerals and energy resources. It has the largest coal reserves in Latin America, and is second to Brazil in hydroelectric potential. Estimates of petroleum reserves in 1995 were 3.1 billion barrels (490,000,000 m3). Colombia also possesses significant amounts of nickel and gold. Other important metals included platinum and silver, which were extracted in much smaller quantities. Colombia also produces copper, small amounts of iron ore, and bauxite. Nonmetallic mined minerals include salt, limestone, sulfur, gypsum, dolomite, barite, feldspar, clay, magnetite, mica, talcum, and marble. Colombia also produces most of the world's emeralds. Despite the variety of minerals available for exploitation, Colombia still had to import substances such as iron, copper, and aluminum to meet its industrial needs.
Equinox Minerals is a mining and exploration company with corporate offices in Perth, Australia and Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It has operations in Peru and Australia. In Zambia it owned the Lumwana Mining Company, but that was bought by Barrick Gold in 2011. Through Liontown Resources Limited and Alturas Minerals Corp., the company has gold and copper-gold exploration interests in Peru and Australia. The Lumwana project which had enough reserves to be productive for 37 years, cost the company one billion dollars to develop. In Zambia it has been credited with supporting social development through projects which aim to build schools, attract professionals to areas around its mine sites. 2010 copper production was 323.4 million pounds 68% higher than in 2009.
Pembina Pipeline is a Canadian corporation that operates transportation and storage infrastructure delivering oil and natural gas to and from parts of Western Canada ; there is also a natural gas processing business that takes place at the Cutbank Complex. Western Canada is the source of all the product transported by its systems. Some of the pipelines and facilities have short term contracts with oil producers while others are long term. For 37 years until 1997 when it went public and established itself as a trust, Pembina was a regular privately owned business. On October 1, 2010 it converted to a corporation from a trust, changing its official name from Pembina Pipeline Income Fund to Pembina Pipeline Corporation. As of 2016 the company had more than 1260 employees, up from 427 in 2010. The company's total assets nearly doubled in 2017.

Canadian Natural Resources Limited, or CNRL or Canadian Natural is a senior Canadian oil and natural gas company that operates primarily in the Western Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba, with offshore operations in the United Kingdom sector of the North Sea, and offshore Côte d'Ivoire and Gabon. The company, which is headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, has the largest undeveloped base in the Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin. It is the largest independent producer of natural gas in Western Canada and the largest producer of heavy crude oil in Canada.

Alberta Clipper is an oil pipeline in North America. It is owned and operated by Enbridge and is part of the extensive Enbridge Pipeline System. The pipeline runs from Hardisty, Alberta, in Canada, to Superior, Wisconsin, in the United States, integrating the company's Canadian oil sands pipeline system with the Lakehead system in the United States.
Detailed engineering are studies which creates a full definition of every aspect of a project development. It includes all the studies to be performed before project construction starts. Detail engineering studies are a key component for every project development across mining, infrastructure, energy, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and oil and gas sectors.
The Mining industry of Laos which has received prominent attention with foreign direct investments (FDI) has, since 2003–04, made significant contributions to the economic condition of Laos. More than 540 mineral deposits of gold, copper, zinc, lead and other minerals have been identified, explored and mined. During 2012, the mining and quarrying sector's contribution to GDP was around 7.0%; during this reporting year the FDI in the mineral sector was of the order of US$662.5 million out of a total trade of $4.7 billion in the country. Laos is now a member of the WTO.











