
Mabo v Queensland is a landmark decision of the High Court of Australia that recognised the existence of Native Title in Australia. It was brought by Eddie Mabo against the State of Queensland and decided on 3 June 1992. The case is notable for being the first in Australia to recognise pre-colonial land interests of Indigenous Australians within the common law of Australia.

Barbecue or barbeque is a term used with significant regional and national variations to describe various cooking methods that employ live fire and smoke to cook the food. The term is also generally applied to the devices associated with those methods, the broader cuisines that these methods produce, and the meals or gatherings at which this style of food is cooked and served. The cooking methods associated with barbecuing vary significantly but most involve outdoor cooking.

The Aboriginal Tent Embassy is a permanent protest occupation site as a focus for representing the political rights of Aboriginal Australians and Torres Strait Islander people. Established on 26 January 1972, and celebrating its 50th anniversary in 2022, it is the longest continuous protest for Indigenous land rights in the world.

Arnhem Land is a historical region of the Northern Territory of Australia. It is located in the north-eastern corner of the territory and is around 500 km (310 mi) from the territorial capital, Darwin. In 1623, Dutch East India Company captain Willem Joosten van Colster sailed into the Gulf of Carpentaria and Cape Arnhem is named after his ship, the Arnhem, which itself was named after the city of Arnhem in the Netherlands.

White Man's Burden is a 1995 American drama film about racism, set in an alternative America where the social and economic positions of black people and white people are reversed. The film was written and directed by Desmond Nakano. The film revolves around Louis Pinnock, a white factory worker, who kidnaps Thaddeus Thomas, a black factory owner, for firing Pinnock over a perceived slight.
Jandamarra or Tjandamurra, known to European settlers as Pigeon, was an Aboriginal Australian man of the Bunuba people who led one of many organised armed insurrections against the European colonisation of Australia. Initially employed as a tracker for the police, he became a fugitive when he was forced to capture his own people. He led a three-year campaign against police and European settlers, achieving legendary status for his hit and run tactics and his abilities to hide and disappear. Jandamarra was eventually killed by another tracker at Tunnel Creek on 1 April 1897. His body was buried by his family at the Napier Range, where it was placed inside a boab tree. Jandamarra's life has been the subject of two novels, Ion Idriess's Outlaws of the Leopold (1952) and Mudrooroo's Long Live Sandawarra (1972), a non-fiction account based on oral tradition, Jandamurra and the Bunuba Resistance, and a stage play.

Napranum is a remote town in the locality of Mission River in the Aboriginal Shire of Napranum, Queensland, Australia. At the 2016 census, the town of Napranum had a population of 950.

The history of Indigenous Australians began at least 65,000 years ago when humans first populated the Australian continental landmasses. This article covers the history of Aboriginal Australian and Torres Strait Islander peoples, two broadly defined groups which each include other sub-groups defined by language and culture.
Heartland, known as Burned Bridge in some countries, is an Australian television drama series that ran on ABC Television in 1994. It ran for 13 episodes and starred Cate Blanchett and Ernie Dingo, as well as a large number of Aboriginal Australian actors.
Indigenous Australians are people with familial heritage from, and/or recognised membership of, the various ethnic groups living within the territory of present day Australia prior to British colonisation. They consist of two distinct groups, which includes many ethnic groups: the Aboriginal Australians of the mainland and many islands, including Tasmania, and the Torres Strait Islanders of the seas between Queensland and Papua New Guinea, located in Melanesia. The term Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples or the person's specific cultural group, is often preferred, though the terms First Nations of Australia, First Peoples of Australia and First Australians are also increasingly common; 812,728 people self-identified as being of Aboriginal and/or Torres Strait Islander origin in the 2021 Australian Census, representing 3.2% of the total population of Australia. Of these Indigenous Australians, 91.4% identified as Aboriginal; 4.2% identified as Torres Strait Islander; while 4.4% identified with both groups. Since 1995, the Australian Aboriginal flag and the Torres Strait Islander flag have been official flags of Australia.
The National Black Theatre (NBT) was a theatre company run by a small group of Aboriginal people based in the Sydney suburb of Redfern which operated from 1972 to 1977. The original concept for the theatre grew out of political struggles, especially the land rights demonstrations, which at the time were being organised by the Black Moratorium Committee. The centre held workshops in modern dancing, tribal dancing, writing for theatre, karate and photography, and provided a venue for new Aboriginal drama. It also ran drama classes under Brian Syron, whose students included Jack Davis, Freddie Reynolds, Maureen Watson, Lillian Crombie, and Hyllus Maris.

Australian studies forms part of the academic field of cultural studies. It involves an examination of what constructs Australia's national identity. This area of scholarship traditionally involves the study of Australian history, society and culture but can be extended to the study of Australian politics and economics. This area of scholarship also includes the study of Australia's Indigenous population, Aboriginals and Torres Strait Islanders.

Robert Lewis Maza, known as Bob Maza, was an Aboriginal Australian actor, playwright and activist.

The Australian frontier wars were the violent conflicts between Indigenous Australians and primarily British settlers during the colonial period of Australia.
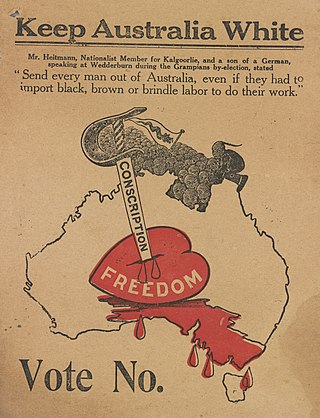
Racism in Australia comprises negative attitudes and views on race or ethnicity which are held by various people and groups in Australia, and have been reflected in discriminatory laws, practices and actions at various times in the history of Australia against racial or ethnic groups.

Jack Charles, also known as Uncle Jack Charles, was an Australian stage and screen actor and activist, known for his advocacy for Aboriginal people. He was involved in establishing the first Indigenous theatre in Australia, co-founding Nindethana Theatre with Bob Maza in Melbourne in 1971. His film credits include the Australian film The Chant of Jimmie Blacksmith (1978), among others, and more recently appeared in TV series Cleverman (2016) and Preppers (2021).

Our Generation is a 2010 Australian documentary film about the struggle of Aboriginal Australians in the Northern Territory to retain their land, culture and freedom.

Indigenous Australian literature is the fiction, plays, poems, essays and other works authored by Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people of Australia.

Noughts + Crosses is a British drama television series based on the Noughts & Crosses novel series by Malorie Blackman. The series is set in an alternative history where black "Cross" people rule over white "Noughts". The first episode aired on BBC One on 5 March 2020, and the remaining episodes premiered on BBC iPlayer on the same day. In May 2021, the BBC announced that a second series had been commissioned.
Qallunaat! Why White People Are Funny is a 2006 satirical documentary film directed by Mark Sandiford and Zebedee Nungak. The documentary-style film reverses the roles between White Canadians and the Inuit of Northern Canada, highlighting the nature of the treatment of the Inuit by White Canadian society.













