
Bacillus is a genus of Gram-positive, rod-shaped bacteria, a member of the phylum Bacillota, with 266 named species. The term is also used to describe the shape (rod) of other so-shaped bacteria; and the plural Bacilli is the name of the class of bacteria to which this genus belongs. Bacillus species can be either obligate aerobes which are dependent on oxygen, or facultative anaerobes which can survive in the absence of oxygen. Cultured Bacillus species test positive for the enzyme catalase if oxygen has been used or is present.

An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form, but it is not a true spore. It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce itself. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries. There are many reports of spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been claimed. There is one report of viable spores of Bacillus marismortui in salt crystals approximately 250 million years old. When the environment becomes more favorable, the endospore can reactivate itself into a vegetative state. Most types of bacteria cannot change to the endospore form. Examples of bacterial species that can form endospores include Bacillus cereus, Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus thuringiensis, Clostridium botulinum, and Clostridium tetani.

Clostridium is a genus of anaerobic, Gram-positive bacterium. Species of Clostridium inhabit soils and the intestinal tract of animals, including humans. This genus includes several significant human pathogens, including the causative agents of botulism and tetanus. It also formerly included an important cause of diarrhea, Clostridioides difficile, which was reclassified into the Clostridioides genus in 2016.

Sterilization refers to any process that removes, kills, or deactivates all forms of life and other biological agents such as prions present in or on a specific surface, object, or fluid. Sterilization can be achieved through various means, including heat, chemicals, irradiation, high pressure, and filtration. Sterilization is distinct from disinfection, sanitization, and pasteurization, in that those methods reduce rather than eliminate all forms of life and biological agents present. After sterilization, an object is referred to as being sterile or aseptic.

A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than sterilization, which is an extreme physical or chemical process that kills all types of life. Disinfectants are generally distinguished from other antimicrobial agents such as antibiotics, which destroy microorganisms within the body, and antiseptics, which destroy microorganisms on living tissue. Disinfectants are also different from biocides—the latter are intended to destroy all forms of life, not just microorganisms. Disinfectants work by destroying the cell wall of microbes or interfering with their metabolism. It is also a form of decontamination, and can be defined as the process whereby physical or chemical methods are used to reduce the amount of pathogenic microorganisms on a surface.

Bacillus subtilis, known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants, humans and marine sponges. As a member of the genus Bacillus, B. subtilis is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. B. subtilis has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. B. subtilis is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies.

Planetary protection is a guiding principle in the design of an interplanetary mission, aiming to prevent biological contamination of both the target celestial body and the Earth in the case of sample-return missions. Planetary protection reflects both the unknown nature of the space environment and the desire of the scientific community to preserve the pristine nature of celestial bodies until they can be studied in detail.
Radioresistance is the level of ionizing radiation that organisms are able to withstand.
Bacillus safensis is a Gram-positive, spore-forming, and rod bacterium, originally isolated from a spacecraft in Florida and California. B. safensis could have possibly been transported to the planet Mars on spacecraft Opportunity and Spirit in 2004. There are several known strains of this bacterium, all of which belong to the Bacillota phylum of Bacteria. This bacterium also belongs to the large, pervasive genus Bacillus. B. safensis is an aerobic chemoheterotroph and is highly resistant to salt and UV radiation. B. safensis affects plant growth, since it is a powerful plant hormone producer, and it also acts as a plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, enhancing plant growth after root colonization. Strain B. safensis JPL-MERTA-8-2 is the only bacterial strain shown to grow noticeably faster in micro-gravity environments than on the Earth surface.
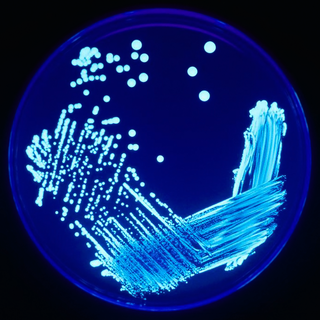
In microbiology, streaking is a technique used to isolate a pure strain from a single species of microorganism, often bacteria. Samples can then be taken from the resulting colonies and a microbiological culture can be grown on a new plate so that the organism can be identified, studied, or tested.
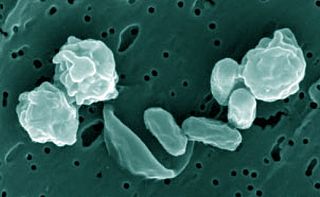
Bacillus odysseyi is a Gram-positive, aerobic, rod-shaped, round-spore- and endospore-forming eubacterium of the genus Bacillus. This novel species was discovered by scientist Myron T. La Duc of NASA’s Biotechnology and Planetary Protection Group, a unit whose purpose is to clean and sterilize spacecraft so as not to have microorganisms contaminate other celestial bodies or foreign microorganisms contaminate Earth, on the surface of the Mars Odyssey in a clean room at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in La Cañada Flintridge before the spacecraft was launched to space. La Duc named the bacterium Bacillus odysseyi sp. nov. after the Odyssey mission. It had apparently evolved to live in the sparse environment of a clean room, and its secondary spore coat makes it especially resistant to radiation.

EXPOSE is a multi-user facility mounted outside the International Space Station (ISS) dedicated to astrobiology. EXPOSE was developed by the European Space Agency (ESA) for long-term spaceflights and was designed to allow exposure of chemical and biological samples to outer space while recording data during exposure.
Moist heat sterilization describes sterilization techniques that use hot water vapor as a sterilizing agent. Heating an article is one of the earliest forms of sterilization practiced. The various procedures used to perform moist heat sterilization process cause destruction of micro-organisms by denaturation of macromolecules.

Bacillus subtilis is a rod-shaped, Gram-positive bacteria that is naturally found in soil and vegetation, and is known for its ability to form a small, tough, protective and metabolically dormant endospore. B. subtilis can divide symmetrically to make two daughter cells, or asymmetrically, producing a single endospore that is resistant to environmental factors such as heat, desiccation, radiation and chemical insult which can persist in the environment for long periods of time. The endospore is formed at times of nutritional stress, allowing the organism to persist in the environment until conditions become favourable. The process of endospore formation has profound morphological and physiological consequences: radical post-replicative remodelling of two progeny cells, accompanied eventually by cessation of metabolic activity in one daughter cell and death by lysis of the other.

The central sterile services department (CSSD), also called sterile processing department (SPD), sterile processing, central supply department (CSD), or central supply, is an integrated place in hospitals and other health care facilities that performs sterilization and other actions on medical devices, equipment and consumables; for subsequent use by health workers in the operating theatre of the hospital and also for other aseptic procedures, e.g. catheterization, wound stitching and bandaging in a medical, surgical, maternity or paediatric ward.

Exobiology Radiation Assembly (ERA) was an experiment that investigated the biological effects of space radiation. An astrobiology mission developed by the European Space Agency (ESA), it took place aboard the European Retrievable Carrier (EURECA), an unmanned 4.5 tonne satellite with a payload of 15 experiments.
Bacillus nealsonii is a species of bacteria first isolated from a spacecraft-assembly facility. Its spores are γ-radiation resistant. It is Gram-positive, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped and produces endospores. Its type strain is FO-92T.
Exposing Microorganisms in the Stratosphere (E-MIST) is a NASA study to determine if a specific microorganism could survive conditions like those on the planet Mars. The study transported Bacillus pumilus bacteria and their spores by helium-filled balloon to the stratosphere of Earth and monitored the ability of the microorganisms to survive in extreme Martian-like conditions such as low pressure, dryness, cold, and ionizing radiation.

The Philippine Nuclear Research Institute (PNRI) is a government agency under the Department of Science and Technology mandated to undertake research and development activities in the peaceful uses of nuclear energy, institute regulations on the said uses, and carry out the enforcement of said regulations to protect the health and safety of radiation workers and the general public.

The Phosphate (Pho) regulon is a regulatory mechanism used for the conservation and management of inorganic phosphate within the cell. It was first discovered in Escherichia coli as an operating system for the bacterial strain, and was later identified in other species. The Pho system is composed of various components including extracellular enzymes and transporters that are capable of phosphate assimilation in addition to extracting inorganic phosphate from organic sources. This is an essential process since phosphate plays an important role in cellular membranes, genetic expression, and metabolism within the cell. Under low nutrient availability, the Pho regulon helps the cell survive and thrive despite a depletion of phosphate within the environment. When this occurs, phosphate starvation-inducible (psi) genes activate other proteins that aid in the transport of inorganic phosphate.














