
Brentwood is a city in Williamson County, Tennessee, United States. The population was 45,373 as of the 2020 United States census. It is a suburb of Nashville and included in the Nashville metropolitan area.

The siege of Vicksburg was the final major military action in the Vicksburg campaign of the American Civil War. In a series of maneuvers, Union Major General Ulysses S. Grant and his Army of the Tennessee crossed the Mississippi River and drove the Confederate Army of Mississippi, led by Lieutenant General John C. Pemberton, into the defensive lines surrounding the fortress city of Vicksburg, Mississippi, leading to the successful siege and Confederate surrender.

The Battle of Fort Donelson was fought from February 11–16, 1862, in the Western Theater of the American Civil War. The Union capture of the Confederate fort near the Tennessee–Kentucky border opened the Cumberland River, an important avenue for the invasion of the South. The Union's success also elevated Brig. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant from an obscure and largely unproven leader to the rank of major general, and earned him the nickname of "Unconditional Surrender" Grant.

The Battle of Franklin was fought on November 30, 1864, in Franklin, Tennessee, as part of the Franklin–Nashville Campaign of the American Civil War. It was one of the worst disasters of the war for the Confederate States Army. Confederate Lieutenant General (LTG) John Bell Hood's Army of Tennessee conducted numerous frontal assaults against fortified positions occupied by the Union forces under Major General (MGEN) John Schofield and was unable to prevent Schofield from executing a planned, orderly withdrawal to Nashville.

The Battle of Nashville was a two-day battle in the Franklin-Nashville Campaign that represented the end of large-scale fighting west of the coastal states in the American Civil War. It was fought at Nashville, Tennessee, on December 15–16, 1864, between the Confederate Army of Tennessee under Lieutenant General John Bell Hood and the Union Army of the Cumberland (AoC) under Major General George H. Thomas. In one of the largest victories achieved by the Union Army during the war, Thomas attacked and routed Hood's army, largely destroying it as an effective fighting force.

The Battle of Harpers Ferry was fought September 12–15, 1862, as part of the Maryland Campaign of the American Civil War. As Confederate Army General Robert E. Lee's Confederate army invaded Maryland, a portion of his army under Major General Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson surrounded, bombarded, and captured the Union garrison at Harpers Ferry, Virginia.

The Tullahoma campaign was a military operation conducted from June 24 to July 3, 1863, by the Union Army of the Cumberland under Maj. Gen. William Rosecrans, and is regarded as one of the most brilliant maneuvers of the American Civil War. Its effect was to drive the Confederates out of Middle Tennessee and to threaten the strategic city of Chattanooga.
The First Battle of Murfreesboro was fought on July 13, 1862, in Rutherford County, Tennessee, as part of the American Civil War. Troops under Confederate cavalry commander Brig. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest surprised and quickly overran a Federal hospital, the camps of several small Union units, and the jail and courthouse in Murfreesboro, Tennessee. All of the Union units surrendered to Forrest, and the Confederates destroyed much of the Union's supplies and destroyed railroad track in the area. The primary consequence of the raid was the diversion of Union forces from a drive on Chattanooga.
The Third Battle of Murfreesboro, also known as Wilkinson Pike or the Cedars, was fought December 5–7, 1864, in Rutherford County, Tennessee, as part of the Franklin-Nashville Campaign of the American Civil War.
The Battle of Thompson's Station took place during the American Civil War on March 5, 1863, in Williamson County, Tennessee.

The Battle of Allatoona, also known as the Battle of Allatoona Pass, was fought October 5, 1864, in Bartow County, Georgia, and was the first major engagement of the Franklin-Nashville Campaign of the American Civil War. A Confederate division under Maj. Gen. Samuel G. French attacked a Union garrison under Brig. Gen. John M. Corse, but was unable to dislodge it from its fortified position protecting the railroad through Allatoona Pass.

The Franklin–Nashville campaign, also known as Hood's Tennessee campaign, was a series of battles in the Western Theater, conducted from September 18 to December 27, 1864, in Alabama, Tennessee, and northwestern Georgia during the American Civil War.
The First Battle of Franklin was fought April 10, 1863, in Williamson County, Tennessee, during the American Civil War. It was a minor engagement in about the same location as that of the more famous Battle of Franklin, which was part of the Franklin-Nashville Campaign.
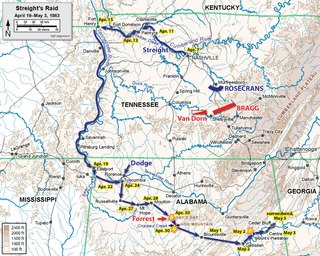
Streight's Raid took place in northern Alabama during the American Civil War. It was led by Union Army Col. Abel Streight and opposed by Confederate Brig. Gen. Nathan Bedford Forrest. Streight's goal was to destroy parts of the Western and Atlantic Railroad, which was supplying the Confederate Army of Tennessee. The raid was poorly supplied and planned, and ended with the defeat of Streight and his 1,700 men at Cedar Bluff, Alabama, by Forrest who bluffed his opponent into surrendering to his 500 men. Streight was additionally hindered by locals throughout his march, while pursued by Forrest, who had the advantage of home territory and the sympathy and aid of the local populace, most famously Emma Sansom.

The Knoxville campaign was a series of American Civil War battles and maneuvers in East Tennessee during the fall of 1863 designed to secure control of the city of Knoxville and with it the railroad that linked the Confederacy east and west, and position the First Corps under Longstreet for return to the Army of Northern Virginia. Union Army forces under Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnside occupied Knoxville, Tennessee, and Confederate States Army forces under Lt. Gen. James Longstreet were detached from Gen. Braxton Bragg's Army of Tennessee at Chattanooga to prevent Burnside's reinforcement of the besieged Federal forces there. Ultimately, Longstreet's Siege of Knoxville ended when Union Maj. Gen. William Tecumseh Sherman led elements of the Army of the Tennessee and other troops to Burnside's relief after Union troops had broken the Confederate siege of Chattanooga. Although Longstreet was one of Gen. Robert E. Lee's best corps commanders in the East in the Army of Northern Virginia, he was unsuccessful in his attempt to penetrate the Knoxville defenses and take the city.
The First Battle of Collierville, also known as the Action at Collierville, was fought during the American Civil War between the United States (Union) and Confederate States. The fighting occurred during a raid in West Tennessee and North Mississippi by Brigadier-General James R. Chalmers, Confederate States Army, commanding the expedition.
Forrest's Expedition into West Tennessee was a raid conducted by Confederate Brigadier General Nathan Bedford Forrest in Tennessee from December 1862 to January 1863, during the American Civil War. Forrest led an expedition of 1,800 to 2,500 men into Union-held West Tennessee to disrupt the supply lines of Major General Ulysses S. Grant, who was campaigning south along the Mississippi River toward Vicksburg.

The 27th Texas Cavalry Regiment, at times also known as Whitfield's Legion or 1st Texas Legion or 4th Texas Cavalry Battalion, was a unit of mounted volunteers that fought in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. First organized as the 4th Texas Cavalry Battalion or Whitfield's Legion, the unit served dismounted at Pea Ridge and First Corinth. Additional companies from Texas were added and the unit was upgraded to the 27th Texas Cavalry Regiment or 1st Texas Legion later in 1862. Still dismounted, the unit fought at Iuka and Second Corinth. The regiment was remounted and fought at Holly Springs in 1862, Thompson's Station in 1863, and at Yazoo City, Atlanta, Franklin, and Third Murfreesboro in 1864. The regiment surrendered to Federal forces in May 1865 and its remaining soldiers were paroled.

The Battle of Egypt Station was an engagement in Mississippi that took place during a successful Union cavalry raid during the American Civil War. A 3,500-man Union cavalry division under Brigadier General Benjamin Grierson defeated Confederate troops led by Franklin Gardner and Samuel J. Gholson. Grierson's raiding cavalry left Memphis, Tennessee on 21 December and first demolished a Confederate supply depot at Verona. Moving south while wrecking bridges and track along the Mobile and Ohio Railroad, the Union raiders encountered the Confederate defenders at Egypt Station. After their victory, Grierson's cavalry headed southwest to Vicksburg which it reached on January 5, 1865. The raiders destroyed a large amount of Confederate supplies and also damaged the Mississippi Central Railroad. Some of the men captured by Grierson's raiders proved to be former Union soldiers who volunteered to fight for the Confederacy rather than languish in prison camps. When John Bell Hood's army retreated into northern Mississippi after the Battle of Nashville, it was unable to obtain supplies because Grierson's raiders had damaged the railroad so badly.
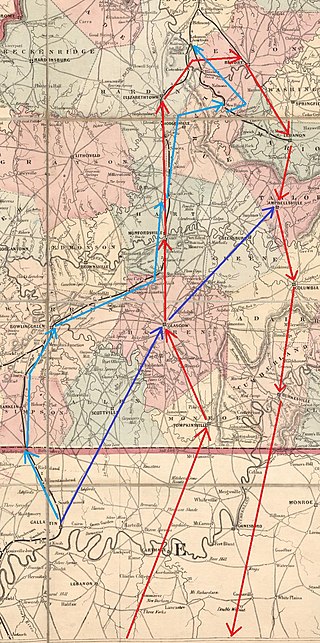
Morgan's Christmas Raid was carried out by Confederate Brigadier General John Hunt Morgan between December 22, 1862, and January 5, 1863. Morgan intended to cut the supply lines to the Union Army of the Cumberland in Tennessee. The Union used the Louisville and Nashville Railroad, and Morgan had identified two 500-foot (150 m) long trestle bridges at Muldraugh Hill that could be burnt. Morgan's 4,000-strong cavalry force left Alexandria, Tennessee, on December 22 and passed into Kentucky on Christmas Eve, defeating part of the 2nd Michigan Cavalry Regiment near Tompkinsville. They fought and defeated an Indiana cavalry detachment on Christmas Day at Bear Wallow, Barren County. The U.S. Army sent forces under Colonel John Marshall Harlan and Major General Joseph J. Reynolds to try to catch Morgan. However, Morgan used ruses to distract his pursuers. Morgan captured a Union stockade at Bonnieville on December 26 and on December 27 captured Elizabethtown before burning the bridges at Muldraugh Hill.
















