Related Research Articles
Sunpadh was an Iranian nobleman from the House of Karen, who incited an uprising against the Abbasid Caliphate in the 8th century.

The Muslim conquest of Persia, also called the Muslim conquest of Iran, the Arab conquest of Persia, or the Arab conquest of Iran, was a major military campaign undertaken by the Rashidun Caliphate between 632 and 654. As part of the early Muslim conquests, which had begun under Muhammad in 622, it led to the fall of the Sasanian Empire and the eventual decline of Zoroastrianism, which had been predominant throughout Persia as the nation's official religion.

The Battle of Nahavand, also spelled Nihavand or Nahawand, was fought in 642 between the Rashidun Muslim forces under caliph Umar and Sasanian Persian armies under King Yazdegerd III. Yazdegerd escaped to the Merv area, but was unable to raise another substantial army. It was a victory for the Rashidun Caliphate and the Persians consequently lost the surrounding cities including Spahan (Isfahan).
The Seven Great Houses of Iran, also known as the seven Parthian clans, were seven feudal aristocracies of Parthian origin, who were allied with the Sasanian court. The Parthian clans all claimed ancestry from Achaemenid Persians.
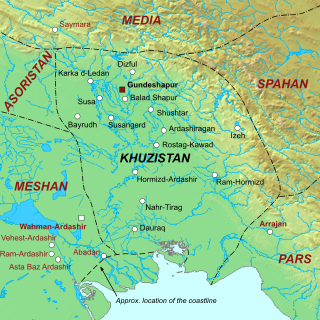
The Muslim conquest of Khuzestan took place from 637/8 to 642, and ended with the acquisition of the rich Khuzestan Province by the Rashidun Caliphate.

Azarmidokht was Sasanian queen (banbishn) of Iran from 630 to 631. She was the daughter of king (shah) Khosrow II. She was the second Sasanian queen; her sister Boran ruled before and after her. Azarmidokht came to power in Iran after her cousin Shapur-i Shahrvaraz was deposed by the Parsig faction, led by Piruz Khosrow, who helped Azarmidokht ascend the throne. Her rule was marked by an attempt of a nobleman and commander Farrukh Hormizd to marry her and come to power. After the queen's refusal, he declared himself an anti-king. Azarmidokht had him killed as a result of a successful plot. She was, however, killed herself shortly afterwards by Rostam Farrokhzad in retaliation for his father's death. She was succeeded by Boran.

The House of Karen, also known as Karen-Pahlav, was one of the Seven Great Houses of Iran during the rule of Parthian and Sassanian Empires. The seat of the dynasty was at Nahavand, about 65 km south of Ecbatana. Members of the House of Karen were of notable rank in the administrative structure of the Sassanian empire in multiple periods of its four century-long history.
Farrukhzad was an Iranian aristocrat from the House of Ispahbudhan and the founder of the Bavand dynasty, ruling from 651 to 665. Originally a powerful servant of the Sasanian king Khosrow II, he, along with several other powerful aristocrats made a conspiracy against the latter and ended his tyrannical rule. They thereafter put Khosrow's son Kavadh II on the throne, whose rule lasted only a few months, before he was killed by a plague, being succeeded by his son Ardashir III, who was only after one year murdered by the rebellious former Sasanian army chief (spahbed) Shahrbaraz, who usurped the throne.
Jalinus was a 7th-century Armenian dynast, who was one of the leading figures in Sasanian Iran. He was the commander of the guard over Khosrow II, during the latter's imprisonment. Jalinus was a Sasanian commander during the Arab conquest of Iran.

Farrukh Hormizd or Farrokh Hormizd, also known as Hormizd V, was an Iranian prince, who was one of the leading figures in Sasanian Iran in the early 7th-century. He served as the military commander (spahbed) of northern Iran. He later came in conflict with the Iranian nobility, "dividing the resources of the country". He was later killed by Siyavakhsh in a palace plot on the orders of Azarmidokht after he proposed to her in an attempt to usurp the Sasanian throne. He had two children, Rostam Farrokhzad and Farrukhzad.
Piruz Khosrow, also known as Piruzan or Firuzan, was a powerful Persian aristocrat who was the leader of the Parsig (Persian) faction that controlled much of the affairs of the Sasanian Empire during the Sasanian civil war of 628-632. He was killed at the Battle of Nahāvand in 642.
The Sasanian civil war of 628–632, also known as the Sasanian Interregnum was a conflict that broke out after the execution of the Sasanian king Khosrow II between the nobles of different factions, notably the Parthian (Pahlav) faction, the Persian (Parsig) faction, the Nimruzi faction, and the faction of general Shahrbaraz. Rapid turnover of rulers and increasing provincial landholder power further diminished the empire. Over a period of four years and fourteen successive kings, the Sasanian Empire weakened considerably, and the power of the central authority passed into the hands of its generals, contributing to its fall.
Mihran-i Bahram-i Razi, better simply known as Mihran Razi, was an Iranian military officer from the Mihran family. He was killed in 637 at the battle of Jalula.

Mihr Hormozd was an Iranian nobleman from the House of Suren. He was the son of Mardanshah, the padgospan of Nemroz, who was later executed by the orders of the Sasanian king Khosrau II. In 628, Khosrau was overthrown by his son Kavadh II, and was taken to prison, where he was shortly executed by Mihr Hormozd who sought to avenge his father's death. However, after the execution, Kavadh had Mihr Hormizd killed.

Muta was a 7th-century Daylamite king, who fought against the Arabs in the battle of Waj Rudh. He was, however, defeated and killed by Nu'aym ibn Muqarrin.

The Battle of Spahan was fought between the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Empire in 642. The Arabs were victorious during the battle, where they reportedly killed the Mihran commander Shahrvaraz Jadhuyih. After the battle, the Arabs made peace with Fadhusfan, the governor of the city. According to Abu No'aym, many people were killed or enslaved after the conquest and the settlement pattern of the region changed. Isfahan capitulated by 644 after a few failed revolts and treaties for paying taxes and tributes in exchange for military protection were drawn up.
Isfandyadh was an Iranian aristocrat from the Ispahbudhan family, who was the ruler of the Sasanian province of Adurbadagan. He was the son of the powerful Sasanian general Farrukhzad, who was the brother of Rostam Farrokhzad and the son of Farrukh Hormizd.

The Battle of Ray was fought between the Sasanians and the Rashidun Caliphate in 651. It was also part of the rivalry between the Ispahbudhan family and the Mihran family.
Hormozd Jadhuyih was a Sasanian commander who is known for his participation at the Battle of Firaz during the Arab invasion of Iran, which resulted in Byzantine-Sasanian defeat. According to al-Tabari, Hormozd's army during the battle consisted of "keepers of chickens and swine." Hormozd may have been the father of the prominent Sasanian general Bahman Jadhuyih, who was already recorded as an old man by 634. Thus Hormozd was probably an old man during the Battle of Firaz.

Parvaneh Pourshariati is an Iranian-born American historian of Middle Eastern studies, scholar, and educator. She is an Associate Professor of History at New York City College of Technology (CUNY), and former president of the Association for the Study of Persianate Societies. She specializes in the late antique, early medieval and modern histories of Iran and the Middle East.
References
- ↑ Parvaneh Pourshariati, The Decline and Fall of the Sasanian Empire, 248.
- 1 2 3 Kamal-ud-Din, Khwaja (1957). The Islamic Review Volume 45. Woking Muslim Mission and Literary Trust. p. 16. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- 1 2 Ibn Jarir at-Tabari, Muhammad (2015). The History of Al-Tabari Vol. 14 The Conquest of Iran A.D. 641-643/A.H. 21-23 (Ebook). Translated by G. Rex Smith. SUNY. ISBN 9781438420394 . Retrieved 7 December 2021.