
Jan Długosz, also known in Latin as Johannes Longinus, was a Polish priest, chronicler, diplomat, soldier, and secretary to Bishop Zbigniew Oleśnicki of Kraków. He is considered Poland's first historian.

Ruthenia is an exonym, originally used in Medieval Latin, as one of several terms for Kievan Rus'. It is also used to refer to the East Slavic and Eastern Orthodox regions of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the Kingdom of Poland, and later the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, corresponding to the territories of modern Belarus, Ukraine, and West European Russia. Historically, the term was used to refer to all the territories of the East Slavs.

Red Ruthenia, or Red Rus' , is a term used since the Middle Ages for the south-western principalities of the Kievan Rus', namely the Principality of Peremyshl and the Principality of Belz. Nowadays the region comprises parts of western Ukraine and adjoining parts of south-eastern Poland. It has also sometimes included parts of Lesser Poland, Podolia, Right-bank Ukraine and Volhynia. Centred on Przemyśl and Belz, it has included major cities such as: Chełm, Zamość, Rzeszów, Krosno and Sanok, as well as Lviv and Ternopil.

Galicia is a historical and geographic region spanning what is now southeastern Poland and western Ukraine, long part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It covers much of the other historic regions of Red Ruthenia and Lesser Poland.

The Principality or, from 1253, Kingdom of Galicia–Volhynia, historically known as the Kingdom of Ruthenia, was a medieval state in Eastern Europe which existed from 1199 to 1349. Its territory was predominantly located in modern-day Ukraine, with parts in Belarus, Poland, Moldova, and Lithuania. Along with Novgorod and Vladimir-Suzdal, it was one of the three most important powers to emerge from the collapse of Kievan Rus'. The main language was Old East Slavic, the predecessor of the modern East Slavic languages, and the official religion was Eastern Orthodoxy.

Leszek the White was Prince of Sandomierz and High Duke of Poland in the years 1194–1198, 1199, 1206–1210, and 1211–1227. During the early stages of his reign, his uncle Duke Mieszko III the Old and cousin Władysław III Spindleshanks, from the Greater Polish branch of the royal Piast dynasty, contested Leszek's right to be High Duke.

Konrad I of Masovia, from the Polish Piast dynasty, was the sixth Duke of Masovia and Kuyavia from 1194 until his death as well as High Duke of Poland from 1229 to 1232 and again from 1241 to 1243.

The House of Ostrogski was one of the more prominent families in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The family spanned from the 14th century Ruthenian noble Daniil Ostrogski to the 17th century Polish members. After the death of Janusz Ostrogski, the last male heir, most of the family's possessions passed to the Zasławski family.

The Galician–Volhynian Chronicle (GVC), also known as Chronicle of Halych–Volhynia and The Dynastic Chronicle of the Romanovichi, is a prominent work of Old Ruthenian literature and historiography covering 1201–1292 in the history of the Principality of Galicia–Volhynia.

Roman Mstislavich, also known as Roman the Great, was Prince of Novgorod (1168–1170), Volhynia, and Galicia. He founded the Romanovichi branch of Rurikids, which would rule Galicia–Volhynia until 1340.
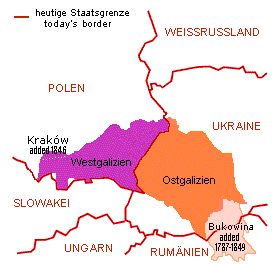
Eastern Galicia is a geographical region in Western Ukraine, having also essential historic importance in Poland.

The Principality of Halych, or Principality of Halychian Rus', was a medieval East Slavic principality, and one of the main regional states within the political scope of Kievan Rus', established by members of the oldest line of Yaroslav the Wise descendants. A characteristic feature of the Halych principality was the important role of the nobility and citizens in political life, and consideration a will which was the main condition for the princely rule. Halych as the capital mentioned in around 1124 as a seat of Ivan Vasylkovych the grandson of Rostislav of Tmutarakan. According to Mykhailo Hrushevsky the realm of Halych was passed to Rostyslav upon the death of his father Vladimir Yaroslavich, but he was banished out of it later by his uncle to Tmutarakan. The realm was then passed to Yaropolk Izyaslavich who was a son of the ruling Grand Prince Iziaslav I of Kiev.
Lechites, also known as the Lechitic tribes, is a name given to certain West Slavic tribes who inhabited modern-day Poland and eastern Germany, and were speakers of the Lechitic languages. Distinct from the Czech–Slovak subgroup, they are the closest ancestors of ethnic Poles and of Pomeranians, Lusatians and Polabians.
Roman Mikhailovich the Old was a Rus' prince of the Olgovichi clan. He was Prince of Bryansk, and probably also Prince of Chernigov, although most primary sources only mention him as Prince of Bryansk.

The siege of Kiev by the Mongols took place between 28 November and 6 December 1240, and resulted in a Mongol victory. It was a heavy morale and military blow to the Principality of Galicia–Volhynia, which was forced to submit to Mongol suzerainty, and allowed Batu Khan to proceed westward into Central Europe.
Bolokhovians, Bolokhoveni, also Bolokhovens, were a 13th-century ethnic group that resided in the vicinity of the Rus' principalities of Halych, Volhynia and Kiev, in the territory known as the "Bolokhovian Land" centered at the city of Bolokhov or Bolokhovo. Their ethnic identity is uncertain; although Romanian scholars, basing on their ethnonym identify them as Romanians, archeological evidence and the Hypatian Chronicle suggest that they were a Slavic people. Their princes, or knyazes, were in constant conflict with Daniel of Galicia, Prince of Halych and Volhynia, between 1231 and 1257. After the Mongols sacked Kiev in 1240, the Bolokhovians supplied them with troops, but the Bolokhovian princes fled to Poland. The Bolokhovians disappeared after Daniel defeated them in 1257.
With the arrival of the Hungarians into the heart of the Central European Plain around 899, Slavic tribes of Vistulans, White Croats, and Lendians found themselves under Hungarian rule. In 955 those areas north of the Carpathian Mountains constituted an autonomous part of the Duchy of Bohemia and remained so until around 972, when the first Polish territorial claims began to emerge. This area was mentioned in 981, when Vladimir the Great of Kievan Rus' claimed the area on his westward way. In the 11th century the area belonged to Poland, then reverted to Kievan Rus'. However, at the end of the 12th century the Hungarian claims to the principality turned up. Finally Casimir III of Poland annexed it in 1340–1349. Low Germans from Prussia and Middle Germany settled parts of northern and western Galicia from the 13th to 18th centuries, although the vast majority of the historic province remained independent from German and Austrian rule.
File Szeretvai was a Hungarian noble and military leader in the first half of the 13th century, who faithfully served kings Andrew II then Béla IV. He participated in various royal campaigns against the Principality of Halych, which allowed him to rise to the ranks of the upper nobility. He functioned as Master of the stewards from 1231 to 1232.

The War for Brest was Prince Casimir II the Just's military campaign against Kievan Rus following the fall of Brest. Casimir quickly captured the city and made efforts to restore Prince Mstislav to the throne of Halych. Despite initial reluctance from some Polish lords, Casimir led his forces into battle against opposing Rus princes. The engagement culminated in a decisive victory for Casimir, resulting in the surrender of Ruthenians and the restoration of Mstislav to the throne.
















