
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit. Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials depending on the type of battery.

A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. The negative electrode of a conventional lithium-ion cell is typically graphite, a form of carbon. This negative electrode is sometimes called the anode as it acts as an anode during discharge. The positive electrode is typically a metal oxide and is sometimes called the cathode as it acts as a cathode during discharge. Positive and negative electrodes remain positive and negative in normal use whether charging or discharging and therefore are clearer terms than anode and cathode, which are reversed during charging.

Molten-salt batteries are a class of battery that uses molten salts as an electrolyte and offers both a high energy density and a high power density. Traditional non-rechargeable thermal batteries can be stored in their solid state at room temperature for long periods of time before being activated by heating. Rechargeable liquid-metal batteries are used for industrial power backup, special electric vehicles and for grid energy storage, to balance out intermittent renewable power sources such as solar panels and wind turbines.
Aluminium–air batteries produce electricity from the reaction of oxygen in the air with aluminium. They have one of the highest energy densities of all batteries, but they are not widely used because of problems with high anode cost and byproduct removal when using traditional electrolytes. This has restricted their use to mainly military applications. However, an electric vehicle with aluminium batteries has the potential for up to eight times the range of a lithium-ion battery with a significantly lower total weight.

The lithium iron phosphate battery or LFP battery is a type of lithium-ion battery using lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material, and a graphitic carbon electrode with a metallic backing as the anode. Because of their lower cost, high safety, low toxicity, long cycle life and other factors, LFP batteries are finding a number of roles in vehicle use, utility-scale stationary applications, and backup power. LFP batteries are cobalt-free. As of September 2022, LFP type battery market share for EVs reached 31%, and of that, 68% was from Tesla and Chinese EV maker BYD production alone. Chinese manufacturers currently hold a near monopoly of LFP battery type production. With patents having started to expire in 2022 and the increased demand for cheaper EV batteries, LFP type production is expected to rise further and surpass lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxides (NMC) type batteries in 2028.

Nanobatteries are fabricated batteries employing technology at the nanoscale, particles that measure less than 100 nanometers or 10−7 meters. These batteries may be nano in size or may use nanotechnology in a macro scale battery. Nanoscale batteries can be combined to function as a macrobattery such as within a nanopore battery.

Lithium iron phosphate or lithium ferro-phosphate (LFP) is an inorganic compound with the formula LiFePO
4. It is a gray, red-grey, brown or black solid that is insoluble in water. The material has attracted attention as a component of lithium iron phosphate batteries, a type of Li-ion battery. This battery chemistry is targeted for use in power tools, electric vehicles, solar energy installations and more recently large grid-scale energy storage.

Lithium cobalt oxide, sometimes called lithium cobaltate or lithium cobaltite, is a chemical compound with formula LiCoO
2. The cobalt atoms are formally in the +3 oxidation state, hence the IUPAC name lithium cobalt(III) oxide.

An electric vehicle battery is a rechargeable battery used to power the electric motors of a battery electric vehicle (BEV) or hybrid electric vehicle (HEV).

A lithium-ion capacitor is a hybrid type of capacitor classified as a type of supercapacitor. It is called a hybrid because the anode is the same as those used in lithium-ion batteries and the cathode is the same as those used in supercapacitors. Activated carbon is typically used as the cathode. The anode of the LIC consists of carbon material which is often pre-doped with lithium ions. This pre-doping process lowers the potential of the anode and allows a relatively high output voltage compared to other supercapacitors.
A potassium-ion battery or K-ion battery is a type of battery and analogue to lithium-ion batteries, using potassium ions for charge transfer instead of lithium ions. It was invented by the Iranian/American chemist Ali Eftekhari in 2004.
Sodium-ion batteries (NIBs or SIBs) are several types of rechargeable batteries, which use sodium ions (Na+) as its charge carriers. In some cases, its working principle and cell construction are similar to those of lithium-ion battery (LIB) types, but it replaces lithium with sodium as the cathode material, which belongs to the same group in the periodic table as lithium and thus has similar chemical properties. In other cases, particularly, aqueous Na-ion batteries are quite different from Li-ion batteries.
Research in lithium-ion batteries has produced many proposed refinements of lithium-ion batteries. Areas of research interest have focused on improving energy density, safety, rate capability, cycle durability, flexibility, and cost.
Huayou Cobalt Co., Ltd primarily operates as a supplier of cobalt and its associated products, such as cobalt tetroxide, cobalt oxide, cobalt carbonate, cobalt hydroxide, cobalt oxalate, cobalt sulfate, and cobalt monoxide. The company is headquartered in the Tongxiang Economic Development Zone of Zhejiang, China.
Simon David Moores is a British businessman and entrepreneur, specializing in the lithium ion battery and electric vehicle industry.
The lithium nickel cobalt aluminium oxides (abbreviated as Li-NCA, LNCA, or NCA) are a group of mixed metal oxides. Some of them are important due to their application in lithium ion batteries. NCAs are used as active material on the positive pole (which is the cathode when the battery is discharged). NCAs are composed of the cations of the chemical elements lithium, nickel, cobalt and aluminium. The most important representatives as of this date have the general formula LiNixCoyAlzO2 with x + y + z = 1. In case of the NCA comprising batteries currently available on the market, which are also used in electric cars and electric appliances, x ≈ 0,8, and the voltage of those batteries is between 3.6 V and 4.0 V, at a nominal voltage of 3.6 V or 3.7 V. A version of the oxides currently in use in 2019 is LiNi0,84Co0,12Al0,04O2.
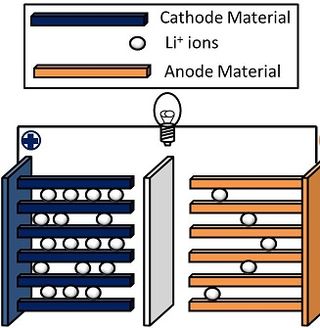
Lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxides (abbreviated NMC, Li-NMC, LNMC, or NCM) are mixed metal oxides of lithium, nickel, manganese and cobalt with the general formula LiNixMnyCo1-x-yO2. These materials are commonly used in lithium-ion batteries for mobile devices and electric vehicles, acting as the positively charged cathode.
A solid-state silicon battery or silicon-anode all-solid-state battery is a type of rechargeable lithium-ion battery consisting of a solid electrolyte, solid cathode, and silicon-based solid anode.

This is a history of the lithium-ion battery.
The electric vehicle supply chain comprises the mining and refining of raw materials and the manufacturing processes that produce lithium ion batteries and other components for electric vehicles. The lithium-ion battery supply chain is a major component of the overall EV supply chain, and the battery accounts for 30%-40% of the value of the vehicle. Lithium, cobalt, graphite, nickel, and manganese are all critical minerals that are necessary for electric vehicle batteries. There is rapidly growing demand for these materials because of growth in the electric vehicle market, which is driven largely by the proposed transition to renewable energy. Securing the supply chain for these materials is a major world economic issue. Recycling and advancement in battery technology are proposed strategies to reduce demand for raw materials. Supply chain issues could create bottlenecks, increase costs of EVs and slow their uptake.










