Kiribati, officially the Republic of Kiribati, is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the central Pacific Ocean. Its permanent population is over 119,000 as of the 2020 census, with more than half living on Tarawa atoll. The state comprises 32 atolls and one remote raised coral island, Banaba. Its total land area is 811 km2 (313 sq mi) dispersed over 3,441,810 km2 (1,328,890 sq mi) of ocean.

The islands which now form the Republic of Kiribati have been inhabited for at least seven hundred years, and possibly much longer. The initial Austronesian peoples’ population, which remains the overwhelming majority today, was visited by Polynesian and Melanesian invaders before the first European sailors visited the islands in the 17th century. For much of the subsequent period, the main island chain, the Gilbert Islands, was ruled as part of the British Empire. The country gained its independence in 1979 and has since been known as Kiribati.

The Gilbert Islands are a chain of sixteen atolls and coral islands in the Pacific Ocean, about halfway between Papua New Guinea and Hawaii. They constitute the main part of the nation of Kiribati.

The Gilbert and Ellice Islands in the Pacific Ocean were part of the British Empire from 1892 to 1976. They were a protectorate from 1892 to 12 January 1916, and then a colony until 1 January 1976. The history of the colony was mainly characterized by phosphate mining on Ocean Island. In October 1975, these islands were divided by force of law into two separate colonies, and they became independent nations shortly thereafter: the Ellice Islands became Tuvalu in 1978, and the Gilbert Islands became part of Kiribati in 1979.

Butaritari is an atoll in the Pacific Ocean island nation of Kiribati. The atoll is roughly four-sided. The south and southeast portion of the atoll comprises a nearly continuous islet. The atoll reef is continuous but almost without islets along the north side. Bikati and Bikatieta islets occupy a corner of the reef at the extreme northwest tip of the atoll. Small islets are found on reef sections between channels on the west side. The lagoon of Butaritari is deep and can accommodate large ships, though the entrance passages are relatively narrow. It is the most fertile of the Gilbert Islands, with relatively good soils and high rainfall. Butaritari atoll has a land area of 13.49 km2 (5.21 sq mi) and a population of 3,224 as of 2015. During World War II, Butaritari was known by United States Armed Forces as Makin Atoll, and was the site of the Battle of Makin. Locally, Makin is the name of a separate but closest atoll, 3 kilometres to the northeast of Butaritari, but close enough to be seen. These two atolls share a dialect of the Gilbertese language.


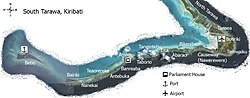
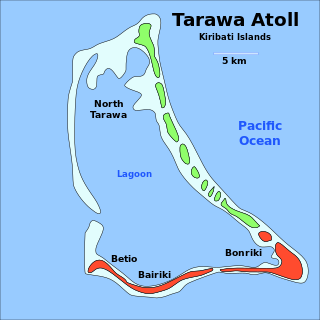
Tarawa is an atoll and the capital of the Republic of Kiribati, in the Micronesia region of the central Pacific Ocean. It comprises North Tarawa, which has 6,629 inhabitants and much in common with other more remote islands of the Gilberts group, and South Tarawa, which has 56,388 inhabitants as of 2015, half of the country's total population. The atoll was the site of the Battle of Tarawa during World War II.

South Tarawa is the capital and hub of the Republic of Kiribati and home to more than half of Kiribati's population. The South Tarawa population centre consists of all the small islets from Betio in the west to Bonriki and Tanaea in the north-east, connected by the South Tarawa main road, with a population of 63,439 as of 2020.

Abemama (Apamama) is an atoll, one of the Gilberts group in Kiribati, and is located 152 kilometres southeast of Tarawa and just north of the Equator. Abemama has an area of 27.37 square kilometres and a population of 3,299 as of 2015. The islets surround a deep lagoon. The eastern part of the atoll of Abemama is linked together by causeways making automobile traffic possible between the different islets. The outlying islands of Abatiku and Biike are situated on the southwestern side of the atoll.

Bonriki International Airport is an international airport in Kiribati, serving as the main gateway to the country. It is located in its capital, South Tarawa, which is a group of islets in the atoll of Tarawa in the Gilbert Islands, precisely on Bonriki.

Nikunau is a low coral atoll in the Gilbert Islands that forms a council district of the Republic of Kiribati. It consists of two parts, with the larger in the northwest, joined by an isthmus about 150 metres (490 ft) wide.

Nonouti is an atoll and district of Kiribati. The atoll is located in the Southern Gilbert Islands, 38 km north of Tabiteuea, and 250 km south of Tarawa. The atoll is the third largest in the Gilbert Islands and is the island where the Roman Catholic religion was first established in Kiribati, in 1888.

Onotoa is an atoll of Kiribati. It is situated in the Gilbert Islands in the Pacific Ocean, 65 km (40 mi) from Tamana, the smallest island in the Gilberts. The population of Onotoa in the 2015 census was 1,393.

Makin is the name of an atoll, chain of islands, located in the Pacific Ocean island nation of Kiribati. Makin is the northernmost of the Gilbert Islands, with a population of 1,990.

Funafuti is the capital of the island nation of Tuvalu. It has a population of 6,320 people, and so it has more people than the rest of Tuvalu combined, with approximately 60% of the population. It consists of a narrow sweep of land between 20 and 400 metres wide, encircling a large lagoon 18 km long and 14 km wide. The average depth of the Funafuti lagoon is about 20 fathoms. With a surface area of 275 square kilometres (106.2 sq mi), it is by far the largest lagoon in Tuvalu. The land area of the 33 islets around the atoll of Funafuti totals 2.4 square kilometres (0.9 sq mi); taken together, they constitute less than one percent of the total area of the atoll. Cargo ships can enter Funafuti's lagoon and dock at the port facilities on Fongafale.

North Tarawa or in Gilbertese Tarawa Ieta, in the Republic of Kiribati, is the string of islets from Buariki at the northern tip of Tarawa atoll to Buota in the South, with a combined population of 6,629 as of 2015. It is administratively separate from neighbouring South Tarawa, and is governed by the Eutan Tarawa Council (ETC), based at Abaokoro.

The Governor of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands was the colonial head of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands civil service from 1892 until 1979.
Vivian Fox-Strangways was a British officer, Resident Commissioner of the partly occupied by Japan Gilbert and Ellice Islands, from 1941 to 1946.

The Japanese occupation of the Gilbert Islands was the period in the history of Kiribati between 1941 and 1945 when Imperial Japanese forces occupied the Gilbert Islands during World War II, in the Pacific War theatre.
Naval Base Tarawa was a naval base built by the United States Navy in 1943 to support the World War II effort. The base was located on Tarawa atoll in the Gilbert Islands in the Central Pacific Ocean. The base was built as one of many advance bases in the island-hopping campaign towards the Empire of Japan. At Naval Base Tarawa the Navy built a seaport, seaplane base and two airbases. Construction started after the Battle of Tarawa ended November 23, 1943, part of Operation Galvanic.