
The Graphics Interchange Format is a bitmap image format that was developed by a team at the online services provider CompuServe led by American computer scientist Steve Wilhite and released on June 15, 1987.
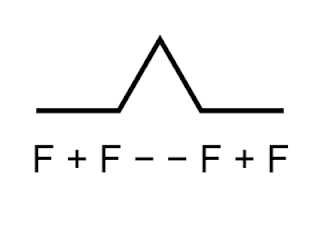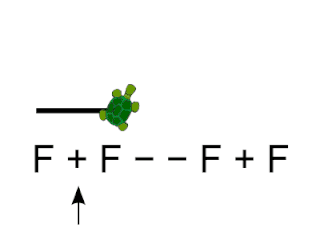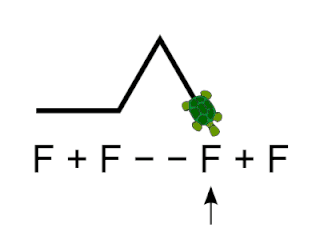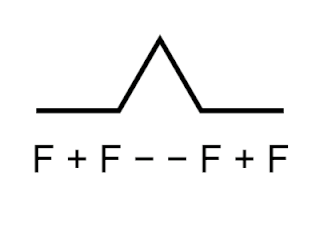
Logo is an educational programming language, designed in 1967 by Wally Feurzeig, Seymour Papert, and Cynthia Solomon. Logo is not an acronym: the name was coined by Feurzeig while he was at Bolt, Beranek and Newman, and derives from the Greek logos, meaning word or thought.

IBM PC compatible computers are similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT, all from computer giant IBM, that are able to use the same software and expansion cards. Such computers were referred to as PC clones, IBM clones or IBM PC clones. The term "IBM PC compatible" is now a historical description only, since IBM no longer sells personal computers after it sold its personal computer division in 2005 to Chinese technology company Lenovo. The designation "PC", as used in much of personal computer history, has not meant "personal computer" generally, but rather an x86 computer capable of running the same software that a contemporary IBM PC could. The term was initially in contrast to the variety of home computer systems available in the early 1980s, such as the Apple II, TRS-80, and Commodore 64. Later, the term was primarily used in contrast to Apple's Macintosh computers.

The KIM-1, short for Keyboard Input Monitor, is a small 6502-based single-board computer developed and produced by MOS Technology, Inc. and launched in 1976. It was very successful in that period, due to its low price and easy-access expandability.

Atari BASIC is an interpreter for the BASIC programming language that shipped with Atari 8-bit computers. Unlike most American BASICs of the home computer era, Atari BASIC is not a derivative of Microsoft BASIC and differs in significant ways. It includes keywords for Atari-specific features and lacks support for string arrays.

Luba Goy is a Canadian actress, comedian and one of the stars of Royal Canadian Air Farce.

The ATASCII character set, from ATARI Standard Code for Information Interchange, alternatively ATARI ASCII, is a character encoding used in the Atari 8-bit home computers. ATASCII is based on ASCII, but is not fully compatible with it.
Sublogic Corporation is an American software development company. It was formed in 1977 by Bruce Artwick, and incorporated in 1978 by Artwick's partner Stu Moment as Sublogic Communications Corporation. Sublogic is best known as the creator of the Flight Simulator series, later known as Microsoft Flight Simulator, but it also created other video games such as Night Mission Pinball, Football, and Adventure on a Boat; educational software; and an Apple II graphics library.

William Allan Van Evera, known by the stage name Billy Van, was a Canadian comedian, actor, and singer.
VirtualMagic Animation, Inc. was an American traditional animation studio and software development company based out of Los Angeles, California. The studio produced animation for television series and commercials, and provided ink and paint services to animated TV series such as The Ren and Stimpy Show and The Simpsons and films such as We're Back! A Dinosaur's Story. Its software division was best known for developing USAnimation, a high-end software package designed to facilitate the traditional animation process using digital technologies.
Interval Research Corporation was founded in 1992 by Paul Allen and David Liddle. It was a Palo Alto laboratory and technology incubator focusing on consumer product applications and services with a focus on the Internet.

SuperPaint was a pioneering graphics program and framebuffer computer system developed by Richard Shoup at Xerox PARC. The system was first conceptualized in late 1972 and produced its first stable image in April 1973. SuperPaint was among the earliest uses of computer technology for creative artworks, video editing, and computer animation, all of which would become major areas within the entertainment industry and major components of industrial design.
The Mechanical Universe...And Beyond is a 52-part telecourse, filmed at the California Institute of Technology, that introduces university level physics, covering topics from Copernicus to quantum mechanics. The 1985-86 series was produced by Caltech and INTELECOM, a nonprofit consortium of California community colleges now known as Intelecom Learning, with financial support from Annenberg/CPB. The series, which aired on PBS affiliate stations before being distributed on LaserDisc and eventually YouTube, is known for its use of computer animation.

Eureka! is a Canadian educational television series which was produced and broadcast by TVOntario in 1980 and 1981. The series was narrated by Billy Van, and featured a series of animated vignettes which taught physics lessons to children. It is currently available online.
Math Patrol was a children's educational television show produced by TVOntario from 1976 to 1978 and aired by the public broadcaster in the late 1970s and the early 1980s.
PICtor is an image file format developed by John Bridges, the principal author of PCPaint, the first Paintbrush program for the PC. It was also the native file format for Pictor Paint and Graphics Animation System for Professionals (GRASP) and became the first widely accepted DOS imaging standard.
Krazy House is a Canadian comedy television miniseries which aired on CBC Television in 1977. It was an anthology series of several different sketch programmes independently written, performed and produced by different performers in different cities. Members of the Royal Canadian Air Farce were involved in writing and performing in Toronto-shot episodes 1, 2 and 5, while episodes 3 and 4 were shot in Vancouver and featured the cast of CBC Radio's Dr. Bundolo's Pandemonium Medicine Show. Episode 6 featured a cast of unknowns, and was not connected to either the Air Farce or Bundolo troupes.
The history of computer animation began as early as the 1940s and 1950s, when people began to experiment with computer graphics – most notably by John Whitney. It was only by the early 1960s when digital computers had become widely established, that new avenues for innovative computer graphics blossomed. Initially, uses were mainly for scientific, engineering and other research purposes, but artistic experimentation began to make its appearance by the mid-1960s – most notably by Dr. Thomas Calvert. By the mid-1970s, many such efforts were beginning to enter into public media. Much computer graphics at this time involved 2-D imagery, though increasingly as computer power improved, efforts to achieve 3-D realism became the emphasis. By the late 1980s, photo-realistic 3-D was beginning to appear in film movies, and by mid-1990s had developed to the point where 3-D animation could be used for entire feature film production.
Rusty Rivets is a Canadian animated television series, and is produced by Arc Productions and Spin Master Entertainment. Rusty Rivets aired for three seasons, simultaneously on Treehouse TV in Canada and on Nickelodeon in the U.S., from November 8, 2016, to May 8, 2020. Inspired by elements of the maker culture, it follows the adventures of a young inventor named Rusty and his team of customized robots.
Acorn System BASIC and Atom BASIC are two closely related dialects of the BASIC programming language developed by Acorn Computers for their early microcomputers like the Acorn System 3 and Acorn Atom. Developed in-house, they have a number of significant idiosyncrasies compared to most BASIC dialects of the home computer era.








