The sand martin, also known as the bank swallow, collared sand martin, or common sand martin, is a migratory passerine bird in the swallow family. It has a wide range in summer, embracing practically the whole of Europe and the Mediterranean countries and across the Palearctic to the Pacific Ocean. It is a Holarctic species also found in North America. It winters in eastern and southern Africa, South America, and the Indian Subcontinent.

The great blue heron is a large wading bird in the heron family Ardeidae, common near the shores of open water and in wetlands over most of North and Central America, as well as far northwestern South America, the Caribbean and the Galápagos Islands. It is occasionally found in the Azores and is a rare vagrant to Europe. An all-white population found in south Florida and the Florida Keys is known as the great white heron. Debate exists about whether this represents a white color morph of the great blue heron, a subspecies of it, or an entirely separate species.

Herons are long-legged, long-necked, freshwater and coastal birds in the family Ardeidae, with 72 recognised species, some of which are referred to as egrets or bitterns rather than herons. Members of the genera Botaurus and Ixobrychus are referred to as bitterns, and, together with the zigzag heron, or zigzag bittern, in the monotypic genus Zebrilus, form a monophyletic group within the Ardeidae. Egrets do not form a biologically distinct group from herons, and tend to be named differently because they are mainly white or have decorative plumes in breeding plumage. Herons, by evolutionary adaptation, have long beaks.

The grey heron is a long-legged wading bird of the heron family, Ardeidae, native throughout temperate Europe and Asia, and also parts of Africa. It is resident in much of its range, but some populations from the more northern parts migrate southwards in autumn. A bird of wetland areas, it can be seen around lakes, rivers, ponds, marshes and on the sea coast. It feeds mostly on aquatic creatures which it catches after standing stationary beside or in the water, or stalking its prey through the shallows.

The great egret (Ardea alba), also known as the common egret, large egret, or great white egret or great white heron, is a large, widely distributed egret. The four subspecies are found in Asia, Africa, the Americas, and southern Europe. Recently, it has also been spreading to more northern areas of Europe. Distributed across most of the tropical and warmer temperate regions of the world, it builds tree nests in colonies close to water.

The little egret is a species of small heron in the family Ardeidae. It is a white bird with a slender black beak, long black legs and, in the western race, yellow feet. As an aquatic bird, it feeds in shallow water and on land, consuming a variety of small creatures. It breeds colonially, often with other species of water birds, making a platform nest of sticks in a tree, bush or reed bed. A clutch of three to five bluish-green eggs is laid and incubated by both parents for about three weeks. The young fledge at about six weeks of age.

The striated heron also known as mangrove heron, little green heron or green-backed heron, is a small heron, about 44 cm tall. Striated herons are mostly sedentary and noted for some interesting behavioral traits. Their breeding habitat is small wetlands in the Old World tropics from west Africa to Japan and Australia, and in South America and the Caribbean. Vagrants have been recorded on Oceanic islands, such as Chuuk and Yap in the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marianas and Palau; the bird recorded on Yap on February 25, 1991, was from a continental Asian rather than from a Melanesian population, while the origin of the bird seen on Palau on May 3, 2005 was not clear.

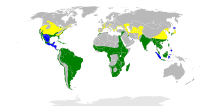
The cattle egret (Bubulcus) is a cosmopolitan genus of heron found in the tropics, subtropics, and warm-temperate zones. According to the IOC bird list, it contains two species, the western cattle egret and the eastern cattle egret, although some authorities regard them as a single species. Despite the similarities in plumage to the egrets of the genus Egretta, it is more closely related to the herons of Ardea. Originally native to parts of Asia, Africa, and Europe, it has undergone a rapid expansion in its distribution and successfully colonised much of the rest of the world in the last century.

The ruby-crowned kinglet is a very small passerine bird found throughout North America. It is a member of the kinglet family. The bird has olive-green plumage with two white wing bars and a white eye-ring. Males have a red crown patch, which is usually concealed. The sexes are identical, and juveniles are similar in plumage to adults. It is one of the smallest songbirds in North America. The ruby-crowned kinglet is not closely related to other kinglets and was moved from Regulus to its own genus, Corthylio, in 2021. Three subspecies are currently recognized.

The reddish egret is a medium-sized heron that is a resident breeder in Central America, the Bahamas, the Caribbean, the Gulf Coast of the United States, and Mexico. The egret is known for its unusual foraging behavior compared to other herons as well as its association with mud flats, its habitat of choice.

The little blue heron is a small heron of the genus Egretta. It is a small, darkly colored heron with a two-toned bill. Juveniles are entirely white, bearing resemblance to the snowy egret. During the breeding season, adults develop different coloration on the head, legs, and feet.

The medium egret, median egret, smaller egret or intermediate egret, is a medium-sized heron. Some taxonomists put the species in the genus Egretta or Mesophoyx. It is a resident breeder in southern and eastern Asia.

The Pacific reef heron, also known as the eastern reef heron or eastern reef egret, is a species of heron found throughout southern Asia and Oceania. It occurs in two colour morphs with either slaty grey or pure white plumage. The sexes are similar in appearance.

Nycticorax is a genus of night herons. The name Nycticorax means "night raven" and derives from the Ancient Greek νύκτος, nuktos "night" and κοραξ, korax, "raven". It refers to the largely nocturnal feeding habits of this group of birds, and the croaking crow-like call of the best known species, the black-crowned night heron.

The nankeen night heron is a heron that belongs to the genus Nycticorax and the family Ardeidae. Due to its distinctive reddish-brown colour, it is also commonly referred to as the rufous night heron. It is primarily nocturnal and is observed in a broad range of habitats, including forests, meadows, shores, reefs, marshes, grasslands, and swamps. The species is 55 to 65 cm in length, with rich cinnamon upperparts and white underparts. The nankeen night heron has a stable population size, and is classified as a species of least concern by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).

Ardea is a genus of herons. These herons are generally large in size, typically 80–100 cm or more in length.

The terrestrial fauna of the Cocos (Keeling) Islands is unsurprisingly depauperate, because of the small land area of the islands, their lack of diverse habitats, and their isolation from large land-masses. However, the fauna dependent on marine resources is much richer.

The cocoi heron is a species of long-legged wading bird in the heron family Ardeidae found across South America. It has predominantly pale grey plumage with a darker grey crest. A carnivore, it hunts fish and crustaceans in shallow water.

Vedanthangal Bird Sanctuary is a 30-hectare (74-acre) protected area located in the Madurantakam taluk of the Chengalpattu District in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. The sanctuary is about 75 kilometres (47 mi) from Chennai on National Highway 45 ([NH45]). It is easily reachable from Madurantakam and Chengalpattu. More than 40,000 birds, from various parts of the world visit the sanctuary during the migratory season every year. Vedanthangal is home to migratory birds such as pintail, garganey, grey wagtail, blue-winged teal, common sandpiper and the like. It has been designated as a protected Ramsar site since 2022.
In the 10th edition of Systema Naturae, published in 1758, the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus described 554 species of bird and gave each a binomial name.