
America was a 19th-century racing yacht and first winner of the America's Cup international sailing trophy.

Peter Duck is the third book in the Swallows and Amazons series by Arthur Ransome. The Swallows and Amazons sail to Crab Island with Captain Flint and Peter Duck, an old sailor, to recover buried treasure. During the voyage the Wildcat is chased by another vessel, the Viper, whose piratical crew are also intending to recover the treasure.

The Flint School was a preparatory school founded by educators George and Betty Stoll. Based in Sarasota, Florida, United States, it operated aboard first one, then two, school ships from 1969 to 1981. Girls as well as boys aged 12 to 18 sailed the world aboard the steel-hulled auxiliary schooners Te Vega, and teQuest while studying an academic curriculum. The school was one of very few educational institutions of any kind during the period to stress free-market or libertarian thought, making it in some ways akin to Hillsdale College. In its pedagogy, the Flint School combined elements from Alan Villiers' earlier seaborne program with Maria Montessori's Casa dei Bambini.

USS Mayflower (PY-1) was a 275 ft (84 m), 2,690 t (2,650 LT) motor vessel originally built as a private yacht that went on to serve in a variety of military, governmental, and commercial roles.

Te Vega is a two-masted, gaff-rigged auxiliary schooner. Originally launched as the Etak, she was designed by New York naval architects Cox & Stevens in 1929 for American businessman Walter Graeme Ladd and his wife, Catherine ("Kate") Everit Macy Ladd. Etak was built at the Friedrich Krupp Germaniawerft shipyard in Kiel, Germany, and launched in 1930. During World War II she served the US Navy as Juniata (IX-77). She is among the largest steel-hulled schooners afloat.

The S.S.S.Lotus is a historic gaff rigged schooner. Her home port is Sodus Bay in Wayne County, New York, United States. She is owned and operated by the "Friends of the Schooner Lotus."

The first USS Machias (PG-5), a schooner-rigged gunboat, was laid down in February 1891 by Bath Iron Works, Bath, Maine. She was launched on 8 December 1891. She was sponsored by Miss Ethel Hyde, daughter of President Hyde of Bath Iron Works and commissioned at Portsmouth Navy Yard, Kittery, Maine, 20 July 1893, Commander Charles J. Train in command.
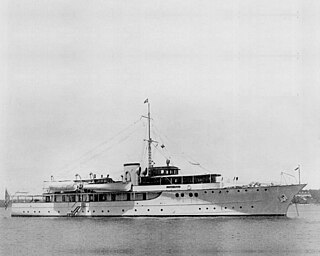
USS Moonstone (PYc-9) was a coastal patrol yacht in the service of the United States Navy. She was built in 1929 as Nancy Baker by Germaniawerft in Kiel, Germany, later renamed Mona, and subsequently acquired by the Navy as the Lone Star on 10 February 1941. Renamed Moonstone and designated PYc-9, she was converted for U.S. Navy service in Jacksonville, Florida, and commissioned on 10 April 1941. She was named for the gemstone moonstone.

USS Hilo (AGP-2) was a converted yacht that saw service as a motor torpedo boat tender in the United States Navy during World War II. It was originally the yacht Caroline built for Eldridge R. Johnson and launched 18 July 1931. Caroline was at the time the second largest yacht and largest American built Diesel yacht. It was built with a laboratory as well as palatial quarters and was loaned and equipped by Johnson for the Johnson-Smithsonian Deep-Sea Expedition of 1933 that explored the Puerto Rico Trench. The yacht was sold in 1938 to William B. Leeds and renamed Moana replacing an earlier Leeds yacht of the same name.
USS Leader (PYc-42) was a Leader-class patrol boat acquired by the U.S. Navy for the task of patrolling coastal areas during World War II when there was the danger of enemy submarine activity.

USS Sturdy (PC-460/PYc-50) was a yacht converted to a patrol boat acquired by the U.S. Navy for the task of patrolling the coastal waters of the U.S. East Coast during World War II. Her primary task was to guard the coastal area against German submarines.

The three-masted schooner Victory Chimes, also known as Edwin and Maud or Domino Effect, is a US National Historic Landmark. She is the last surviving Chesapeake Ram schooner. The boat on the Maine State Quarter is meant to resemble the Victory Chimes.
USS Felicia (PYc-35) was a yacht acquired by the United States Navy during World War II. Felicia was outfitted as a patrol craft by the Navy, and was assigned to patrol the New England waters. She was based out of Newport, Rhode Island until 16 December 1943 when she was based out of Boston, Massachusetts, as a training ship for naval cadets at Harvard University. Post-war she was decommissioned and transferred to the Maritime Commission.

S/Y Argo is a two-masted Marconi rigged schooner. She is owned and operated by Seamester Study Abroad Programs as one of three sail training vessels the company operates. Argo is certified and inspected by the British Maritime and Coastguard Agency as a Category “0” vessel, allowing her unrestricted operation in the world's oceans. She is registered in Road Town, Tortola, British Virgin Islands.

USS Opal (PYc-8), formerly the yacht named Coronet (1928), was a patrol boat in the United States Navy during World War II and then served in the Ecuadorian navy.
USS Onkahye was a topsail schooner of the United States Navy. A unique ship in the American Navy under sail, the vessel occupied a significant place in ship development, being the only converted sailing yacht to serve on a distant station before the American Civil War. Its design was influential and it is considered the model for modern American sailing yachts.

Sea Cloud is a sailing cruise ship owned by Sea Cloud Cruises of Hamburg, Germany. Launched as a private yacht as Hussar V for Marjorie Merriweather Post in 1931, she later served as a weather ship for the United States Coast Guard and United States Navy during World War II, when she became the U.S. military's first racially integrated warship since the American Civil War. After the war, Sea Cloud was returned to private ownership, serving as a yacht for numerous people, including as presidential yacht of the Dominican Republic. Since 1979, Sea Cloud has been used as a cruise ship.

The Shearwater is an 81.5-foot (24.8 m) wooden schooner docked in Lower Manhattan in New York City in the U.S. state of New York. The schooner was designed by Theodore Donald Wells and built by the Rice Brothers Corporation in East Boothbay, Maine in 1929. During World War II, it was requisitioned into the United States Coast Guard to patrol for German U-boats. The Shearwater completed a circumnavigation of the world in the early-1980s and later worked as a research laboratory for the University of Pennsylvania's Institute of Environmental Medicine. Docked about 200 yards (180 m) west of the site of the World Trade Center, it is operated by Manhattan by Sail, which gives 90-minute-long tours of New York Harbor, and is licensed to carry 48 passengers. The schooner was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2009.
When and If is a yacht designed by John Alden and commissioned by then Colonel George S. Patton, a widely regarded American war hero. It was built in 1939 as a private yacht by boatbuilder F.F. Pendleton in Wiscasset, Maine. It was constructed of double planked mahogany over black locust frames and an oak keel.

Mariette is a classic two-masted gaff schooner, designed and built by Nathanael Greene Herreshoff in 1915 for Harold S. Vanderbilt. She now sails out of Antibes, France, under the French flag.
















