Related Research Articles

The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScript.

Markuplanguage refers to a text-encoding system consisting of a set of symbols inserted in a text document to control its structure, formatting, or the relationship between its parts. Markup is often used to control the display of the document or to enrich its content to facilitating automated processing. A markup language is a set of rules governing what markup information may be included in a document and how it is combined with the content of the document in a way to facilitate use by humans and computer programs. The idea and terminology evolved from the "marking up" of paper manuscripts, which is traditionally written with a red pen or blue pencil on authors' manuscripts.

The Standard Generalized Markup Language is a standard for defining generalized markup languages for documents. ISO 8879 Annex A.1 states that generalized markup is "based on two postulates":
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable.
DocBook is a semantic markup language for technical documentation. It was originally intended for writing technical documents related to computer hardware and software, but it can be used for any other sort of documentation.

In computing, a hyperlink, or simply a link, is a digital reference to data that the user can follow or be guided by clicking or tapping. A hyperlink points to a whole document or to a specific element within a document. Hypertext is text with hyperlinks. The text that is linked from is known as anchor text. A software system that is used for viewing and creating hypertext is a hypertext system, and to create a hyperlink is to hyperlink. A user following hyperlinks is said to navigate or browse the hypertext.
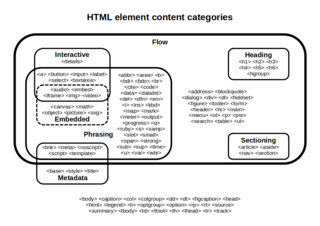
An HTML element is a type of HTML document component, one of several types of HTML nodes. The first used version of HTML was written by Tim Berners-Lee in 1993 and there have since been many versions of HTML. The most commonly used version is HTML 4.01, which became official standard in December 1999. An HTML document is composed of a tree of simple HTML nodes, such as text nodes, and HTML elements, which add semantics and formatting to parts of document. Each element can have HTML attributes specified. Elements can also have content, including other elements and text.
YAML is a human-readable data-serialization language. It is commonly used for configuration files and in applications where data is being stored or transmitted. YAML targets many of the same communications applications as Extensible Markup Language (XML) but has a minimal syntax which intentionally differs from Standard Generalized Markup Language (SGML). It uses both Python-style indentation to indicate nesting, and a more compact format that uses [...] for lists and {...} for maps thus JSON files are valid YAML 1.2.
In web development, "tag soup" is a pejorative for syntactically or structurally incorrect HTML written for a web page. Because web browsers have historically treated structural or syntax errors in HTML leniently, there has been little pressure for web developers to follow published standards, and therefore there is a need for all browser implementations to provide mechanisms to cope with the appearance of "tag soup", accepting and correcting for invalid syntax and structure where possible.
A lightweight markup language (LML), also termed a simple or humane markup language, is a markup language with simple, unobtrusive syntax. It is designed to be easy to write using any generic text editor and easy to read in its raw form. Lightweight markup languages are used in applications where it may be necessary to read the raw document as well as the final rendered output.
JavaScript Style Sheets (JSSS) was a stylesheet language technology proposed by Netscape Communications in 1996 to provide facilities for defining the presentation of webpages. It was an alternative to the Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) technology.
The term CDATA, meaning character data, is used for distinct, but related, purposes in the markup languages SGML and XML. The term indicates that a certain portion of the document is general character data, rather than non-character data or character data with a more specific, limited structure.
In HTML, div and span tags are elements used to define parts of a document, so that they are identifiable when a unique classification is necessary. Where other HTML elements such as p (paragraph), em (emphasis), and so on, accurately represent the semantics of the content, the additional use of span and div tags leads to better accessibility for readers and easier maintainability for authors. Where no existing HTML element is applicable, span and div can valuably represent parts of a document so that HTML attributes such as class, id, lang, or dir can be applied.
Semantic HTML is the use of HTML markup to reinforce the semantics, or meaning, of the information in web pages and web applications rather than merely to define its presentation or look. Semantic HTML is processed by traditional web browsers as well as by many other user agents. CSS is used to suggest its presentation to human users.
Extensible HyperText Markup Language (XHTML) is part of the family of XML markup languages. It mirrors or extends versions of the widely used HyperText Markup Language (HTML), the language in which Web pages are formulated.

Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is a style sheet language used for describing the presentation of a document written in a markup language such as HTML or XML. CSS is a cornerstone technology of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and JavaScript.
A structured document is an electronic document where some method of markup is used to identify the whole and parts of the document as having various meanings beyond their formatting. For example, a structured document might identify a certain portion as a "chapter title" rather than as "Helvetica bold 24" or "indented Courier". Such portions in general are commonly called "components" or "elements" of a document.
HTML attributes are special words used inside the opening tag to control the element's behaviour. HTML attributes are a modifier of an HTML element type. An attribute either modifies the default functionality of an element type or provides functionality to certain element types unable to function correctly without them. In HTML syntax, an attribute is added to an HTML start tag.

In web development, the CSS box model refers to how HTML elements are modeled in browser engines and how the dimensions of those HTML elements are derived from CSS properties. It is a fundamental concept for the composition of HTML webpages. The guidelines of the box model are described by web standards World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) specifically the CSS Working Group. For much of the late-1990s and early 2000s there had been non-standard compliant implementations of the box model in mainstream browsers. With the advent of CSS2 in 1998, which introduced the box-sizing property, the problem had mostly been resolved.
XHTML+RDFa is an extended version of the XHTML markup language for supporting RDF through a collection of attributes and processing rules in the form of well-formed XML documents. XHTML+RDFa is one of the techniques used to develop Semantic Web content by embedding rich semantic markup. Version 1.1 of the language is a superset of XHTML 1.1, integrating the attributes according to RDFa Core 1.1. In other words, it is an RDFa support through XHTML Modularization.
References
- ↑ "4.4.4 The blockquote element — HTML5". World Wide Web Consortium . Retrieved 11 November 2015.
- ↑ HTML definition of ‘blockquote’