Related Research Articles
In computing, a file server is a computer attached to a network that provides a location for shared disk access, i.e. storage of computer files that can be accessed by the workstations that are able to reach the computer that shares the access through a computer network. The term server highlights the role of the machine in the traditional client–server scheme, where the clients are the workstations using the storage. A file server does not normally perform computational tasks or run programs on behalf of its client workstations.
Internet Small Computer Systems Interface or iSCSI is an Internet Protocol-based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities. iSCSI provides block-level access to storage devices by carrying SCSI commands over a TCP/IP network. iSCSI facilitates data transfers over intranets and to manage storage over long distances. It can be used to transmit data over local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), or the Internet and can enable location-independent data storage and retrieval.

Network-attached storage (NAS) is a file-level computer data storage server connected to a computer network providing data access to a heterogeneous group of clients. The term "NAS" can refer to both the technology and systems involved, or a specialized device built for such functionality.
The Write Anywhere File Layout (WAFL) is a proprietary file system that supports large, high-performance RAID arrays, quick restarts without lengthy consistency checks in the event of a crash or power failure, and growing the filesystems size quickly. It was designed by NetApp for use in its storage appliances like NetApp FAS, AFF, Cloud Volumes ONTAP and ONTAP Select.

Xsan is Apple Inc.'s storage area network (SAN) or clustered file system for macOS. Xsan enables multiple Mac desktop and Xserve systems to access shared block storage over a Fibre Channel network. With the Xsan file system installed, these computers can read and write to the same storage volume at the same time. Xsan is a complete SAN solution that includes the metadata controller software, the file system client software, and integrated setup, management and monitoring tools.
Lustre is a type of parallel distributed file system, generally used for large-scale cluster computing. The name Lustre is a portmanteau word derived from Linux and cluster. Lustre file system software is available under the GNU General Public License and provides high performance file systems for computer clusters ranging in size from small workgroup clusters to large-scale, multi-site systems. Since June 2005, Lustre has consistently been used by at least half of the top ten, and more than 60 of the top 100 fastest supercomputers in the world, including the world's No. 1 ranked TOP500 supercomputer in November 2022, Frontier, as well as previous top supercomputers such as Fugaku, Titan and Sequoia.
ATA over Ethernet (AoE) is a network protocol developed by the Brantley Coile Company, designed for simple, high-performance access of block storage devices over Ethernet networks. It is used to build storage area networks (SANs) with low-cost, standard technologies.
A NetApp FAS is a computer storage product by NetApp running the ONTAP operating system; the terms ONTAP, AFF, ASA, FAS are often used as synonyms. "Filer" is also used as a synonym although this is not an official name. There are three types of FAS systems: Hybrid, All-Flash, and All SAN Array:
- NetApp proprietary custom-build hardware appliances with HDD or SSD drives called hybrid Fabric-Attached Storage
- NetApp proprietary custom-build hardware appliances with only SSD drives and optimized ONTAP for low latency called ALL-Flash FAS
- All SAN Array build on top of AFF platform, and provide only SAN-based data protocol connectivity.
A clustered file system is a file system which is shared by being simultaneously mounted on multiple servers. There are several approaches to clustering, most of which do not employ a clustered file system. Clustered file systems can provide features like location-independent addressing and redundancy which improve reliability or reduce the complexity of the other parts of the cluster. Parallel file systems are a type of clustered file system that spread data across multiple storage nodes, usually for redundancy or performance.
metaSAN is cross-platform Storage Area Network (SAN) management software developed and sold by Tiger Technology. The product ceased to be developed by the company from 2014, however it will be supported until the end of 2016.
Ceph is a free and open-source software-defined storage platform that provides object storage, block storage, and file storage built on a common distributed cluster foundation. Ceph provides completely distributed operation without a single point of failure and scalability to the exabyte level, and is freely available. Since version 12 (Luminous), Ceph does not rely on any other, conventional filesystem and directly manages HDDs and SSDs with its own storage backend BlueStore and can expose a POSIX filesystem.
StorNext File System (SNFS), colloquially referred to as StorNext is a shared disk file system made by Quantum Corporation. StorNext enables multiple Windows, Linux and Apple workstations to access shared block storage over a Fibre Channel network. With the StorNext file system installed, these computers can read and write to the same storage volume at the same time enabling what is known as a "file-locking SAN." StorNext is used in environments where large files must be shared, and accessed simultaneously by users without network delays, or where a file must be available for access by multiple readers starting at different times. Common use cases include multiple video editor environments in feature film, television and general video post production.

A storage area network (SAN) or storage network is a computer network which provides access to consolidated, block-level data storage. SANs are primarily used to access data storage devices, such as disk arrays and tape libraries from servers so that the devices appear to the operating system as direct-attached storage. A SAN typically is a dedicated network of storage devices not accessible through the local area network (LAN).
Cluster Shared Volumes (CSV) is a feature of Failover Clustering first introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 for use with the Hyper-V role. A Cluster Shared Volume is a shared disk containing an NTFS or ReFS (ReFS: Windows Server 2012 R2 or newer) volume that is made accessible for read and write operations by all nodes within a Windows Server Failover Cluster.
Metadata controller is a storage area network (SAN) technology for managing file locking, space allocation and data access authorization. This is needed when several clients are given block level access to the same disk volume, data storage sharing.
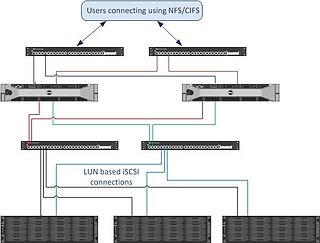
Dell Fluid File System, or FluidFS, is a shared-disk filesystem made by Dell that provides distributed file systems to clients. Customers buy an appliance: a combination of purpose-built network-attached storage (NAS) controllers with integrated primary and backup power supplies attached to block level storage via the iSCSI or Fiber Channel protocol. A single Dell FluidFS appliance consists of two controllers operating in concert connecting to the back-end storage area network (SAN). Depending on the storage capacity requirements and user preference, FluidFS version 4 NAS appliances can be used with Compellent or EqualLogic SAN arrays. The EqualLogic FS7600 and FS7610 connect to the client network and to Dell's EqualLogic arrays with either 1 Gbit/s (FS7600) or 10 Gbit/s (FS7610) iSCSI protocol. For Compellent, FluidFS is available with either 1 Gbit/s or 10 Gbit/s iSCSI connectivity to the client network and connection to the backend Compellent SAN can be either 8 Gbit/s Fibre Channel or 10 Gbit/s iSCSI.
Object storage is a computer data storage that manages data as objects, as opposed to other storage architectures like file systems which manages data as a file hierarchy, and block storage which manages data as blocks within sectors and tracks. Each object typically includes the data itself, a variable amount of metadata, and a globally unique identifier. Object storage can be implemented at multiple levels, including the device level, the system level, and the interface level. In each case, object storage seeks to enable capabilities not addressed by other storage architectures, like interfaces that are directly programmable by the application, a namespace that can span multiple instances of physical hardware, and data-management functions like data replication and data distribution at object-level granularity.

Dell Technologies PowerFlex, is a commercial software-defined storage product from Dell Technologies that creates a server-based storage area network (SAN) from local server storage using x86 servers. It converts this direct-attached storage into shared block storage that runs over an IP-based network.
ONTAP or Data ONTAP or Clustered Data ONTAP (cDOT) or Data ONTAP 7-Mode is NetApp's proprietary operating system used in storage disk arrays such as NetApp FAS and AFF, ONTAP Select, and Cloud Volumes ONTAP. With the release of version 9.0, NetApp decided to simplify the Data ONTAP name and removed the word "Data" from it, and remove the 7-Mode image, therefore, ONTAP 9 is the successor of Clustered Data ONTAP 8.
References
- ↑ Jimmie Chang (28 September 2006). "Dataquest Insight: China Research Lab Case Study Shows Benefits of 'Homegrown' Advanced Technology". ID Number: G00142484. Gartner. p. 2. Archived from the original on September 27, 2012.
- ↑ James Rogers (27 October 2007). "FalconStor Launches China Venture". Network Computing. Archived from the original on 19 March 2012. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- ↑ "CAS Joins Forces With FalconStor". News release. 26 October 2007. Archived from the original on 19 March 2012. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- ↑ "BlueWhale". Portfolio: Asia. VantagePoint Capital Partners. Archived from the original on 2 October 2011. Retrieved 15 July 2011.
- ↑ "Blue Whale File System to be used for Olympic Satellite". Chinese Academy of Sciences. 21 June 2006. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 15 July 2011.