A land mine, or landmine, is an explosive weapon concealed under or camouflaged on the ground, and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it.

The percussion cap, percussion primer, or caplock, introduced in the early 1820s, is a type of single-use percussion ignition device for muzzle loader firearm locks enabling them to fire reliably in any weather condition. Its invention gave rise to the caplock mechanism or percussion lock system which used percussion caps struck by the hammer to set off the gunpowder charge in rifles and cap and ball firearms. Any firearm using a caplock mechanism is a percussion gun. Any long gun with a cap-lock mechanism and rifled barrel is a percussion rifle. Cap and ball describes cap-lock firearms discharging a single bore-diameter spherical bullet with each shot.
An explosive booster is a sensitive explosive charge that acts as a bridge between a conventional detonator and a low-sensitivity explosive such as TNT. By itself, the initiating detonator would not deliver sufficient energy to set off the low-sensitivity charge. However, it detonates the primary charge, which then delivers an explosive shockwave that is sufficient to detonate the secondary, main, high-energy charge.

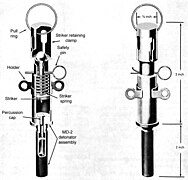
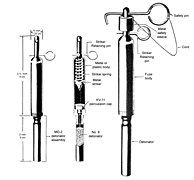
In an explosive, pyrotechnic device, or military munition, a fuse is the part of the device that initiates function. In common usage, the word fuse is used indiscriminately. However, when being specific, the term fuse describes a simple pyrotechnic initiating device, like the cord on a firecracker whereas the term fuze is used when referring to a more sophisticated ignition device incorporating mechanical and/or electronic components, such as a proximity fuze for an M107 artillery shell, magnetic or acoustic fuze on a sea mine, spring-loaded grenade fuze, pencil detonator, or anti-handling device.

A firing pin or striker is a part of the firing mechanism of a firearm that impacts the primer in the base of a cartridge and causes it to fire. In firearms terminology, a striker is a particular type of firing pin where a compressed spring acts directly on the firing pin to provide the impact force rather than it being struck by a hammer.

The Israeli Combat Engineering Corps is the combat engineering forces of the Israel Defense Forces.

In anti-tank warfare, an anti-tank mine is a type of land mine designed to damage or destroy vehicles including tanks and armored fighting vehicles.

A tripwire is a passive triggering mechanism. Typically, a wire or cord is attached to a device for detecting or reacting to physical movement.

The RGD-5 is a post–World War II Soviet anti-personnel fragmentation grenade, designed in the early 1950s. The RGD-5 was accepted into service with the Soviet Army in 1954. It was widely exported, and is still in service with many armies in the Middle East and the former Soviet bloc.

The TM 31-210 Improvised Munitions Handbook is a 256 page United States Army technical manual intended for the United States Army Special Forces. It was first published in 1969 by the Department of the Army.

The M16 mine is a United States-made bounding anti-personnel mine. It was based on captured plans of the World War II era German S-mine and has similar performance. The mine consists of a cast iron body in a thin steel sleeve. A central fuze well on the top of the mine is normally fitted with a pronged M605 pressure/tension (tripwire) fuze. Sufficient pressure on the prongs or tension on an attached tripwire causes the release of a striker. The freed striker is forced into a percussion cap which ignites a short pyrotechnic delay. The purpose of this delay is to allow the victim to move off the top of the mine, to prevent its upward movement from being blocked. Once the delay has burned through, a 4.5-gram black powder charge is ignited, which launches the inner iron body of the mine up into the air. The charge also ignites a second pair of pyrotechnic delays.

An anti-personnel mine or anti-personnel landmine (APL) is a form of mine designed for use against humans, as opposed to an anti-tank mine, which target vehicles. APLs are classified into: blast mines and fragmentation mines; the latter may or may not be a bounding mine.

The OZM-3, OZM-4 and OZM-72 are Soviet manufactured bounding type anti-personnel mines. (fragmentation-barrier mine, in the Russian and other post-Soviet armies as informally called "frog mine" or "witch" )

The PMN series of blast anti-personnel mines were designed and manufactured in the Soviet Union. They are one of the most widely used and commonly found devices during demining operations. They are sometimes nicknamed "black widow" because of their dark casings.
The M7 is a small, metal-cased United States anti-tank blast mine that was used during the Second World War. It was based on the British Hawkins grenade. Approximately 2.5 million were produced before production ceased, and although it has long since been withdrawn from U.S. service, it can be found in Angola, Burma, Cambodia, Chad, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Korea, Lebanon, Myanmar, Somalia, Thailand, and Zambia.

An anti-handling device is an attachment to or an integral part of a landmine or other munition such as some fuze types found in general-purpose air-dropped bombs, cluster bombs and sea mines. It is designed to prevent tampering or disabling, or to target bomb disposal personnel. When the protected device is disturbed, it detonates, killing or injuring anyone within the blast area. There is a strong functional overlap of booby traps and anti-handling devices.

A tripflare is a device used by military forces to secure an area and to guard against infiltration. It consists of tripwire around the area, linked to one or more flares. When the tripwire is triggered, as by someone unsuspectingly disturbing it, the flare is activated and begins burning. The light from the flare simultaneously warns that the perimeter may have been breached and also gives light for investigating. In defensive operations, tripflares are usually placed in predetermined kill zones with machine guns sighted on them.
In military munitions, a fuze is the part of the device that initiates function. In some applications, such as torpedoes, a fuze may be identified by function as the exploder. The relative complexity of even the earliest fuze designs can be seen in cutaway diagrams.

A grenade is an explosive weapon typically thrown by hand, but can also refer to a shell shot from the muzzle of a rifle or a grenade launcher. A modern hand grenade generally consists of an explosive charge ("filler"), a detonator mechanism, an internal striker to trigger the detonator, an arming safety secured by a transport safety. The user removes the transport safety before throwing, and once the grenade leaves the hand the arming safety gets released, allowing the striker to trigger a primer that ignites a fuze, which burns down to the detonator and explodes the main charge.

The A.P. (anti-personnel) Shrapnel Mine is a British bounding mine of World War II.