
Puget Sound is a sound of the Pacific Northwest, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean, and part of the Salish Sea. It is located along the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins, with one major and two minor connections to the open Pacific Ocean via the Strait of Juan de Fuca—Admiralty Inlet being the major connection and Deception Pass and Swinomish Channel being the minor.

In physical geography, a fjord or fiord is a long, narrow inlet with steep sides or cliffs, created by a glacier. Fjords exist on the coasts of Antarctica, British Columbia (Canada), Chile, Denmark, Germany, Greenland (Denmark), the Faroe Islands (Denmark), Montenegro, Iceland, Ireland, Kamchatka (Russia), the Kerguelen Islands (France), Newfoundland and Labrador (Canada), New Zealand, Norway, Novaya Zemlya (Russia), Nunavut (Canada), Quebec (Canada), Argentina, Russia, South Georgia Island, Tasmania (Australia), Scotland and the states of Washington, Maine, and Alaska. Norway's coastline is estimated to be 29,000 km (18,000 mi) long with its nearly 1,200 fjords, but only 2,500 km (1,600 mi) long excluding the fjords.

Olympia is the capital of the U.S. state of Washington and the county seat and largest city of Thurston County. It is 60 miles (100 km) southwest of the state's most populous city, Seattle, and is a cultural center of the southern Puget Sound region.

Thurston County is a county located in the U.S. state of Washington. As of the 2020 census, its population was 294,793. The county seat and largest city is Olympia, the state capital.
Tumwater is a city in Thurston County, Washington, United States. The population was 25,350 at the 2020 census. The city is situated near where the Deschutes River enters Budd Inlet, the southernmost point of Puget Sound; it also borders the state capital of Olympia to the north. Tumwater is the oldest permanent Anglo-American settlement on Puget Sound.

The Squaxin Island Tribe are the descendants of several Lushootseed clans organized under the Squaxin Island Indian Reservation, a Native American tribal government in western Washington state.

The Strait of Georgia or the Georgia Strait is an arm of the Salish Sea between Vancouver Island and the extreme southwestern mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada, and the extreme northwestern mainland coast of Washington, United States. It is approximately 240 kilometres (150 mi) long and varies in width from 20 to 58 kilometres. Along with the Strait of Juan de Fuca and Puget Sound, it is a constituent part of the Salish Sea.

The Deschutes River is a 50-mile-long (80 km) river in the U.S. state of Washington. Its headwaters are in the Bald Hills in Lewis County, and it empties into Budd Inlet of Puget Sound at Olympia in Thurston County. It was given its name by French fur traders, who called it Rivière des Chutes, or "River of the Falls", a translation of the First Nations name for the site.

The Stillaguamish River is a river in the northwestern region of the U.S. state of Washington. It is mainly composed of two forks, the longer North Fork Stillaguamish and the South Fork Stillaguamish. The two forks join near Arlington. From there the Stillaguamish River proper flows for 22 miles (35 km) to Puget Sound. The river's watershed drains part of the Cascade Range north of Seattle.
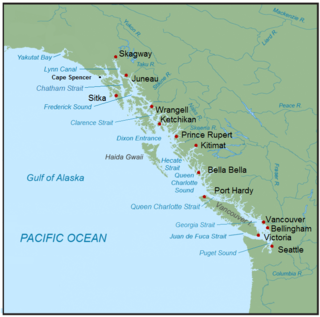
The Inside Passage is a coastal route for ships and boats along a network of passages which weave through the islands on the Pacific Northwest coast of the North American Fjordland. The route extends from southeastern Alaska in the United States, through western British Columbia in Canada, to northwestern Washington state in the United States. Ships using the route can avoid some of the bad weather in the open ocean and may visit some of the many isolated communities along the route. The Inside Passage is heavily travelled by cruise ships, freighters, tugs with tows, fishing craft, pleasure craft, and ships of the Alaska Marine Highway, BC Ferries, and Washington State Ferries systems. Coast Guard vessels of both Canada and the United States patrol and transit in the Passage.

The Tumwater Falls are a series of cascades on the Deschutes River in Tumwater, Washington, United States. They are located near where the river empties into Budd Inlet, a southerly arm of Puget Sound in Olympia.

Capitol Lake is a 3 kilometer long, 260-acre (1.1 km2) artificial lake at the mouth of Deschutes River in Tumwater/Olympia, Washington. The Olympia Brewery sits on Capitol Lake in Tumwater, just downstream from where the Tumwater Falls meet the artificial lake. The Washington State Department of Enterprise Services (DES) manages the lake, as part of The Washington State Capitol Campus.

The Salish Sea is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean located in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. state of Washington. It includes the Strait of Georgia, the Strait of Juan de Fuca, Puget Sound, and an intricate network of connecting channels and adjoining waterways.

The history of Olympia, Washington, includes long-term habitation by Native Americans, charting by a famous English explorer, settlement of the town in the 1840s, the controversial siting of a state college in the 1960s and the ongoing development of arts and culture from a variety of influences.

Totten Inlet lies in the southern end of Puget Sound in the U.S. state of Washington. The inlet extends 9 miles (14 km) southwest from the western end of Squaxin Passage, and much of the county line between Mason and Thurston counties runs down the center of it. A spit extends west for about 300 feet (91 m) from Steamboat Island. The inlet shoals gradually to near Burns Point, 100 feet high, on the south shore, where it bares at low tide.
Eld Inlet is an inlet located at the southern end of Puget Sound in Thurston County, Washington. It is the second southernmost arm of Puget Sound after neighboring Budd Inlet.

Indian Creek is a stream in Thurston County in the U.S. state of Washington. It is a 3-mile Olympian creek. Its source is a wetland along the northern end of South Bay Road. It enters Budd Inlet at East Bay, having first joined with Moxlie Creek. It can most easily be accessed between Boulevard Road and Frederick Road along the Karen Fraser Woodland Trail. American Indian settlements near the creek's course may account for the name.

Mud Bay is the southernmost reach of Puget Sound, at Eld Inlet just outside the city limits of Olympia, Washington. The name Eld Inlet was officially bestowed after a member of the U.S. Navy's Wilkes Expedition, but "Mud Bay" is a local, informal adoption.

South Puget Sound is the southern reaches of Puget Sound in Southwest Washington, in the United States' Pacific Northwest. It is one of five major basins encompassing the entire Sound, and the shallowest basin, with a mean depth of 37 meters (121 ft). Exact definitions of the region vary: the state's Department of Fish and Wildlife counts all of Puget Sound south of the Tacoma Narrows for fishing regulatory purposes. The same agency counts Mason, Jefferson, Kitsap, Pierce and Thurston Counties for wildlife management. The state's Department of Ecology defines a similar area south of Colvos Passage.
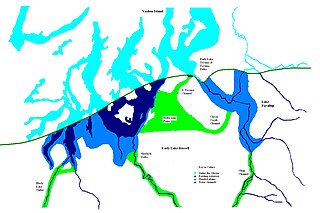
During the Vashon Glaciation a series of lakes formed along the southern margin of the Cordilleran Ice Cap. In the Puget Sound depression, a series of lakes developed, of which Lake Russell was the largest and the longest lasting. Early Lake Russell’s surface was at 160 ft (49 m) above sea level, draining across the divide at Shelton, Washington into early Glacial Lake Russell. When the ice margin receded northward, the lake expanded. When it reached the Clifton channel outlet, the water levels dropped to 120 ft (37 m) above sea level. The new longer and lower level lake is referred to as Lake Hood. The glacier continued to retreat until the northern outlet of the Hood Canal was reached as the water level equalized with Glacial Lake Russell becoming part of that body of water.




















