
Butter is a dairy product made from the fat and protein components of churned cream. It is a semi-solid emulsion at room temperature, consisting of approximately 80% butterfat. It is used at room temperature as a spread, melted as a condiment, and used as a fat in baking, sauce-making, pan frying, and other cooking procedures.

A dairy is a place where milk is stored and where butter, cheese and other dairy products are made, or a place where those products are sold. It may be a room, a building or a larger establishment. In the United States, the word may also describe a dairy farm or the part of a mixed farm dedicated to milk for human consumption, whether from cows, buffaloes, goats, sheep, horses or camels.

The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) is the agricultural policy of the European Union. It implements a system of agricultural subsidies and other programmes. It was introduced in 1962 and has since then underwent several changes to reduce the EEC budget cost and consider rural development in its aims. It has however, been criticised on the grounds of its cost, its environmental, and humanitarian effects.
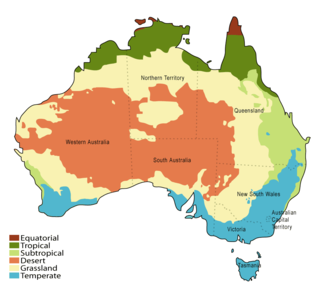
Although Australia is mostly arid, the nation is a major agricultural producer and exporter, with over 325,300 employed in agriculture, forestry and fishing as of February 2015. Agriculture and its closely related sectors earn $155 billion-a-year for a 12% share of GDP. Farmers and grazers own 135,997 farms, covering 61% of Australia's landmass. Across the country there is a mix of irrigation and dry-land farming. The success of Australia to become a major agricultural power despite the odds is facilitated by its policies of long-term visions and promotion of agricultural reforms that greatly increased the country's agricultural industry.

A price floor is a government- or group-imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product, good, commodity, or service. A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective. The equilibrium price, commonly called the "market price", is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the (equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change, often described as the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Governments use price floors to keep certain prices from going too low.

Government cheese is processed cheese provided to welfare beneficiaries, Food Stamp recipients, and the elderly receiving Social Security in the United States, as well as to food banks and churches. This processed cheese was used in military kitchens during World War II and has been used in schools since the 1950s.

Agriculture, farming, and fishing form the primary sector of industry of the Japanese economy together with the Japanese mining industry, but together they account for only 1.3% of gross national product. Only 20% of Japan's land is suitable for cultivation, and the agricultural economy is highly subsidized.

Agriculture in Thailand is highly competitive, diversified and specialized and its exports are very successful internationally. Rice is the country's most important crop, with some 60 percent of Thailand's 13 million farmers growing it on almost half of Thailand's cultivated land. Thailand is a major exporter in the world rice market. Rice exports in 2014 amounted to 1.3 percent of GDP. Agricultural production as a whole accounts for an estimated 9-10.5 percent of Thai GDP. Forty percent of the population work in agriculture-related jobs. The farmland they work was valued at US$2,945/rai in 2013. Most Thai farmers own fewer than eight ha (50 rai) of land.
A buffer stock scheme is an attempt to use commodity storage for the purposes of stabilising prices in an entire economy or an individual (commodity) market. Specifically, commodities are bought when a surplus exists in the economy, stored, and are then sold from these stores when economic shortages in the economy occur.
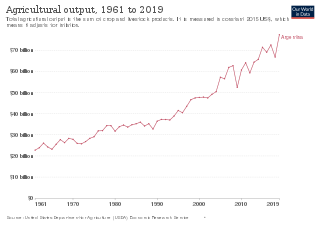
Agriculture is one of the bases of Argentina's economy.

Agriculture is one of the dominant parts of Senegal's economy, despite the fact that Senegal lies within the drought-prone Sahel region. As only about 5% of the land is irrigated, Senegal continues to rely on rain-fed agriculture. Agriculture occupies about 75% of the workforce. Despite a relatively wide variety of agricultural production, the majority of farmers produce for subsistence needs. Millet, rice, corn, and sorghum are the primary food crops grown in Senegal. Production is subject to drought and threats of pests such as locusts, birds, fruit flies, and white flies. Moreover, the effects of climate change in Senegal are expected to severely harm the agricultural economy due to extreme weather such as drought, as well as increased temperatures.

Many farmers in India depend on animal husbandry for their livelihood. In addition to supplying milk, meat, eggs, wool, their castings (dung) and hides, animals, mainly bullocks, are the major source of power for both farmers and dairies. Thus, animal husbandry plays an important role in the rural economy. The gross value of output from this sector was 8,123 billion Rupees in FY 2015–16.
Uganda's favorable soil conditions and climate have contributed to the country's agricultural success. Most areas of Uganda have usually received plenty of rain. In some years, small areas of the southeast and southwest have averaged more than 150 millimeters per month. In the north, there is often a short dry season in December and January. Temperatures vary only a few degrees above or below 20 °C but are moderated by differences in altitude.

In New Zealand, agriculture is the largest sector of the tradable economy. The country exported NZ$46.4 billion worth of agricultural products in the 12 months to June 2019, 79.6% of the country's total exported goods. The agriculture, forestry and fisheries sector directly contributed $12.653 billion of the national GDP in the 12 months to September 2020, and employed 143,000 people, 5.9% of New Zealand's workforce, as of the 2018 census.

The share of agriculture in Austria in the Austrian economy declined steadily after World War II, agriculture continues to represent an important element of the economy because of its social and political significance. The Chamber of Agriculture remains on an equal level with the chambers of commerce and labor, although its members produce only a fraction of the GDP that industrial and commercial workers produce.

Agriculture in Spain is important to the national economy. The primary sector activities accounting for agriculture, husbandry, fishing and silviculture represented a 2.7% of the Spanish GDP in 2017, with an additional 2.5% represented by the agrofood industry.

Dairy farming is one of the largest agricultural sectors in Canada. Dairy has a significant presence in all of the provinces and is one of the top two agricultural commodities in seven out of ten provinces.

Canada's supply management, abbreviated SM, is a national agricultural policy framework used across the country, which controls the supply of dairy, poultry and eggs through production and import controls and pricing mechanisms. The supply management system was authorized by the 1972 Farm Products Agencies Act, which established the two national agencies that oversee the system. The Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada federal department is responsible for both the Canadian Dairy Commission and its analogue for eggs, chicken and turkey products, the Farm Products Council of Canada. Five national supply management organizations, the SM-5 Organizations — Egg Farmers of Canada (EFC), Turkey Farmers of Canada (TFC), Chicken Farmers of Canada (CFC), the Canadian Hatching Egg Producers (CHEP) and the Ottawa-based Canadian Dairy Commission (CDC), a Crown corporation — in collaboration with provincial and national governing agencies, organizations and committees, administer the supply management system.

Trump administration farmer bailouts are a series of United States bailout programs introduced during the presidency of Donald Trump as a consequence of his "America First" economic policy to help US farmers suffering due to the US-China trade war and trade disputes with European Union, Japan, Canada, Mexico, and others. China and respectively European reconcilable tariffs imposed on peanut butter, soybeans, orange juice, and other agriculture products had hit hard, especially swing states, such as Iowa, Ohio, and Wisconsin.

Dairy plays a significant part in numerous aspects of Indian society, including cuisine, religion, culture, and the economy.


















