Related Research Articles

Positron emission tomography (PET) is a functional imaging technique that uses radioactive substances known as radiotracers to visualize and measure changes in metabolic processes, and in other physiological activities including blood flow, regional chemical composition, and absorption. Different tracers are used for various imaging purposes, depending on the target process within the body. For example, 18
F
-FDG is commonly used to detect cancer, NaF18
F
is widely used for detecting bone formation, and oxygen-15 is sometimes used to measure blood flow.
A CT scan, also known as computed tomography scan is a medical imaging technique used in radiology (x-ray) to obtain detailed internal images of the body noninvasively for diagnostic purposes. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers or radiology technologists.

The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) is an agency of the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) that has authority over the security of transportation systems within, and connecting to the United States. It was created as a response to the September 11 attacks to improve airport security procedures and consolidate air travel security under a dedicated federal administrative law enforcement agency.

An X-ray generator is a device that produces X-rays. Together with an X-ray detector, it is commonly used in a variety of applications including medicine, X-ray fluorescence, electronic assembly inspection, and measurement of material thickness in manufacturing operations. In medical applications, X-ray generators are used by radiographers to acquire x-ray images of the internal structures of living organisms, and also in sterilization.

Airport security includes the techniques and methods used in an attempt to protect passengers, staff, aircraft, and airport property from accidental/malicious harm, crime, terrorism, and other threats.

Tomographic reconstruction is a type of multidimensional inverse problem where the challenge is to yield an estimate of a specific system from a finite number of projections. The mathematical basis for tomographic imaging was laid down by Johann Radon. A notable example of applications is the reconstruction of computed tomography (CT) where cross-sectional images of patients are obtained in non-invasive manner. Recent developments have seen the Radon transform and its inverse used for tasks related to realistic object insertion required for testing and evaluating computed tomography use in airport security.

Backscatter X-ray is an advanced X-ray imaging technology. Traditional X-ray machines detect hard and soft materials by the variation in x-ray intensity transmitted through the target. In contrast, backscatter X-ray detects the radiation that reflects from the target. It has potential applications where less-destructive examination is required, and can operate even if only one side of the target is available for examination.

Explosive detection is a non-destructive inspection process to determine whether a container contains explosive material. Explosive detection is commonly used at airports, ports and for border control.

A baggage handling system (BHS) is a type of conveyor system installed in airports that transports checked luggage from ticket counters to areas where the bags can be loaded onto airplanes. A BHS also transports checked baggage coming from airplanes to baggage claims or to an area where the bag can be loaded onto another airplane.
Bernard Marshall Gordon is an American engineer, inventor, entrepreneur, and philanthropist. He is considered "the father of high-speed analog-to-digital conversion".
Terahertz tomography is a class of tomography where sectional imaging is done by terahertz radiation. Terahertz radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a frequency between 0.1 and 10 THz; it falls between radio waves and light waves on the spectrum; it encompasses portions of the millimeter waves and infrared wavelengths. Because of its high frequency and short wavelength, terahertz wave has a high signal-to-noise ratio in the time domain spectrum. Tomography using terahertz radiation can image samples that are opaque in the visible and near-infrared regions of the spectrum. Terahertz wave three-dimensional (3D) imaging technology has developed rapidly since its first successful application in 1997, and a series of new 3D imaging technologies have been proposed successively.

A full-body scanner is a device that detects objects on or inside a person's body for security screening purposes, without physically removing clothes or making physical contact. Unlike metal detectors, full-body scanners can detect non-metal objects, which became an increasing concern after various airliner bombing attempts in the 2000s and some scanners can also detect swallowed items or hidden in body cavities of a person. Starting in 2007, full-body scanners started supplementing metal detectors at airports and train stations in many countries.

A millimeter wave scanner is a whole-body imaging device used for detecting objects concealed underneath a person’s clothing using a form of electromagnetic radiation. Typical uses for this technology include detection of items for commercial loss prevention, smuggling, and screening for weapons at government buildings and airport security checkpoints.

Rapiscan Systems is an American privately held company that specialises in walk-through metal detectors and X-ray machines for screening airport luggage and cargo. The company is owned by OSI Systems.

Industrial computed tomography (CT) scanning is any computer-aided tomographic process, usually X-ray computed tomography, that uses irradiation to produce three-dimensional internal and external representations of a scanned object. Industrial CT scanning has been used in many areas of industry for internal inspection of components. Some of the key uses for industrial CT scanning have been flaw detection, failure analysis, metrology, assembly analysis and reverse engineering applications. Just as in medical imaging, industrial imaging includes both nontomographic radiography and computed tomographic radiography.

American Science and Engineering Inc, (AS&E) is an American manufacturer of advanced X-ray equipment and related technologies, founded in 1958 by Martin Annis, PHd. Annis asked George W. Clark to join him in starting his company. Their primary work in the beginning was as a developer for NASA. Annis brought on as Chairman of the Board of Directors, Bruno Rossi, PhD, of Bruno Rossi of MIT to help guide their efforts. Rossi had earlier confirmed the existence of cosmic rays, and postulated that black holes would emit tremendous bursts of cosmic radiation as they swallowed celestial objects. At the urging of Rossi, Annis brought on board Riccardo Giacconi, from Italy, to work on the effort to develop a detector. As a consultant to American Science and Engineering, Inc., Rossi initiated the rocket experiments that discovered the first extra-solar source of X-rays, Scorpius X-1.[120].[121]. Despite Rossi's pivotal discoveries and work in this area, in 2002 Richardo Giacconi alone won the Nobel prize for its discovery and invention Nobel Prize in Physics. The AS&E team made possible the Einstein Observatory. Throughout his tenure as president of AS&E, Annis was a leading inventor/scientist for the company, including inventing the backscatter technology, which enabled the detection of plastic explosives, he also invented the body scanner, originally developed as a machine to detect contraband in/on people for prisons, but later adopted for use in airports. Body scanners are now standard as part of pre-boarding security screenings in airports around the world.. AS&E also produced the first 4th generation CT scanner for commercial use in 1976.

Positron emission tomography–magnetic resonance imaging (PET–MRI) is a hybrid imaging technology that incorporates magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) soft tissue morphological imaging and positron emission tomography (PET) functional imaging.
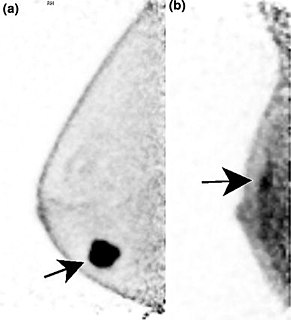
Positron emission mammography (PEM) is a nuclear medicine imaging modality used to detect or characterise breast cancer. Mammography typically refers to x-ray imaging of the breast, while PEM uses an injected positron emitting isotope and a dedicated scanner to locate breast tumors. Scintimammography is another nuclear medicine breast imaging technique, however it is performed using a gamma camera. Breasts can be imaged on standard whole-body PET scanners, however dedicated PEM scanners offer advantages including improved resolution.

The history of X-ray computed tomography dates back to at least 1917 with the mathematical theory of the Radon transform In October 1963, William H. Oldendorf received a U.S. patent for a "radiant energy apparatus for investigating selected areas of interior objects obscured by dense material". The first clinical CT scan was performed in 1971 using a scanner invented by Sir Godfrey Hounsfield.
Airport privacy involves the right of personal privacy for passengers when it comes to screening procedures, surveillance, and personal data being stored at airports. This practice intertwines airport security measures and privacy specifically the advancement of security measures following the 9/11 attacks in the United States and other global terrorist attacks. Several terrorist attacks, such as 9/11, have led airports all over the world to look to the advancement of new technology such as body and baggage screening, detection dogs, facial recognition, and the use of biometrics in electronic passports. Amidst the introduction of new technology and security measures in airports and the growing rates of travelers there has been a rise of risk and concern in privacy.
References
- ↑ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2006-04-27. Retrieved 2006-09-10.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Minsk National Airport deploys Rapiscan RTT 110 aviation baggage security screen". Airport Technology. 2014-04-08. Retrieved 2022-06-21.
- ↑ "Explosive Detection System - Bag / Parcel Screening | RTT". Rapiscan Systems. 2018-03-15. Retrieved 2022-06-21.
- ↑ Megherbi, N.; Flitton, G.T.; Breckon, T.P. (September 2010). "A Classifier based Approach for the Detection of Potential Threats in CT based Baggage Screening". Proc. International Conference on Image Processing (PDF). IEEE. pp. 1833–1836. doi:10.1109/ICIP.2010.5653676. ISBN 978-1-4244-7992-4. S2CID 3679917 . Retrieved 5 November 2013.
- ↑ Megherbi, N.; Han, J.; Flitton, G.T.; Breckon, T.P. (September 2012). "A Comparison of Classification Approaches for Threat Detection in CT based Baggage Screening". Proc. International Conference on Image Processing (PDF). IEEE. pp. 3109–3112. doi:10.1109/ICIP.2012.6467558. ISBN 978-1-4673-2533-2. S2CID 6924816 . Retrieved 5 November 2013.
- Airport Control and Security Systems, CATs at the airport, 1 November 2000
- Boeing Airport Security, Explosives Detection Systems (EDS)