
Cannabis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: Cannabis sativa, Cannabis indica, and Cannabis ruderalis; C. ruderalis may be included within C. sativa; all three may be treated as subspecies of a single species, C. sativa; or C. sativa may be accepted as a single undivided species. The genus is widely accepted as being indigenous to and originating from Asia.
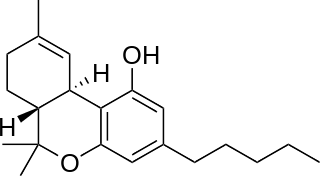
Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is the principal psychoactive constituent of cannabis and one of at least 113 total cannabinoids identified on the plant. Although the chemical formula for THC (C21H30O2) describes multiple isomers, the term THC usually refers to the Delta-9-THC isomer with chemical name (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Like most pharmacologically active secondary metabolites of plants, THC is a lipid found in cannabis, assumed to be involved in the plant's evolutionary adaptation, putatively against insect predation, ultraviolet light, and environmental stress.

Cannabis sativa is an annual herbaceous flowering plant indigenous to Eastern Asia, but now of cosmopolitan distribution due to widespread cultivation. It has been cultivated throughout recorded history, used as a source of industrial fiber, seed oil, food, recreation, religious and spiritual moods and medicine. Each part of the plant is harvested differently, depending on the purpose of its use. The species was first classified by Carl Linnaeus in 1753. The word sativa means "things that are cultivated."

Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid discovered in 1940. It is one of 113 identified cannabinoids in cannabis plants, along with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and accounts for up to 40% of the plant's extract. As of 2019, clinical research on CBD included studies related to anxiety, cognition, movement disorders, and pain, but there is insufficient high-quality evidence that cannabidiol is effective for these conditions. Nevertheless, CBD is a popular herbal dietary supplement, widely promoted with unproven claims of particular therapeutic benefits. The global market size for CBD was predicted to exceed US$47 billion by 2028.

Cannabis indica is an annual plant species in the family Cannabaceae which produces large amounts of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and is cultivated for purposes including hashish in India. The high concentrations of THC provide euphoric effects making it popular for use both as a recreational drug, alternative medicine, and a clinical research drug.

Cannabis tea is a cannabis-infused drink prepared by steeping various parts of the cannabis plant in hot or cold water. Cannabis tea is commonly recognized as an alternative form of preparation and consumption of the cannabis plant, more popularly known as marijuana, pot, or weed. This plant has long been recognized as an herbal medicine employed by health professionals worldwide to ease symptoms of disease, as well as a psychoactive drug used recreationally and in spiritual traditions. Though less commonly practiced than popular methods like smoking or consuming edibles, drinking cannabis tea can produce comparable physical and mental therapeutic effects. Such effects are largely attributed to the THC content of the tea, levels of which are drastically dependent on individual preparation techniques involving volume, amount of cannabis, and boiling time. Also in common with these administration forms of cannabis is the heating component performed before usage. Due to the rather uncommon nature of this particular practice of cannabis consumption in modern times, the research available on the composition of cannabis tea is limited and based broadly around what is known of cannabis as it exists botanically.

Caryophyllene, more formally (−)-β-caryophyllene, (BCP), is a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene that is a constituent of many essential oils, especially clove oil, the oil from the stems and flowers of Syzygium aromaticum (cloves), the essential oil of Cannabis sativa, rosemary, and hops. It is usually found as a mixture with isocaryophyllene and α-humulene, a ring-opened isomer. Caryophyllene is notable for having a cyclobutane ring, as well as a trans-double bond in a 9-membered ring, both rarities in nature.

Cannabigerol (CBG) is one of more than 120 identified cannabinoid compounds found in the plant genus Cannabis. Cannabigerol is the decarboxylated form of cannabigerolic acid, the parent molecule from which other cannabinoids are synthesized.

Cannabis strains are either pure or hybrid varieties of the plant genus Cannabis, which encompasses the species C. sativa, C. indica, and C. ruderalis.

A depside is a type of polyphenolic compound composed of two or more monocyclic aromatic units linked by an ester bond. Depsides are most often found in lichens, but have also been isolated from higher plants, including species of the Ericaceae, Lamiaceae, Papaveraceae and Myrtaceae.

Prenylated flavonoids or prenylflavonoids are a sub-class of flavonoids. They are widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom. Some are known to have phytoestrogenic or antioxidant properties. They are given in the list of adaptogens in herbalism. Chemically they have a prenyl group attached to their flavonoid backbone. It is usually assumed that the addition of hydrophobic prenyl groups facilitate attachment to cell membranes. Prenylation may increase the potential activity of its original flavonoid.

Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid is a precursor of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), an active component of cannabis.

Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA) synthase is an enzyme responsible for catalyzing the formation of THCA from cannabigerolic acid (CBGA). THCA is the direct precursor of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the principal psychoactive component of cannabis, which is produced from various strains of Cannabis sativa. Therefore, THCA synthase is considered to be a key enzyme controlling cannabis psychoactivity. Polymorphisms of THCA synthase result in varying levels of THC in Cannabis plants, resulting in "drug-type" and "fiber-type" C. sativa varieties.

Cannabinodiol (CBND), also known as cannabidinodiol, cannabinoid that is present in the plant Cannabis sativa at low concentrations. It is the fully aromatized derivative of cannabidiol (CBD) and can occur as a product of the photochemical conversion of cannabinol (CBN).
Research has shown that Humulus lupulus and Cannabis sativa are closely related, and it may be possible to create novel strains of hops that express valuable chemicals similar to commercial hemp. Both hops and cannabis contain terpenes and terpenoids; tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) is a terpenoid. Hops lack the enzyme that could convert cannabigerolic acid into THC or CBD, but it could be inserted using genetic engineering as was done in 2019 for yeast.

Cannabichromenic acid (CBCA) is minor cannabinoid and precursor of cannabichromene.

Hexahydrocannabinol (HHC) is a hydrogenated derivative of tetrahydrocannabinol. It is a naturally occurring phytocannabinoid that has rarely been identified as a trace component in Cannabis sativa, but can also be produced synthetically by hydrogenation of cannabis extracts. HHC was first synthesized in 1947 by Roger Adams using natural THC found in Cannabis sativa. Several research groups have successfully synthesized (+)-HHC and (-)-HHC using citronellal and olivetol, as well as other related compounds. While similar compounds have previously been identified in cannabis, hexahydrocannabinol itself has rarely been isolated from the plant. The de Las Heras group in 2020 took lipid extract from Cannabis sativa seeds and discovered 43 cannabinoids in the crude extract; one of them being hexahydrocannabinol. It has two diastereomers at the methyl (9) position. HHC is typically made from Δ8-THC, or Δ9-THC. There are no double bonds in the cyclohexyl ring like D8/D9 have—they have been removed from the structure and hydrogens have been added to the compound. Similar structural analogs of HHC has been demonstrated to bind to the CB1 receptor and produces cannabinoid effects in animals, with the 9β-HHC enantiomer being much more active than 9α-HHC. While HHC has been shown to bind to the CB1 receptor, it binds with weaker affinity than THC, which has typically been an indication that it is not as intoxicating as typical THC. Since HHC is found naturally in the cannabis plant, humans have likely been unknowingly consuming small amounts of this cannabinoid for centuries.

Cannabicitran (CBTC) is a phytocannabinoid first isolated in 1974 as a trace component of Cannabis sativa, Structurally related compounds can be found in some other plants. It is not psychoactive, but was found to reduce intraocular pressure in tests on rabbits, which may reflect agonist activity at the NAGly receptor that is known to be a target of many structurally related cannabinoids.
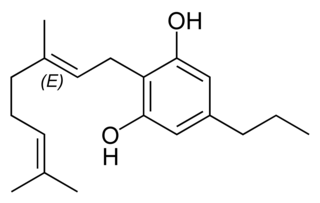
Cannabigerovarin (CBGV), the propyl homolog of cannabigerol (CBG), is a cannabinoid present in Cannabis. There is no observation related to the psychoactive or psychotropic effects of CBGV when consumed or inhaled. The possible benefits of cannabigerovarin in human bodies are painkilling and anti-inflammatory properties to treat conditions like fibromyalgia and arthritis, the treatment and improvement of the dry-skin syndrome, cancer treatment by reducing the growth of cancer cells in patients who have leukemia. According to the pain-relieving effects of this natural cannabinoid, it can be helpful to treat patients who were undergoing drug exposure like chemotherapy or radiation therapy. In addition, cannabigerol metabolism increases and has a better absorption from the body when paired with cannabigerovarin.

Cannabis (/ˈkænəbɪs/) is commonly known as marijuana or hemp and has two known strains: Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica, both of which produce chemicals to deter herbivory. The chemical composition includes specialized terpenes and cannibinoids, mainly tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and cannabidiol (CBD). These substances play a role in defending the plant from pathogens including insects, fungi, viruses and bacteria. THC and CBD are stored mostly in the trichomes of the plant, and can cause psychological and physical impairment in the user, via the endocannabinoid system and unique receptors. THC increases dopamine levels in the brain, which attributes to the euphoric and relaxed feelings cannabis provides. As THC is a secondary metabolite, it poses no known effects towards plant development, growth, and reproduction. However, some studies show secondary metabolites such as cannabinoids, flavonoids, and terpenes are used as defense mechanisms against biotic and abiotic environmental stressors.





















